Daily Current Affairs : 5-July-2024
The Aditya-L1 assignment has made a vast fulfillment in space exploration by way of correctly completing its first halo orbit across the Sun-Earth Lagrangian factor L1. This marks a main milestone for India’s space research, as the undertaking progresses in the direction of its intention of studying the Sun in greater detail.
Understanding the Mission and Its Importance
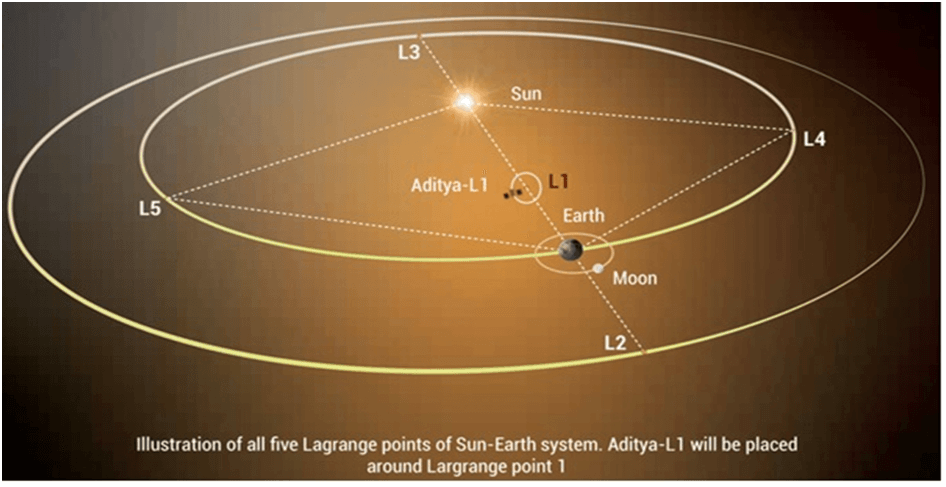
Launched on September 2, 2023, the Aditya-L1 spacecraft is designed to examine the Sun from the precise vantage factor of the Lagrangian factor L1, located about 1.5 million kilometers from Earth. This location provides a continuous and uninterrupted view of the Sun, making it perfect for solar observations. The spacecraft was inserted into its targeted halo orbit on January 6, 2024, after completing several complicated maneuvers.
The Lagrangian points are positions in space where the gravitational forces of the Sun and Earth balance out, allowing objects to remain in a stable position relative to the two large bodies. Aditya-L1’s halo orbit around L1 is a complex path that requires precise calculations and control.
The Role of Flight Dynamics in the Success
Successfully placing Aditya-L1 into the halo orbit required advanced knowledge of space dynamics, including how the spacecraft would respond to various perturbing forces, such as the gravitational influence of the Sun and Earth. This orbit is not a perfect circle but a large, looping path that allows the spacecraft to stay in position while continuously observing the Sun.
Key elements of the successful orbit insertion include:
- Precise Modelling of Dynamics: Detailed simulations and predictions were required to account for all the forces at play.
- Advanced Flight Dynamics Software: The successful execution of these maneuvers has validated the state-of-the-art flight dynamics software developed by URSC (U R Rao Satellite Centre) and ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation).
- Continuous Monitoring: The spacecraft in this orbit will complete a full revolution around L1 every 178 days, ensuring that it can continuously monitor solar activity.
Important Points:
- Aditya-L1 Mission Overview:
- Launched on September 2, 2023, by ISRO.
- Aimed at studying the Sun from the Sun-Earth Lagrangian point L1, 1.5 million kilometers from Earth.
- Successfully inserted into its targeted halo orbit on January 6, 2024.
- Significance of Lagrangian Point L1:
- L1 provides a continuous, uninterrupted view of the Sun, ideal for solar observations.
- The Lagrangian points are positions where gravitational forces from the Sun and Earth balance out, offering stability for spacecraft.
- Orbit Details:
- Aditya-L1’s orbit around L1 is a “halo orbit,” a complex, looping path that allows the spacecraft to maintain its position relative to the Sun and Earth.
- It takes 178 days for the spacecraft to complete one full revolution around the L1 point.
- Role of Flight Dynamics:
- Successful insertion into the halo orbit required advanced understanding of space dynamics and perturbing forces (e.g., gravitational influences).
- The orbit was not circular but a complex trajectory requiring precise planning and control.
- Key Elements of Success:
- Precise Modelling of Dynamics: Simulations were crucial for accounting for various forces.
- Advanced Flight Dynamics Software: The mission validated the cutting-edge flight dynamics software developed by URSC and ISRO.
- Continuous Monitoring: The spacecraft will continuously monitor solar activity, completing one revolution around L1 every 178 days.
- Future Impact:
- The Aditya-L1 mission will provide valuable data to understand solar phenomena, influencing space weather, and communication systems on Earth.
Why In News
The Aditya-L1 spacecraft has successfully completed its first halo orbit around the Sun-Earth Lagrangian point L1, marking a major achievement in India’s space exploration efforts. This successful maneuver not only demonstrates the spacecraft’s ability to maintain a stable position in a complex orbit but also paves the way for unprecedented solar observations from this strategic vantage point.
MCQs about Aditya-L1 Spacecraft’s Successful Halo Orbit Achievement
-
What is the primary objective of the Aditya-L1 mission?
A. To study the Moon
B. To study the Sun
C. To explore Mars
D. To study Earth’s atmosphere
-
What is the significance of the Lagrangian point L1 for the Aditya-L1 spacecraft?
A. It provides a stable position for spacecraft to observe the Sun continuously.
B. It allows spacecraft to avoid gravitational pull from Earth.
C. It is used to send spacecraft to other planets.
D. It provides a direct route for space missions to Mars.
-
How long does it take for the Aditya-L1 spacecraft to complete one full revolution around the L1 point in its halo orbit?
A. 365 days
B. 178 days
C. 90 days
D. 240 days
-
What was the role of flight dynamics software in the success of the Aditya-L1 mission?
A. It helped calculate the spacecraft’s fuel requirements.
B. It was used to develop the spacecraft’s physical structure.
C. It was crucial for accurately placing the spacecraft into its halo orbit.
D. It allowed the spacecraft to communicate with Earth.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


