Daily Current Affairs : 13-July-2023
The Anthropocene Working Group (AWG) has recently announced significant findings regarding the beginning of the Anthropocene epoch. Geologists have examined sediments at Crawford Lake, located in Ontario, Canada, and have uncovered evidence that suggests the Anthropocene epoch started sometime between 1950 and 1954. These sediments have captured the fallout from various human activities, including the burning of fossil fuels, nuclear weapon explosions, and the dumping of plastic and fertilizers on land and in water bodies.
Understanding the Anthropocene Epoch:
The Anthropocene epoch is a term coined by Nobel Prize-winning chemist Paul Crutzen and biology professor Eugene Stoermer in 2000. It refers to the current geological time interval marked by significant changes in Earth’s ecosystem due to human impact, particularly since the mid-20th century. This epoch is characterized by numerous phenomena, including global warming, sea-level rise, ocean acidification, mass-scale soil erosion, the emergence of deadly heat waves, and the deterioration of the biosphere.
The Earth’s Geological Time Scale:
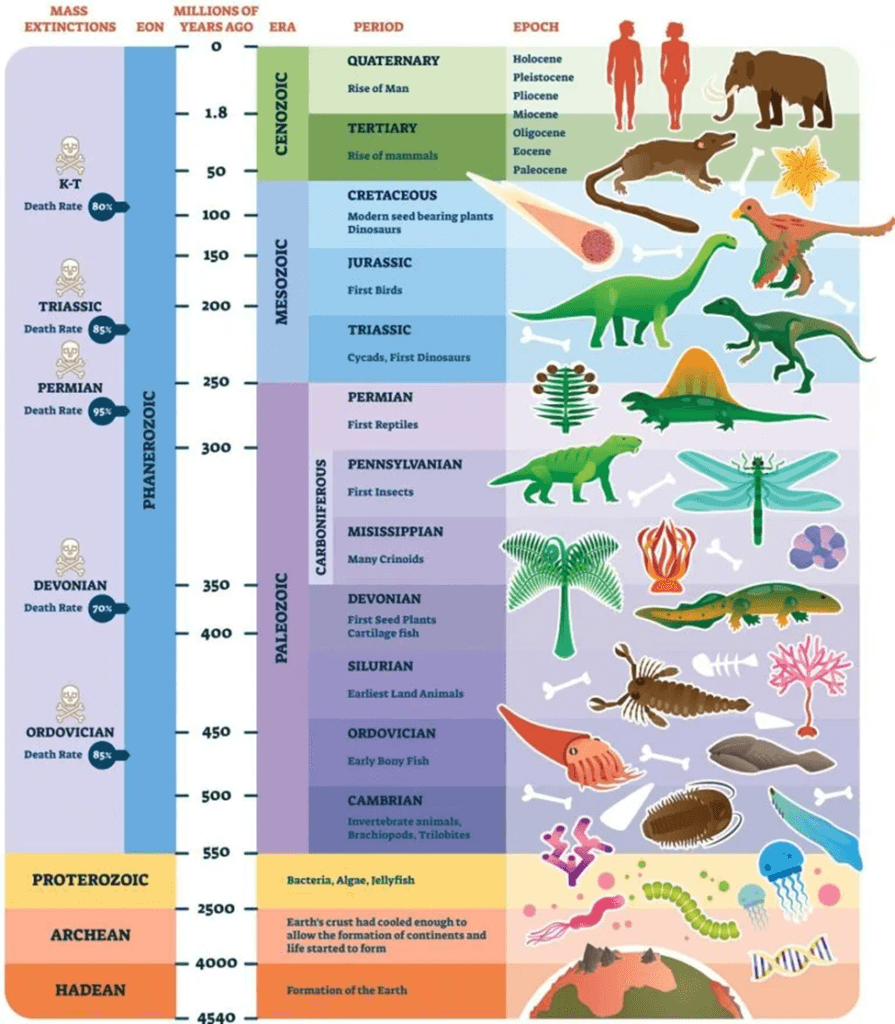
To comprehend the significance of the Anthropocene epoch, it is essential to understand how the Earth’s geological time is divided. The geological time scale comprises five broad categories: eons, epochs, eras, periods, and ages. Eons represent the broadest category, while age represents the smallest. Each of these categories is further divided into sub-categories. Earth’s history is characterized by four eons: Hadeon (the oldest), Archean, Proterozoic, and Phanerozoic (the youngest). Boundaries on the geological time scale often correspond to the origination or extinction of specific fossils, which is known as the principle of faunal succession. Different kinds of fossils are associated with different time intervals.
Current Geological Classification:
As of now, we find ourselves in the Phanerozoic eon, Cenozoic era, Quaternary period, Holocene epoch, and Meghalayan age. The Holocene epoch began approximately 11,700 years ago, marking the end of the last ice age. However, the recent findings from Crawford Lake suggest that the Anthropocene epoch represents a clear shift from the Holocene epoch, taking Earth’s system beyond its normal bounds.
Important Points:
- Geologists found evidence at Crawford Lake in Ontario, Canada, suggesting the beginning of the Anthropocene epoch.
- The Anthropocene epoch is marked by significant changes in Earth’s ecosystem due to human impact, particularly since the mid-20th century.
- Human activities such as burning fossil fuels, nuclear weapon explosions, plastic and fertilizer dumping, have been captured in the lake’s sediments.
- The Anthropocene Working Group estimates that the new epoch started between 1950 and 1954.
- This epoch represents a clear shift from the Holocene epoch, which began about 11,700 years ago.
- The term “Anthropocene” was coined in 2000 by Paul Crutzen and Eugene Stoermer.
- The epoch is characterized by various phenomena, including global warming, sea-level rise, ocean acidification, soil erosion, heatwaves, and biosphere deterioration.
- Earth’s geological time scale is divided into eons, epochs, eras, periods, and ages.
- The current geological classification places us in the Phanerozoic eon, Cenozoic era, Quaternary period, Holocene epoch, and Meghalayan age.
- Understanding the Anthropocene epoch is vital to address its challenges and promote sustainable practices for the future of our planet.
Why In News
Geologists have extensively analyzed the sediments at Crawford Lake in Canada’s Ontario, unearthing compelling evidence that unequivocally marks the dawn of the Anthropocene epoch. This groundbreaking discovery not only sheds light on humanity’s profound impact on the planet but also serves as a poignant reminder of the need for sustainable practices to safeguard our future.
MCQs about Anthropocene
-
What term refers to the present geological time interval characterized by significant changes in Earth’s ecosystem due to human impact?
A. Holocene epoch
B. Pleistocene epoch
C. Anthropocene epoch
D. Mesozoic era
-
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the Anthropocene epoch?
A. Global warming
B. Mass-scale soil erosion
C. Meteor impacts
D. Ocean acidification
-
What evidence did geologists find at Crawford Lake to support the beginning of the Anthropocene epoch?
A. Tree ring analysis
B. Analysis of ice cores from glaciers
C. Sediments from Crawford Lake
D. Fossil records from ancient oceans
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


