Daily Current Affairs : 11-July-2023
In the fight against climate change, experts emphasize the urgent need for carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology. This essay explores the concept of CCS, its significance in reducing pollution, and the challenges it faces. CCS involves capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from industrial processes and storing them underground, preventing the release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
Understanding Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
CCS is a method to capture and trap carbon beneath the Earth’s surface, primarily in geological formations. Unlike carbon dioxide removal (CDR), which focuses on removing CO2 from the atmosphere, CCS aims to prevent the gas from being released in the first place. This technology is particularly applicable to sectors such as steel and cement production, as well as power generation from fossil fuels.
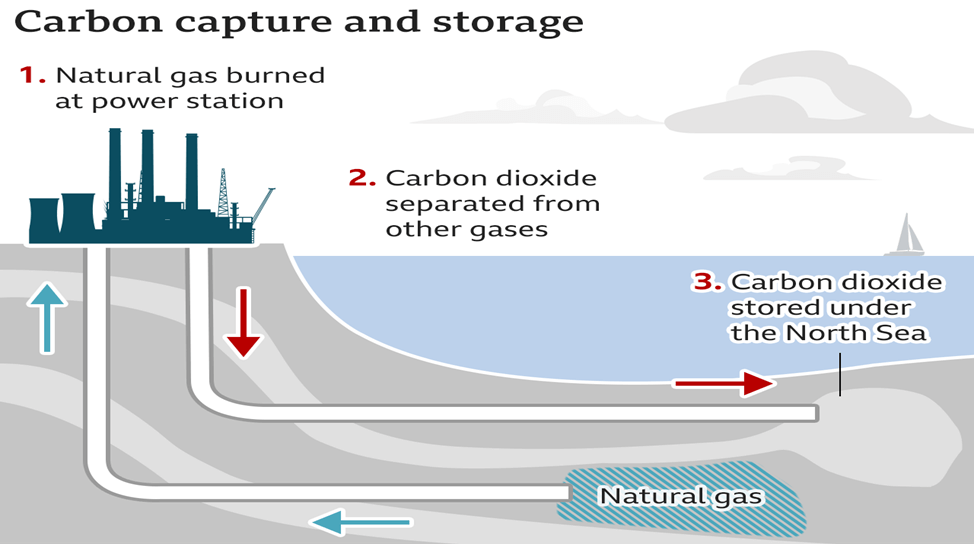
Steps of Carbon Capture and Storage
- Capturing the carbon dioxide for storage:
- Separating CO2 from other gases produced in industrial processes, including power plants, steel factories, and cement plants.
- Concentrated streams of CO2 are collected and undergo scrubbing and cleaning processes to prepare them for storage.
- Transport:
- The captured CO2 is compressed and transported to storage sites.
- Transport can occur via pipelines, road transport, or ships, ensuring the safe delivery of CO2 to the designated storage location.
- Storage:
- Injecting the captured CO2 into deep underground rock formations for permanent storage.
- The geological formations securely trap the CO2, preventing its release into the atmosphere.
Challenges and Concerns
- Failure to capture enough carbon:
- Some energy companies have prioritized drilling for oil rather than investing in effective carbon capture technologies.
- Lobbying against regulations to reduce fossil fuel production undermines efforts to capture carbon effectively.
- Emphasizing societal shifts, such as reducing energy demand, instead of relying solely on technology, has hindered progress.
- Lack of commitment:
- Despite decades of research and development, there are only 30 operational CCS facilities worldwide.
- Numerous planned CCS projects have been canceled or indefinitely postponed, indicating a lack of commitment to the technology.
- Leakages:
- Leakage of stored CO2 from underground sites poses environmental risks and undermines the intended emissions reduction.
- Proper monitoring and preventive measures are essential to minimize the potential damage caused by leakages.
Main Methods of CCS
- Post Combustion:
- Involves removing CO2 from flue gases generated by burning fossil fuels.
- Specialized technologies separate CO2 from other emissions produced during industrial processes.
- Pre-Combustion:
- Carried out before burning fossil fuels, converting them into a mixture of CO2 and hydrogen.
- This method enables easier separation of CO2 for storage.
- Oxyfuel:
- This technology burns fossil fuels in almost pure oxygen, creating CO2 and steam.
- The resulting CO2 is easier to capture, as other gases are eliminated during combustion.
Important Points:
- Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is crucial in reducing pollution in sectors with limited clean technologies.
- CCS involves capturing CO2 emissions from industrial processes and storing them underground.
- It differs from carbon dioxide removal (CDR), which focuses on removing CO2 from the atmosphere.
- Steps of CCS: capture, transport, and storage in geological formations.
- Challenges include the failure to capture enough carbon, lack of commitment, and concerns over leakages.
- Main methods of CCS: post combustion, pre-combustion, and oxyfuel.
- CCS is particularly applicable to steel and cement production and fossil fuel-based power generation.
- Only 30 operational CCS facilities exist globally, with many planned projects canceled or postponed.
- Proper monitoring and preventive measures are essential to minimize CO2 leakage risks.
- Governments, industries, and policymakers should prioritize CCS development and implementation.
Why In News
Experts emphasize that the urgent implementation of carbon capture and storage technology is essential for mitigating pollution in industries where the adoption of alternative clean technologies lags behind. By effectively capturing and sequestering planet-heating gases underground, we can take a significant step towards achieving a more sustainable and environmentally conscious future.
MCQs about Carbon Capture and Storage
-
What is the primary goal of carbon capture and storage (CCS)?
A. To remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere.
B. To transport CO2 emissions from industrial processes.
C. To prevent the release of CO2 into the atmosphere.
D. To store CO2 in above-ground containers.
-
Which step is involved in the CCS process?
A. Separating CO2 from the atmosphere.
B. Compressing CO2 for transportation.
C. Converting fossil fuels into CO2 and hydrogen.
D. Injecting CO2 into underground rock formations.
-
What are some challenges faced by carbon capture and storage (CCS)?
A. Lack of commitment and insufficient operational facilities.
B. Inability to capture enough hydrogen gas.
C. Leakage of CO2 from underground storage sites.
D. Reliance on societal shifts rather than technology.
-
Which CCS method burns fossil fuels in almost pure oxygen to create CO2 and steam?
A. Post Combustion.
B. Pre-Combustion.
C. Oxyfuel.
D. Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR).
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


