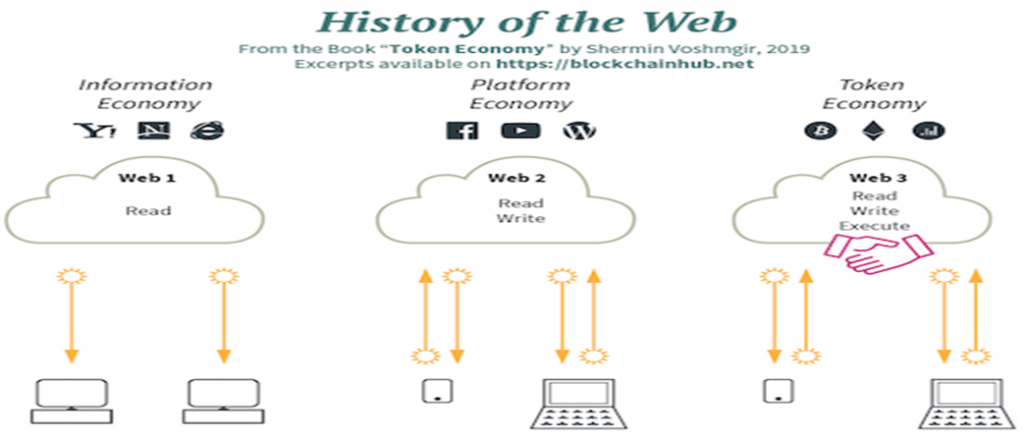
Web3 is the next generation of the internet that leverages blockchain technology to create a more open and transparent web. Unlike Web2, which is characterised by centralisation and control by large corporations, Web3 is decentralised, giving users greater control over their data and digital assets. This essay will explore the key features of Web3, how it differs from Web2, the challenges it faces, and its applications.
Key Features of Web3
Control over Data: Web3 offers users greater control over their data and digital assets. With Web3, users can perform peer-to-peer transactions and interactions, which means that they are in control of their data and can choose whom they share it with.
Privacy and Security: Unlike Web2, which relies on centralised intermediaries, Web3 offers options for greater privacy and security of content and transactions.
Decentralised Applications and Smart Contracts: Another key feature of Web3 is the ability to create and use decentralised applications (dApps) and smart contracts. These dApps can be used for a variety of purposes, such as social media, finance, gaming, and more.
How is Web3 different from Web2?
Centralisation vs. Decentralisation: Web2 is centralised, meaning that data is stored on centralised servers owned and controlled by large corporations. In contrast, Web3 is decentralised, meaning that data is stored on a decentralised network of computers that are owned and controlled by the users themselves.
Intermediaries vs Peer-to-Peer: Web2 relies heavily on intermediaries such as banks, social media platforms, and online marketplaces to facilitate transactions and interactions. Web3 enables peer-to-peer transactions and interactions, meaning that users can transact directly with one another without the need for intermediaries.
Data Ownership and Control: In Web2, large corporations like Facebook and Google have significant control over user data and can monetise it in ways that users may not be comfortable with. In Web3, users can choose to share data only with those they trust. In Web2, users must trust intermediaries to keep their data and transactions secure. In Web3, users can trust the network itself to keep their data and transactions secure.
Challenges for Web3
Scalability: The current infrastructure of blockchain networks can only handle a limited number of transactions per second. This limits the potential for Web3 to be used for high-volume applications like social media and online marketplaces.
User Adoption: While blockchain technology has been around for over a decade, it is still relatively unknown. Many users are not familiar with the concept of decentralisation, which could hinder adoption.
Interoperability: Web3 is being built by a wide range of developers and organisations, each with their own unique vision for how the technology should be implemented. This could lead to issues with interoperability between different Web3 applications.
Complexity: Web3 technology requires a certain level of technical expertise to use and understand. This may be a barrier to adoption for some users who are not comfortable with technology or do not have the necessary technical knowledge.
Applications of Web3
Cryptocurrencies: Cryptocurrencies are built on blockchain technology, which is a key component of Web3. These digital currencies enable secure, decentralised transactions without the need for intermediaries.
Decentralised Finance (DeFi): DeFi is a movement that aims to build a new financial system on top of blockchain technology. DeFi applications enable users to borrow, lend, and trade cryptocurrencies without the need for traditional financial intermediaries.
User-Centric Networks: Web3 is being used to create decentralised social networks like Mastodon, which are designed to be more user-centric. Web3 is also being used to develop decentralised identity verification systems.
Why In News
Web3 is a term used to describe the next phase of the Internet, which is decentralised and built on top of blockchain technology. It aims to provide users with greater control over their data and digital assets, while also offering more privacy and security compared to Web2.
MCQs about Challenges and Applications of Web3 Technology
-
What is Web3?
A. A decentralised web built on top of existing Internet infrastructure that leverages blockchain technology to create a more open and transparent web.
B. A centralised web built on top of existing Internet infrastructure that leverages blockchain technology to create a more closed and opaque web.
C. A web-based game that utilises blockchain technology.
D. None of the above.
-
What is the main difference between Web2 and Web3?
A. Centralisation vs. Decentralisation.
B. Web2 is built on blockchain technology, whereas Web3 is not.
C. Web3 relies heavily on intermediaries such as banks, social media platforms, and online marketplaces to facilitate transactions and interactions.
D. None of the above.
-
What is the key feature of Web3 that provides users with greater control over their data and digital assets?
A. Control over data.
B. Privacy and security.
C. Decentralised applications and smart contracts.
D. None of the above.
-
What is blockchain?
A. A centralised digital technology for storing data.
B. A decentralised digital technology for storing data.
C. A type of programming language.
D. A method of storing data on paper documents.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


