China’s space program has set its sights on ambitious goals, aiming to place astronauts on the moon before 2030 and expand the country’s orbiting space station. This development comes amid the backdrop of a rivalry with the United States for achieving new milestones in outer space. While the US aims to put astronauts back on the lunar surface by the end of 2025, China is determined to establish its presence and contribute to lunar scientific exploration and technological experiments.
China’s Lunar Exploration Program:
China’s commitment to lunar exploration is evident in its plans to put astronauts on the moon within the next decade. This endeavor seeks to build on the successes of previous missions and establish China as a major player in space exploration. Key points include:
- China’s first manned space mission in 2003 made it the third country, after the USSR and the US, to send a person into space.
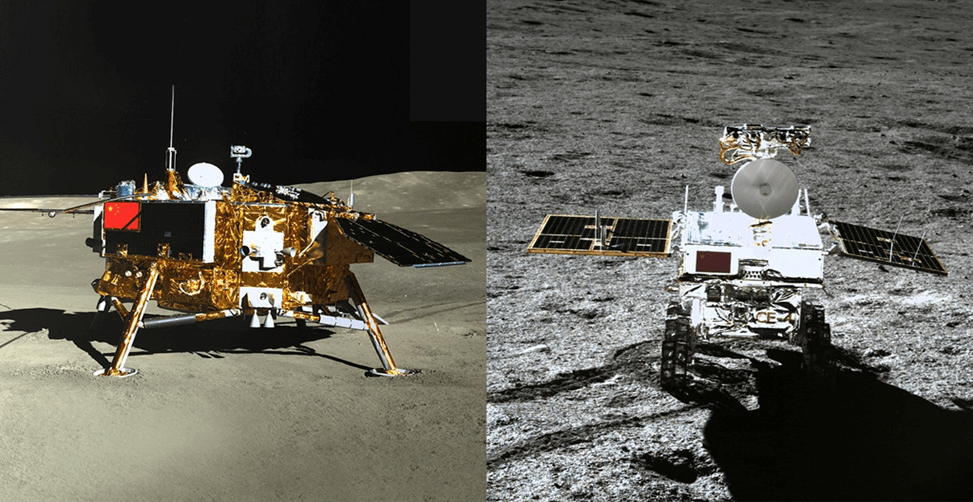
- China has already undertaken successful uncrewed missions to the moon, including the deployment of a rover.
- China’s space program has also achieved the remarkable feat of sending a rover to Mars, showcasing its growing capabilities in planetary exploration.
The Race for Space Dominance:
China’s latest announcement regarding its lunar plans is fueled by competition with the United States. The US has set a goal to return astronauts to the moon’s surface by the end of 2025, leveraging collaborations with private sector players such as SpaceX and Blue Origin. China’s determination to outpace the US in reaching new milestones in space exploration is an integral driving force behind its endeavors.
China’s Orbiting Space Station:
In addition to lunar exploration, China is actively expanding its orbiting space station. The country’s space agency is focused on maintaining a continuous human presence in space, conducting experiments, and pushing the boundaries of scientific research. Key details include:
- The three crew members aboard China’s Shenzhou-16 mission are set to replace the crew that has been aboard the orbiting station for the past six months.
- China’s goal is to establish its own space station, as it was excluded from the international Space Station mainly due to objections from the United States.
- Building its own space station provides China with a platform to conduct its own experiments and develop advanced technologies.
Important Points:
- China plans to place astronauts on the moon before 2030 🚀
- China aims to achieve its first manned lunar landing and conduct scientific exploration 🌕🔬
- China’s space program is driven by competition with the US for space dominance 🌍🏆
- The US aims to put astronauts on the moon by the end of 2025 with the help of private sector players like SpaceX and Blue Origin 🇺🇸🌕
- China’s Shenzhou-16 mission will replace the crew that has been on the orbiting station for the past six months 🚀🛰️
- China has successfully launched uncrewed missions to the moon and sent a rover to Mars 🌕🚀🤖
- China built its own space station after being excluded from the international Space Station due to objections from the US 🛰️🇨🇳🌍
- China’s space program aims to establish a continuous human presence in space and push the boundaries of scientific research 🚀🔬
- China’s lunar exploration and space station development signify its determination to become a leading force in space exploration 🌕🚀🌍
Why In News
China’s space program has embarked on a mission of grand ambitions, setting its target to land astronauts on the moon before 2030 and bolster its orbiting space station. This endeavor unfolds against the backdrop of an intense rivalry with the United States, as both nations strive to surpass each other’s accomplishments in the realm of outer space. While the US endeavors to return astronauts to the lunar surface by the conclusion of 2025, China remains resolute in establishing its presence and making substantial contributions to lunar scientific exploration and technological experiments.
MCQs about China’s Lunar Exploration
-
Which country aims to place astronauts on the moon before 2030?
A. United States
B. China
C. Russia
D. India
-
What was the significance of China’s first manned space mission in 2003?
A. It made China the first country to reach the moon.
B. It marked China’s entry into the space race.
C. It led to the establishment of China’s own space station.
D. It resulted in the successful deployment of a rover on Mars.
-
Why did China build its own space station?
A. To collaborate with international space agencies.
B. Due to objections from the United States.
C. To share scientific data with other countries.
D. As part of a joint venture with Russia.
-
What is the main driving force behind China’s lunar exploration and space station plans?
A. Collaboration with private sector players.
B. Competition with Russia in space exploration.
C. The need to establish a continuous human presence in space.
D. Rivalry with the United States for space dominance.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


