Daily Current Affairs : 31-October-2023
In a significant scientific breakthrough, researchers at IITM Pune have successfully demonstrated the potential of cloud seeding to enhance rainfall, particularly in regions facing acute water scarcity. This innovative experiment, conducted in Solapur city, yielded an impressive 18% relative enhancement in rainfall, equivalent to approximately 8.67mm more precipitation. This achievement holds immense promise for mitigating water shortages and managing drought conditions.
The Experiment: Cloud Aerosol Interaction and Precipitation Enhancement Experiment (CAIPEEX phase-4)
The experiment, carried out during the summer monsoons of 2018 and 2019, aimed to investigate the efficacy of hygroscopic seeding in deep convective clouds. Utilizing two aircraft, the study involved seeding 150 out of 276 chosen convective clouds in Solapur city. The seeding process utilized calcium chloride flares, strategically released at the base of warm convective clouds during their growing stage.
Significant Findings and Implications:
- Cloud seeding alone cannot entirely alleviate droughts but can augment rainfall by 18%, providing a partial solution to water requirements.
- Undertaking cloud seeding as catchment-scale projects could effectively manage drought conditions.
- The study has yielded detailed protocols and technical guidance for planning and executing cloud seeding projects in India.
- Notably, 20-25% of cumulus clouds produce rainfall when seeded correctly, highlighting the importance of precise seeding techniques.
Cost-Effectiveness and Future Prospects:
- The approximate cost of producing water through cloud seeding was found to be 18 paisa per liter.
- Furthermore, utilizing indigenous seeding aircraft could reduce costs by more than 50%, making cloud seeding a financially viable solution for water-scarce regions.
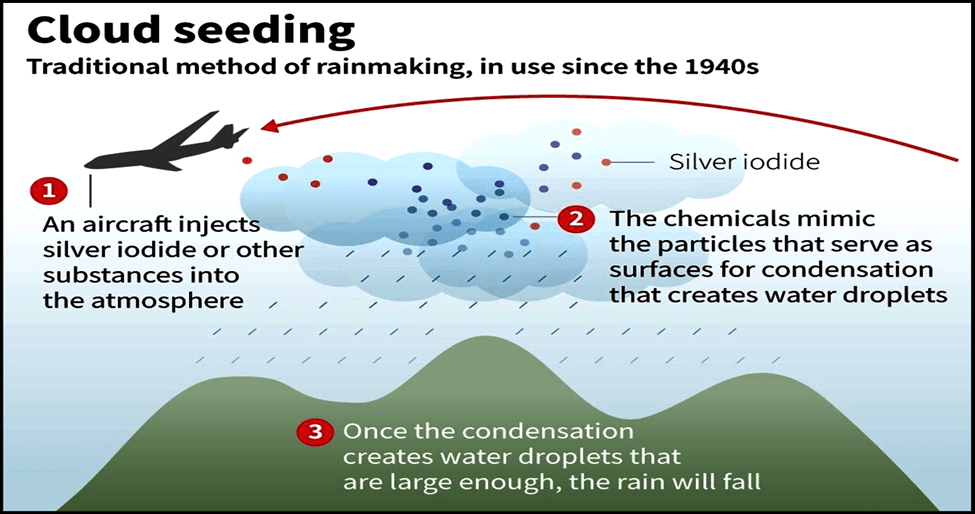
Important Points:
- Successful cloud seeding experiment in Solapur achieved an 18% relative enhancement in rainfall, providing approximately 8.67mm more precipitation.
- The experiment aimed to investigate the efficacy of hygroscopic seeding in deep convective clouds and develop a cloud seeding protocol.
- It utilized two aircraft and calcium chloride flares for seeding 150 out of 276 chosen convective clouds.
- Cloud seeding can partially address water requirements but cannot completely mitigate droughts.
- Undertaking cloud seeding at catchment-scale can help manage drought conditions effectively.
- The study provides detailed protocols and technical guidance for cloud seeding in India.
- 20-25% of cumulus clouds produce rainfall when seeded correctly.
- The approximate cost of producing water through cloud seeding was 18 paisa per liter.
- Using indigenous seeding aircraft could reduce costs by over 50%, making cloud seeding a cost-effective solution for water-scarce regions.
Why In News
IITM Pune’s groundbreaking research proves that cloud seeding has the potential to induce rainfall, offering a promising solution to water scarcity in drought-prone regions. The study highlights the importance of further exploration in this field to harness the full benefits of cloud seeding technology.
MCQs about Cloud Seeding’s Impact on Water-Scarce Regions
-
What was the primary objective of the Cloud Aerosol Interaction and Precipitation Enhancement Experiment (CAIPEEX phase-4)?
A. To reduce drought conditions in Solapur city
B. To investigate the efficacy of hygroscopic seeding in deep convective clouds and develop a cloud seeding protocol
C. To study cloud patterns in Western Ghats
D. To measure air pollution levels in Solapur city
-
What type of particles are introduced into clouds during cloud seeding to enhance rainfall?
A) Water droplets
B) Ice crystals
C) Calcium chloride particles
D) Dust particles
-
In which city was the cloud seeding experiment conducted, resulting in an 18% relative enhancement in rainfall?
A) Mumbai
B) Solapur
C) Pune
D) Delhi
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


