Coal Bed Methane (CBM) is a form of natural gas that can be extracted from coal deposits or coal seams. The extraction of CBM is a significant challenge for India, considering its dependence on coal-based power generation and the country’s vast reserves of coal.
Prospects of CBM Extraction in India
- India is ranked fifth in the world for proven coal reserves, with the bulk of reserves located in the Gondwana sediments of eastern India.
- All current CBM producing blocks in India are located in eastern India, specifically in the Damodar Koel valley and Son valley.
- Despite having a CBM Prognosticated Resource of 92 TCF, the in-place reserves established is only 10 TCF, indicating a significant potential for CBM extraction in India.
- In 1997, the Government of India formulated a policy to extract CBM from coal-bearing areas before the mining of coal.
- A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between the Ministry of Coal and the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas to work cooperatively for CBM development.
- The policy allows for CBM extraction by coal mine owners or through an agency, which can be an Indian company or a joint venture.
Challenges of CBM Extraction in India
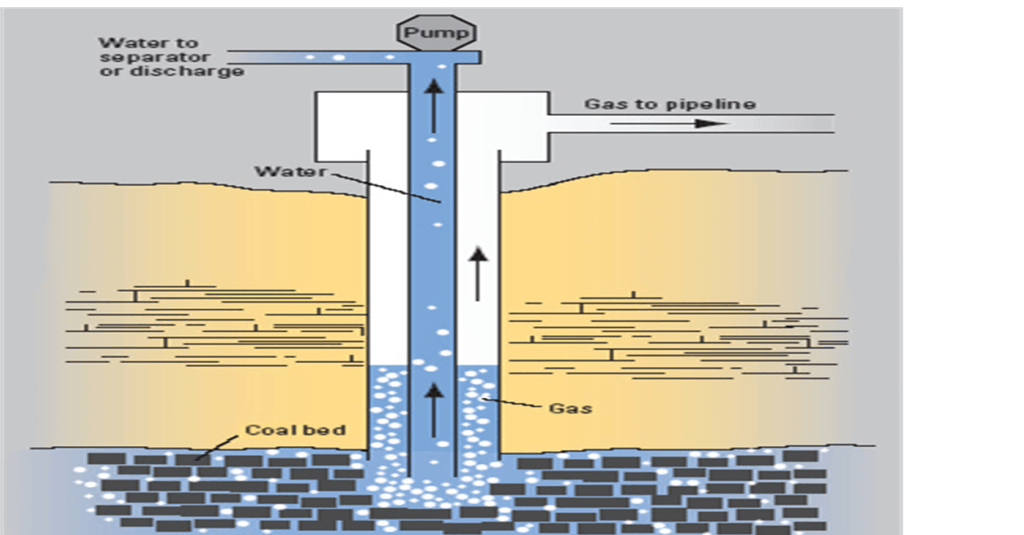
- The extraction of CBM involves pumping large volumes of water out of coal seams to reduce the hydrostatic pressure and liberate the gas.
- The produced water from CBM wells has high salinity due to dissolved sodium bicarbonate ions or chlorides, making it unsuitable for certain agricultural activities and creating disposal challenges.
- CBM extraction can have adverse and long-term chemical or physical effects on soil structure.
- Methane is the main component of CBM and has up to 72 times more global warming potential per unit mass than CO2.
- The release of methane during CBM extraction can significantly contribute to global warming.
- Proper monitoring and mitigation measures are necessary to prevent the release of methane into the atmosphere.
Uses of CBM
CBM has several industrial applications, including power generation, manufacturing fertilizers and plastics, and as a transportation fuel. Therefore, the extraction of CBM can provide an alternative source of energy and reduce India’s dependence on coal-based power generation.
Why In News
The Union Minister of Coal, Mines, and Parliamentary Affairs recently informed the Lok Sabha about the status of coal bed methane extraction in India. The Minister highlighted the government’s efforts to promote the development of CBM in the country and shared important details regarding the policy framework and potential of CBM extraction in India.
MCQs on Coal Bed Methane Extraction in India
-
What is the primary component of Coal Bed Methane (CBM)?
A. Methane
B. Carbon dioxide
C. Natural gas
D. Coal dust
-
Which region in India hosts the bulk of India’s coal reserves and all the current CBM producing blocks?
A. Western India
B. Southern India
C. Eastern India
D. Northern India
-
What is the global warming potential (GWP) of methane compared to CO2?
A. Methane has up to 72 times more GWP than CO2
B. Methane has up to 10 times more GWP than CO2
C. Methane has up to 50 times more GWP than CO2
D. Methane has up to 100 times more GWP than CO2
-
What is the primary challenge in the disposal of produced water during CBM extraction?
A. Produced water has a high salinity
B. Produced water contains harmful chemicals
C. Produced water is difficult to transport
D. Produced water is highly flammable
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


