Daily Current Affairs : 7-December-2023
Pompe disease, a rare genetic disorder, recently claimed the life of India’s first diagnosed patient, shedding light on the challenges associated with this condition. This essay explores the genetic causes, enzymatic functions, consequences of enzyme deficiency, patterns of onset, and available treatments for Pompe disease.
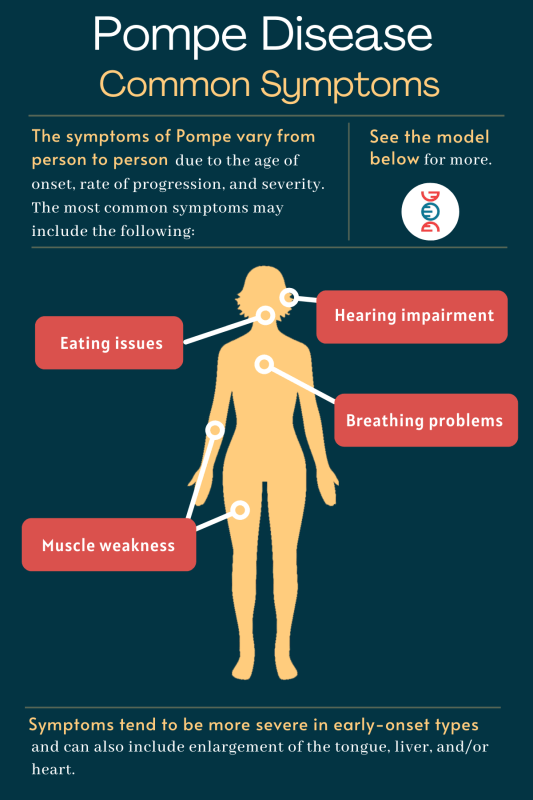
Pompe Disease Overview:
Pompe disease, affecting approximately one in a million children, stems from mutations in the GAA gene. This gene plays a pivotal role in producing the enzyme acid alpha-glucosidase, essential for breaking down glycogen into glucose within lysosomes.
Genetic Causes:
- Mutations in the GAA gene lead to Pompe disease.
- The GAA gene is responsible for producing acid alpha-glucosidase.
Enzymatic Function and Malfunction:
- Acid alpha-glucosidase is crucial in lysosomes for glycogen breakdown.
- GAA gene mutations impede this process, causing glycogen accumulation.
Consequences of Enzyme Deficiency:
- Excessive glycogen in lysosomes results in organ and muscle damage.
- Symptoms include muscle weakness, respiratory difficulties, cardiac issues, and swallowing problems.
Patterns of Onset:
- Infantile-onset: Symptoms emerge within months of birth.
- Late-onset: Symptoms develop later in life, during childhood or adulthood.
Impact on Population:
- Pompe disease affects both males and females equally.
Available Treatments:
- Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) is the primary treatment for Pompe disease.
Important Points:
- Pompe Disease Overview:
- Rare genetic disorder affecting approximately one in a million children.
- Caused by mutations in the GAA gene, crucial for producing acid alpha-glucosidase.
- Genetic Causes:
- Mutations in the GAA gene lead to Pompe disease.
- The GAA gene is responsible for producing acid alpha-glucosidase.
- Enzymatic Function and Malfunction:
- Acid alpha-glucosidase is essential for breaking down glycogen into glucose within lysosomes.
- GAA gene mutations impede this process, causing glycogen accumulation.
- Consequences of Enzyme Deficiency:
- Excessive glycogen in lysosomes results in organ and muscle damage.
- Symptoms include muscle weakness, respiratory difficulties, cardiac issues, and swallowing problems.
- Patterns of Onset:
- Infantile-onset: Symptoms emerge within months of birth.
- Late-onset: Symptoms develop later in life, during childhood or adulthood.
- Impact on Population:
- Pompe disease affects both males and females equally.
- Available Treatments:
- Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) is the primary treatment for Pompe disease.
Why In News
Recently, India’s first patient diagnosed with Pompe disease, a rare genetic disorder caused by the buildup of glycogen in the body’s cells, died after spending nearly six years in a semi-comatose state, highlighting the urgent need for increased awareness and research to improve the diagnosis and treatment of such rare diseases.
MCQs about Decoding Pompe Disease
-
What is the primary cause of Pompe disease?
A. Excessive glycogen
B. Mutations in the GAA gene
C. Enzyme Replacement Therapy
D. Respiratory difficulties
-
How does Pompe disease affect lysosomes?
A. Enhances glycogen breakdown
B. Causes lysosomal dysfunction
C. Prevents glycogen accumulation
D. Promotes enzyme production
-
What is the primary function of acid alpha-glucosidase?
A. Muscle strengthening
B. Glycogen breakdown in lysosomes
C. Cardiac regulation
D. Respiratory support
-
Which treatment is considered the main approach for Pompe disease?
A. Surgery
B. Physical therapy
C. Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT)
D. Antibiotic therapy
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


