Daily Current Affairs : 9-August-2023
In the wake of a recent coup in the West African nation of Niger, the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) has emerged as a key player in the region’s efforts to address the crisis and restore stability. ECOWAS, established in 1975 through the Lagos Treaty, was created with the primary goal of promoting economic integration among its member states. This essay delves into the role of ECOWAS in the context of the Niger coup, providing insight into the organization’s purpose, its member states, and its broader aims.
About ECOWAS
ECOWAS comprises 15 member states, including Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, Cote d’Ivoire, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, Senegal, and Togo. Collectively, these countries are home to around 400 million people, representing a diverse and culturally rich region. ECOWAS aims to foster not only economic cooperation but also social and cultural ties among its member states.
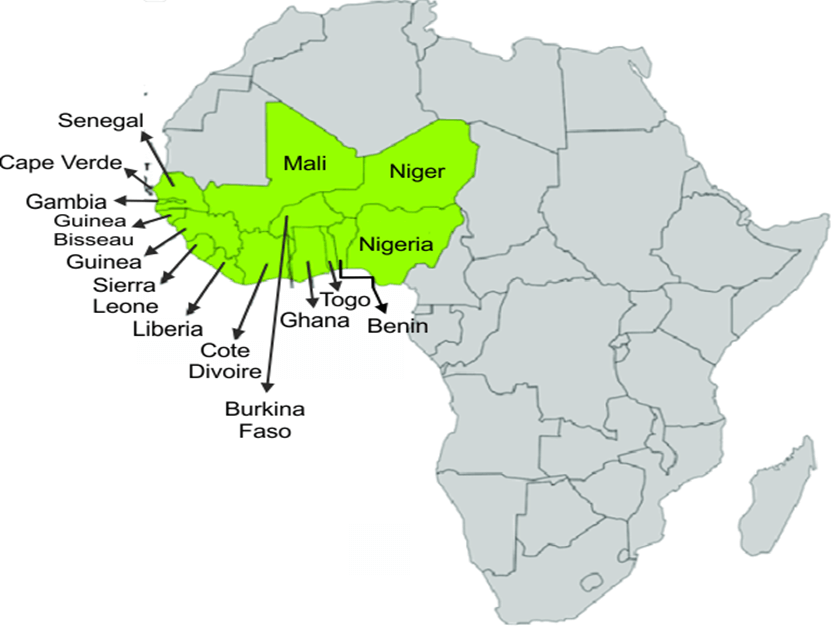
Promoting Economic Integration
One of ECOWAS’s fundamental objectives is to establish a single common currency and a large trading bloc that spans various sectors, such as industry, transport, telecommunications, energy, and financial matters. This vision of economic integration seeks to facilitate seamless trade and investment opportunities among member states, ultimately driving economic growth and development across the region. Additionally, ECOWAS envisions the creation of a borderless and well-integrated region, encouraging the movement of people, goods, and services.
ECOWAS’s Organizational Structure
At the heart of ECOWAS’s organizational structure is the Chairman of the Authority of Heads of State and Government. This position is held by the current Head of State and Government of a member state, who is appointed by fellow Heads of State and Government to lead the organization’s affairs for a one-year term. This rotating leadership ensures a collective and collaborative approach to decision-making, enabling different member states to contribute their perspectives and expertise.
ECOWAS’s Role in the Niger Coup
In light of the recent coup in Niger, ECOWAS swiftly mobilized its efforts to address the crisis and promote stability in the region. The organization condemned the coup and called for the immediate restoration of constitutional order. ECOWAS’s proactive stance highlighted its commitment to democratic governance and its willingness to take decisive action to prevent political instability.
Diplomatic Engagement and Conflict Resolution
ECOWAS engaged in diplomatic efforts to mediate the situation and facilitate dialogue between the coup leaders, the ousted government, and other relevant stakeholders. Through its mediation initiatives, ECOWAS aimed to find a peaceful and negotiated solution to the crisis, avoiding further escalation of violence and instability.
Economic Sanctions and Regional Cooperation
To exert pressure on the coup leaders and encourage a return to constitutional order, ECOWAS implemented targeted economic sanctions. These sanctions, ranging from travel bans to asset freezes, demonstrated the organization’s resolve to uphold democratic norms and principles. Furthermore, ECOWAS leveraged its regional influence to garner support from neighboring countries and international partners, reinforcing the importance of collective action in maintaining regional stability.
Important Points:
Primary Objectives:- Foster a single common currency.
- Create a large trading bloc encompassing industry, transport, telecommunications, energy, finance, and social and cultural matters.
- Establish a borderless and well-integrated region.
- Organizational Structure:
- Headed by the Chairman of the Authority of Heads of State and Government.
- The Chairman, a current Head of State and Government, leads for one year.
- Ensures collective decision-making and diverse perspectives.
- ECOWAS’s Role in Niger Coup:
- Swift Response to Crisis:
- Condemned the coup in Niger.
- Called for the immediate restoration of constitutional order.
- Diplomatic Efforts:
- Initiated mediation and dialogue between coup leaders, ousted government, and stakeholders.
- Aimed at peaceful and negotiated resolution to prevent further violence.
- Economic Sanctions:
- Implemented targeted sanctions (travel bans, asset freezes) to pressure coup leaders.
- Demonstrated commitment to democratic norms and principles.
- Regional Cooperation:
- Leveraged regional influence to garner support from neighboring countries.
- Sought collaboration with international partners to maintain regional stability.
- Promotion of Democratic Governance:
- ECOWAS’s actions highlighted its dedication to democratic principles.
- Actively engaged to prevent political instability.
- Swift Response to Crisis:
Why In News
In a recent coup in the West African nation of Niger, the regional bloc ECOWAS, known as the Economic Community of West African States, has prominently assumed an assertive and diplomatic role, swiftly mobilizing its member states to engage in proactive mediation and restore stability to the region.As the situation unfolds, ECOWAS continues to demonstrate its commitment by leveraging its collective influence to facilitate negotiations and foster a peaceful transition of power, underlining the bloc’s pivotal role in safeguarding democratic norms and regional security.
MCQs about ECOWAS
-
What is the primary goal of ECOWAS?
A. To establish a military alliance among member states.
B. To promote economic integration among West African countries.
C. To create a single global currency.
D. To focus solely on social and cultural matters.
-
Who is the Chairman of the Authority of Heads of State and Government in ECOWAS?
A. A representative elected by the United Nations.
B. A rotating position held by the Head of State and Government of a member state.
C. An appointed military leader.
D. An international diplomat chosen by member states.
-
What actions did ECOWAS take in response to the Niger coup?
A. Ignored the coup and focused on other regional matters.
B. Implemented economic sanctions against neighboring countries.
C. Condemned the coup, called for restoration of constitutional order, and engaged in diplomatic efforts.
D. Expelled Niger from the organization.
-
What does ECOWAS envision for the West African region in terms of integration?
A. To establish a single global government.
B. To create a heavily regulated trade environment.
C. To promote borderless movement of people, goods, and services, and foster economic cooperation.
D. To prioritize individual member state interests over regional cooperation.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


