Daily Current Affairs : 1-July-2023
The recent launch of the Euclid space telescope marks a significant milestone in our understanding of the universe. This groundbreaking telescope is set to play a crucial role in unraveling the mysteries of dark matter, a substance that constitutes a substantial portion of our cosmos. we will explore the concept of dark matter, what it is not, and delve into the fascinating realm of dark energy. Furthermore, we will discuss the Euclid space telescope and how it is poised to advance our knowledge in the study of dark matter.
Understanding Dark Matter
Dark matter, as the name suggests, refers to substances that do not absorb, reflect, or emit light, rendering them invisible to our traditional means of detection. It is a non-interacting substance, which adds to its enigmatic nature. While we have gained knowledge about approximately 5 percent of the universe, the remaining 95 percent is composed of dark matter (27 percent) and dark energy (68 percent).
What Dark Matter is Not
To comprehend dark matter better, it is essential to understand what it is not. Dark matter does not manifest itself in the form of visible matter, such as stars and planets that we observe. Additionally, it does not resemble dark clouds of normal matter, consisting of baryons, which are particles composing familiar matter. Furthermore, dark matter is distinct from antimatter, as the absence of unique gamma rays produced during the annihilation of antimatter with matter indicates its dissimilarity.
Composition of Dark Matter
The primary reason for the invisibility of dark matter lies in its minimal interaction with electromagnetic forces, including visible light, X-rays, and radio waves. Nonetheless, the effects of dark matter can be observed through its gravitational force. The prevailing belief is that dark matter is composed of exotic particles like axions or WIMPs (Weakly Interacting Massive Particles). Due to its inability to absorb, reflect, or emit light, identifying dark matter poses an immense challenge.
Understanding Dark Energy
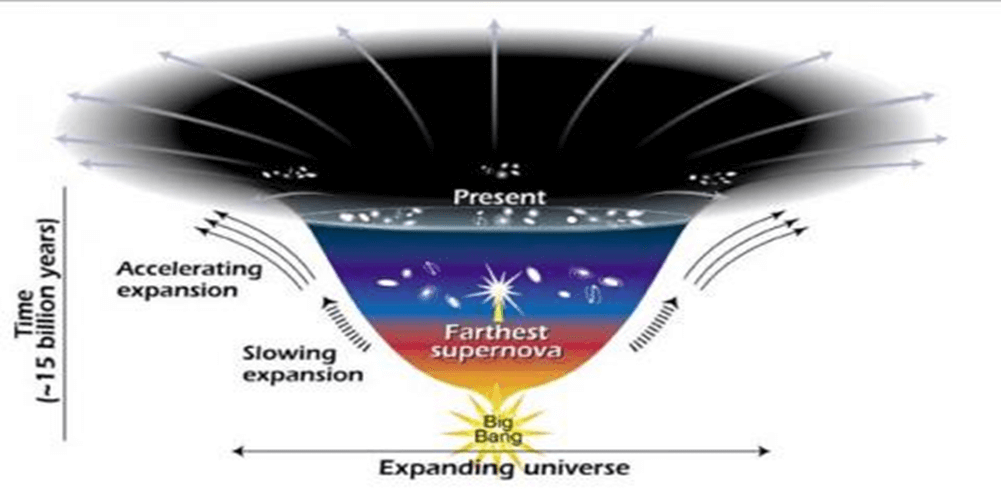
Apart from dark matter, another intriguing aspect of the universe is dark energy. Dark energy is a theoretical form of energy proposed by physicists to explain the accelerated expansion of the universe. It acts as an “anti-gravity” force, exerting negative pressure and stretching the fabric of spacetime. Unlike gravity, which pulls cosmic objects together, dark energy drives them apart at an accelerating pace.
The Euclid Space Telescope: Advancing Dark Matter Studies
In this quest for knowledge, the Euclid space telescope emerges as a vital instrument. Equipped with state-of-the-art technology, the Euclid telescope is designed to probe the depths of the universe, shedding light on the mysteries of dark matter. Its primary objective is to map the distribution of dark matter and dark energy on a cosmic scale, providing invaluable insights into the composition and behavior of these elusive entities.
Capabilities of the Euclid Space Telescope
The Euclid space telescope boasts impressive capabilities that make it uniquely suited for the study of dark matter. Some notable features and missions of the telescope include:
- Redshift Survey: Euclid will conduct a large-scale redshift survey, allowing astronomers to measure the distance of galaxies accurately. By observing the clustering of galaxies, scientists can infer the presence and influence of dark matter.
- Weak Lensing: Weak gravitational lensing is a phenomenon caused by the gravitational influence of dark matter on light. Euclid will employ precise measurements of weak lensing effects to create detailed maps of the distribution of dark matter, revealing its intricate structures.
- Galaxy Clusters: By studying the formation and evolution of galaxy clusters, Euclid will deepen our understanding of the role dark matter plays in shaping the cosmic web.
- Spectroscopy: Euclid will also conduct spectroscopic observations to study the properties of galaxies and their connection to dark matter.
Important Points:
- Dark matter is a mysterious substance that does not absorb, reflect, or emit light, making it invisible to traditional detection methods.
- It constitutes approximately 27 percent of the universe, with dark energy accounting for 68 percent.
- Dark matter is not visible matter, dark clouds of normal matter (baryons), or antimatter.
- It is believed to be composed of exotic particles like axions or WIMPs.
- Dark matter’s invisibility stems from its minimal interaction with electromagnetic forces, although its gravitational effects can be observed.
- Dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that drives the accelerating expansion of the universe, acting as an “anti-gravity” force.
- The Euclid space telescope is a groundbreaking instrument designed to study dark matter and dark energy.
- Euclid will conduct a redshift survey to measure the distance of galaxies accurately.
- Weak lensing observations with Euclid will map the distribution of dark matter and reveal its structures.
- Studying galaxy clusters with Euclid will deepen our understanding of the role of dark matter in shaping the cosmic web.
- Euclid will use spectroscopy to investigate the properties of galaxies and their connection to dark matter.
- The launch of Euclid marks a significant advancement in our exploration of the universe and offers potential breakthroughs in astrophysics.
Why In News
The recently launched Euclid space telescope is set to revolutionize the study of dark matter, taking a pivotal role in unraveling the mysteries of the universe’s most elusive substance. Equipped with advanced instruments and cutting-edge technology, Euclid is poised to provide unprecedented insights into the nature and distribution of dark matter, shaping our understanding of the cosmos like never before.
MCQs about Dark Matter
-
Why is dark matter difficult to detect?
A. It emits visible light.
B. It interacts with electromagnetic forces.
C. It absorbs radio waves.
D. It reflects X-rays.
-
What is the primary role of the Euclid space telescope?
A. Exploring dark energy.
B. Mapping the distribution of dark matter.
C. Studying galaxy clusters.
D. Observing redshift of galaxies.
-
What does dark energy do to the expansion of the universe?
A. Causes it to contract.
B. Slows down its expansion.
C. Halts its expansion.
D. Accelerates its expansion.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


