The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently issued strict guidelines regarding the use of First Loss Default Guarantee (FLDG) arrangements in digital lending. The FLDG model is a lending arrangement between banks/NBFCs and fintech or lending service providers (LSPs) where the LSP compensates the lender in case of borrower defaults. This essay explores the significance of the RBI’s guidelines and their impact on the digital lending ecosystem.
Understanding FLDG Arrangements:
- Definition: FLDG arrangements involve LSPs providing credit enhancement features, such as a first loss guarantee, for a certain percentage of loans generated by them.
- Purpose: The FLDG model aims to protect lenders against default risks and ensure the smooth functioning of digital lending.
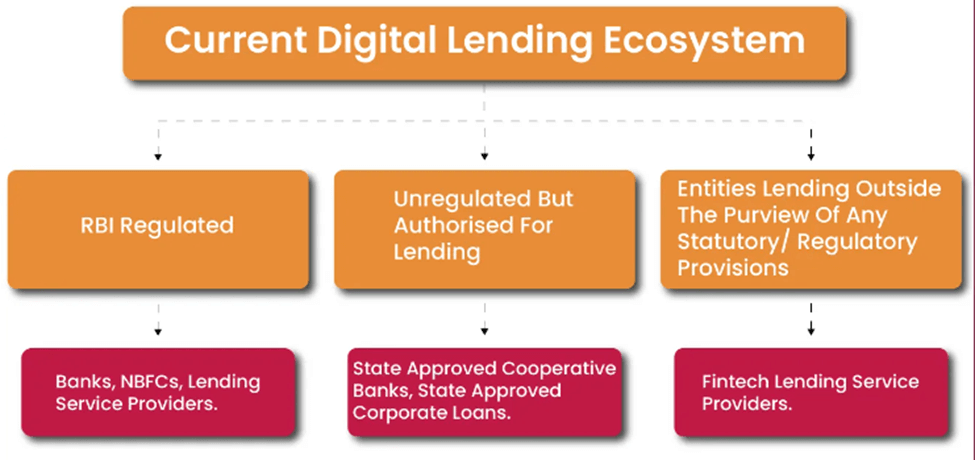
Role of Lending Service Providers (LSPs):
- Overview: LSPs are technology-driven players in the lending space that perform various functions on behalf of banks or NBFCs.
- Functions: LSPs assist in customer acquisition, underwriting support, pricing support, disbursement, servicing, monitoring, and recovery of loans.
- RBI Guidelines: LSPs must comply with outsourcing guidelines set by the RBI to maintain regulatory compliance.
Reasons for RBI’s Concerns:
- Systemic Risk: The RBI expressed reservations about the FLDG model, fearing it could pose a systemic risk.
- Unregulated Practices: Some fintechs engaged in balance-sheet lending without meeting the principal business criteria to remain outside regulation.
- Operational Risks: Increased reliance on third-party service providers led to higher operational risks, prompting regulated entities to discontinue such arrangements.
The RBI’s Guidelines:
- Incorporation: LSPs providing DLG must be incorporated as companies under the Companies Act, 2013.
- Default Cover: The new framework permits default cover for up to 5% of the loan portfolio, invoked within a maximum overdue period of 120 days.
- Reduced Risk: Previously, entities offered almost 100% FLDG, exposing lenders to high risk. The new guidelines mitigate this risk.
- Disclosure: LSPs must publish the number of portfolios and respective amounts covered under the guarantee arrangement on their website.
- Guarantee Forms: Banks can accept DLG in digital lending if provided in the form of cash deposits, fixed deposits with a lien, or bank guarantees.
Significance of the Guidelines:
- Inclusion of Small and Medium Fintechs: The guidelines facilitate the entry of small and medium fintechs into digital lending partnerships with banks or NBFCs.
- Transparent and Efficient Operations: The well-defined structure enables all players to participate effectively and transparently in the digital lending space.
- Enhanced Credit Penetration: The guidelines contribute to the orderly development of the digital lending ecosystem and increase credit penetration in the economy.
Important Points:
- RBI issued strict guidelines on First Loss Default Guarantee (FLDG) arrangements in digital lending 📜💼
- FLDG model: Lending arrangement where fintech/LSP compensates banks/NBFCs in case of borrower defaults 💰🤝
- Lending Service Providers (LSPs): New-age players in lending, perform various lender functions using technology platforms 🚀💻
- RBI’s concerns: FLDG arrangements may pose systemic risk and involve unregulated practices 🚫📉
- RBI’s guidelines aim to mitigate risks and ensure regulatory compliance in digital lending 💪✅
- Guidelines limit default cover to 5% of loan portfolio, invoked within 120 days of overdue 📉⌛
- Earlier, entities offered almost 100% FLDG, exposing lenders to high risk 📈😱
- LSPs must disclose portfolios and amounts covered under guarantee arrangements on their websites 🔍💼
- Banks can accept DLG in the form of cash deposits, fixed deposits with lien, or bank guarantees 💵🏦
- Guidelines facilitate entry of small and medium fintechs into digital lending partnerships 🤝📈
- Well-defined structure promotes transparency, efficiency, and participation in digital lending 🏗️🔍💼
- Guidelines contribute to orderly development of digital lending ecosystem and enhance credit penetration in the economy 📈💸🌐
Why In News
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently implemented stringent guidelines that not only permit but also regulate the utilization of First Loss Default Guarantee (FLDG) arrangements within the digital lending sector. These guidelines aim to foster a safer lending environment by establishing robust risk mitigation mechanisms for digital lenders.
MCQs about FLDG Arrangements in Digital Lending
-
What is the purpose of First Loss Default Guarantee (FLDG) arrangements in digital lending?
A. To protect borrowers from default risks
B. To ensure higher profits for fintech companies
C. To compensate lenders in case of borrower defaults
D. To regulate the functioning of non-banking financial companies (NBFCs)
-
What prompted the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to issue guidelines on FLDG arrangements?
A. Concerns about the profitability of fintech companies
B. Increasing reliance on third-party service providers by lenders
C. Regulatory compliance issues faced by banks
D. Encouragement from the government to promote digital lending
-
How do the RBI guidelines promote transparency in FLDG arrangements?
A. Requiring LSPs to disclose the number and amount of portfolios covered
B. Restricting the involvement of fintech companies in digital lending
C. Mandating banks to publish the details of their lending partners
D. Encouraging lenders to rely solely on internal credit assessment processes
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


