The Enforcement Directorate (ED) in India has registered a case against the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) India under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) for alleged foreign exchange violation. Let’s dive into what FEMA is, its objectives, and its applicability.
The Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA)
FEMA came into effect in 1999 as a successor to the Foreign Exchange Regulation Act (FERA) of 1973. It was formulated to fill all the loopholes and drawbacks of FERA in the post-liberalisation India. FEMA was introduced to de-regularize and have a liberal economy in India. The act outlines the formalities and procedures for the dealings of all foreign exchange transactions in India.
Objectives of FEMA
The main objective of FEMA was to facilitate external trade and payments. FEMA was also formulated to assist the orderly development and maintenance of the Indian forex market. The act outlines the formalities and procedures for the dealings of all foreign exchange transactions in India. These transactions have been classified into two categories: Capital Account Transactions and Current Account Transactions.
Capital Account Transactions comprise all capital transactions and recognize domestic investment in foreign assets and foreign investment in domestic. On the other hand, Current Account Transactions comprise trade of merchandise. Current Account transactions involve inflow and outflow of money to and from the country/countries during a year, due to the trading/rendering of commodity, service, and income. The current account is an indicator of an economy’s status.
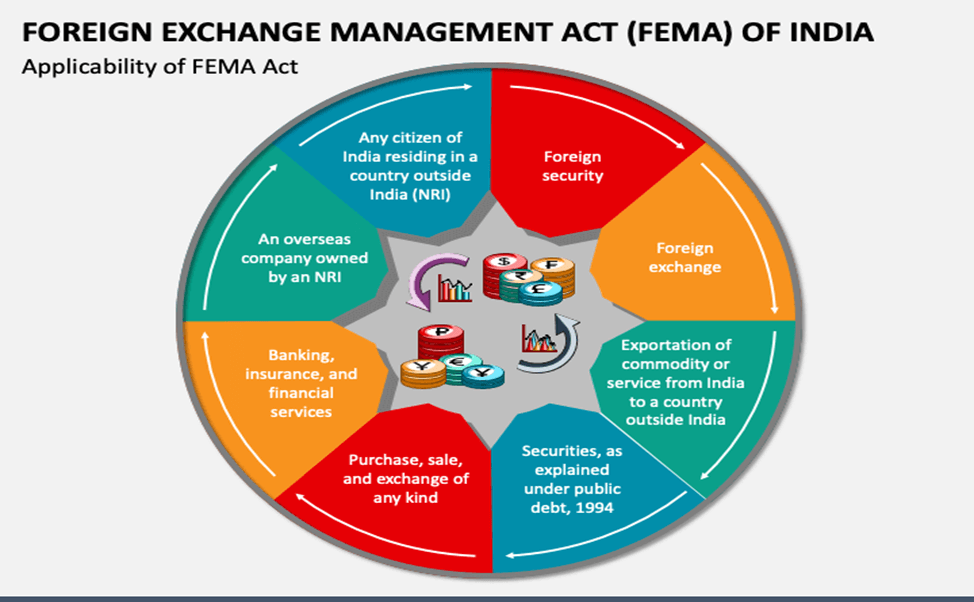
Applicability of FEMA Act
FEMA is applicable to the whole of India and is equally applicable to agencies and offices located outside India that are owned or managed by an Indian Citizen. FEMA is applicable to foreign exchange, foreign security, exportation of any commodity and/or service from India to a country outside India, importation of any commodity and/or services from outside India, securities as defined under Public Debt Act 1994, purchase, sale and exchange of any kind (i.e. Transfer), banking, financial and insurance services, any overseas company owned by an NRI (Non-Resident Indian) and the owner is 60% or more, any citizen of India residing in the country or outside (NRI).
Comparison of FEMA and FERA
| FERA | FEMA |
| Passed in 1973 | Passed in 1999 |
| Conceived with the notion that foreign exchange is a scarce resource | Created with the idea that foreign exchange is an asset |
| Main goal was to save foreign exchange | Main goal is to manage foreign exchange |
| Limited definition of “authorized person” | Broader definition of “authorized person” |
| Banking units not considered authorized persons | Banking units fall under the meaning of authorized persons |
| Violations punishable by law at all times | Breaking FEMA regulations is a civil crime |
| No provision for a tribunal | Special Director (Appeals) and Special Tribunal provided |
| Direct punishment clause for individuals who broke guidelines | Guilty individuals must pay a fine and can be put in jail if the fine is not paid within 90 days |
Why In News
The case pertains to the alleged violation of FEMA regulations by the BBC India, which the ED is investigating. The investigation is ongoing, and further details are yet to be released.
MCQs about Foreign Exchange Management Act in India
-
What is the objective of the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA)?
A. To facilitate external trade and payments
B. To regulate foreign exchange transactions
C. To control foreign investment in domestic assets
D. To de-regularize the Indian economy
-
What are the two categories of foreign exchange transactions under FEMA?
A. Capital Account Transactions and Current Account Transactions
B. Inward Investment Transactions and Outward Investment Transactions
C. Short-term Transactions and Long-term Transactions
D. Import Transactions and Export Transactions
-
What is the applicability of the FEMA Act?
A. It is applicable to the whole of India and agencies and offices located outside India that are owned or managed by an Indian Citizen
B. It is only applicable to foreign exchange transactions conducted within India
C. It is applicable to foreign exchange, foreign security, and exportation of commodities from India
D. It is applicable to foreign exchange, foreign security, and importation of commodities into India
-
What is the difference between Capital Account Transactions and Current Account Transactions?
A. Capital Account Transactions involve domestic investment in foreign assets and foreign investment in domestic assets, while Current Account Transactions involve trade of merchandise.
B. Capital Account Transactions involve inflow and outflow of money to and from the country/countries during a year, while Current Account Transactions are an indicator of an economy’s status.
C. Capital Account Transactions are related to securities as defined under Public Debt Act 1994, while Current Account Transactions involve banking, financial, and insurance services.
D. Capital Account Transactions involve the purchase, sale, and exchange of any kind, while Current Account Transactions involve the importation and exportation of commodities and services.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


