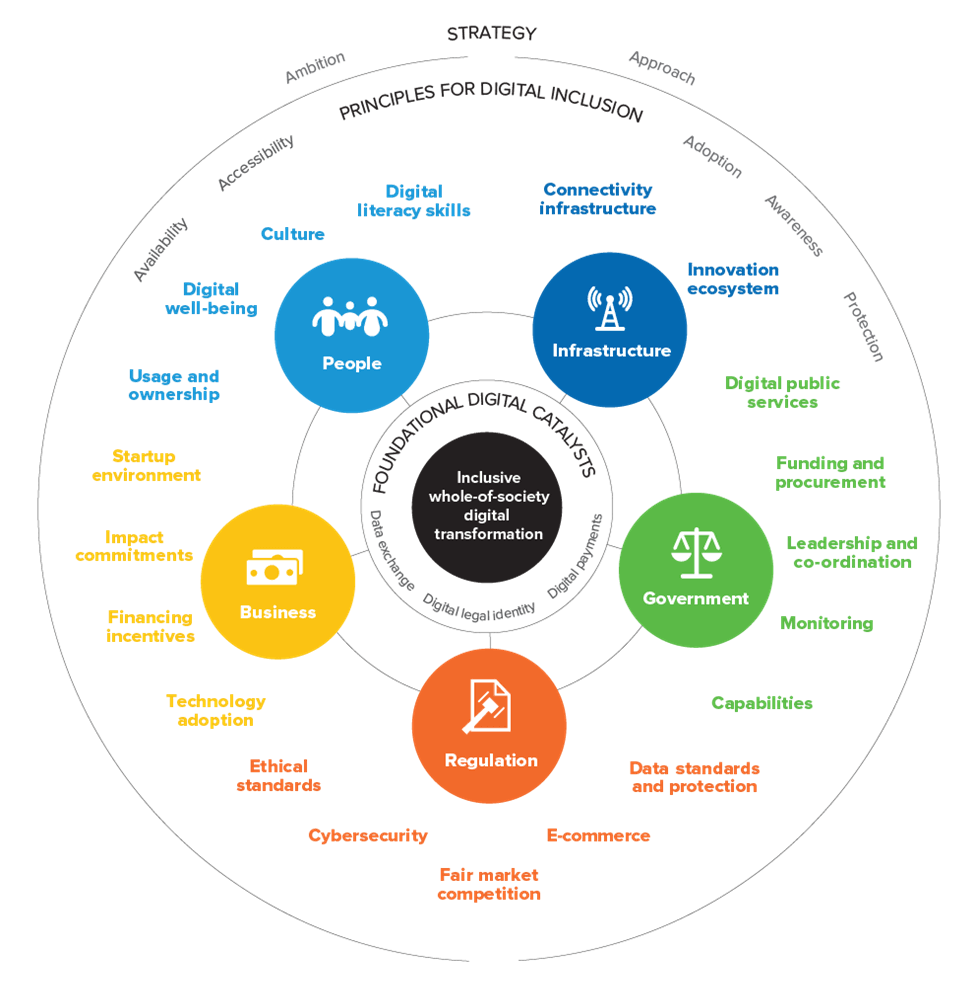
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) refers to a set of platforms and blocks that enable the delivery of essential services to people, empowering citizens and improving lives through digital inclusion. The DPI is made up of three foundational blocks, which mediate the flow of people, money, and information. These are the digital identity system (Aadhar), the real-time fast payment system (UPI), and a platform for safely sharing personal data without compromising privacy.
The Need for DPI
Public infrastructure has been a critical element in human progress throughout history. Infrastructure has been vital to facilitating the flow of people, money, and information, and it has fostered public and private innovation, generating considerable value creation in societies. The DPI has emerged as a feasible model due to its low cost, interoperability, and scalable design, safeguarding against monopolies and digital colonization.
India’s Thriving DPI Ecosystem
India has been a pioneer in the development of DPI, and its DPI ecosystem is one of the most robust in the world. The government has prioritized the development of DPI in recent years, and there have been several initiatives aimed at building a thriving DPI ecosystem.
India’s DPI ecosystem has been designed through a unique partnership between governments (Union and States), regulators, the private sector, selfless volunteers, startups, and academia/think tanks. India’s thriving DPI ecosystem is central to delivering on its economic promise, and it is key to achieving the country’s audacious goals of becoming a $5 trillion economy and the world’s third-largest economy within a decade.
Key Components of DPI in India
Digital Identity: The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) has developed Aadhaar, a unique identification system that provides every Indian citizen with a unique identification number based on their biometric data. Aadhaar is used for a variety of purposes, including as a digital identity proof for availing government services.
Unified Payment Interface: UPI enables anyone with a bank account to make real-time digital payments using a mobile device. UPI is a payments system that runs on a central server operated by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), a non-profit organization that is responsible for its management.
DigiYatra and DigiLocker: DigiYatra is a Biometric Enabled Seamless Travel (BEST) experience based on a facial recognition system (FRS), again through a partnership between industry and government, which ensures seamless identification of passengers at key checkpoints such as airport entry, security check, and boarding gate clearance.
Cybersecurity: The government has established the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In), which is responsible for responding to cybersecurity incidents and ensuring the security of India’s digital infrastructure.
Challenges with DPI
One of the significant challenges facing DPI is the weaponization of data and technology or Digital Colonization, resulting in a loss of agency, sovereignty, and privacy. Proactively deliberating on how to build good DPI is key to avoiding such challenges.
Why In News
India’s digital public infrastructure (DPI), commonly known as India Stack, is the result of a collaborative effort between the government (both Union and State), regulators, private sector entities, volunteers, startups, and academia/think tanks. This unique partnership has enabled India to develop three essential DPIs, making it the first country to achieve this feat. These foundational DPIs include a digital identity system (Aadhar), a real-time fast payment system (UPI), and a secure platform for sharing personal data without compromising privacy.
MCQs on Foundational Components of India’s DPI Ecosystem
-
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) refers to:
A. A set of platforms and blocks that enable the delivery of essential services to people, empowering citizens and improving lives through digital inclusion.
B. A physical infrastructure that has facilitated progress throughout history.
C. A network of private businesses that operate in the digital space.
D. An exclusive network that prioritizes the flow of information over people and money.
-
What are the three foundational blocks that make up the DPI ecosystem in India?
A. Digital identity system, real-time fast payment system, and a platform for safely sharing personal data.
B. Physical infrastructure, digital storage, and data analytics.
C. Social media, e-commerce, and online entertainment.
D. GPS tracking, facial recognition, and voice assistants.
-
What is the major challenge facing DPI?
A. Digital colonization and weaponization of data and technology.
B. Incompatibility and lack of scalability.
C. Insufficient funding from the government.
D. Slow adoption rate by the public.
-
What is the UIDAI?
A. The Unique Identification Authority of India.
B. The National Payments Corporation of India.
C. The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team.
D. The government agency responsible for building physical infrastructure.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


