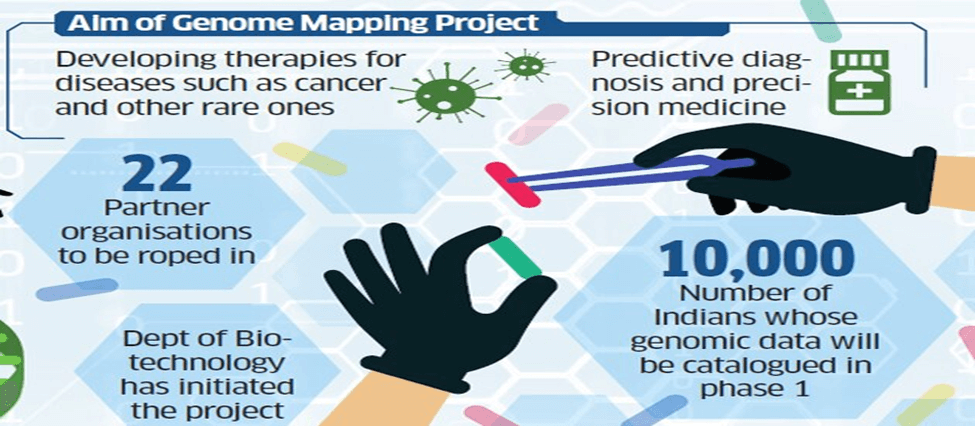
The Genome India Project is a three-year initiative launched by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) to sequence 10,000 Indian human genomes and create a database. As of now, the project has sequenced close to 7,000 genomes, with 3,000 available for public access by researchers. Around 20 institutions across India are involved in the project, with the Centre for Brain Research, Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bangalore, handling the analysis and coordination.
Data Collection and Priority Areas
The project aims to collect data through a simple blood test conducted by investigators in hospitals. The information will then be added to biobanks. Some of the priority areas for the project are precision health, rare genetic disorders, mutation spectrum of genetic and complex diseases in the Indian population, genetic epidemiology of multifactorial lifestyle diseases, and translational research.
Significance of the Project
The Indian population consists of over 4,600 population groups, and many of them are endogamous, contributing to genetic diversity. Thus, the Indian population harbors distinct variations, and disease-causing mutations are often amplified within some of these groups.
Therefore, findings from population-based or disease-based human genetics research from other populations of the world cannot be extrapolated to Indians. The creation of a database of Indian genomes will allow researchers worldwide to learn about genetic variants unique to India’s population groups and use them to customize drugs and therapies. Genome sequencing can also aid in designing genome-wide association chips, which will facilitate large-scale genetic studies in a cost-effective manner.
Understanding Genome Sequencing
Genome sequencing is a technique that reads and interprets genetic information found within DNA or RNA. The human genome consists of over three billion genetic letters, and sequencing methods can only handle short stretches of DNA at a time. Every organism has a unique genome sequence, and sequencing can read and interpret genetic information found within DNA or RNA.
Significance of Genome Sequencing
Genome sequencing is important in understanding mutations that increase virus infectivity, studying vaccine efficacy, tracing mutations, developing vaccines, and gathering vital information. The knowledge generated through vital research assists in developing diagnostics, potential therapeutics, and vaccines for potential diseases in the future.
Challenges in Genome Sequencing in India
The Genome India Project has faced challenges due to the very high target of sequencing at least 5% of the samples, insufficient reagents and tools necessary to scale up the process, and a low capacity of the ten laboratories involved in the project. Additionally, sample collection requires sorting and packaging samples and RNA preparations for shipping in a cold chain to sequencing centers, along with recording extensive metadata to make sequence information useful.
Way Ahead
The Genome India Project reflects India’s progress in gene therapies, precision medicine, and its movement towards emerging next-generation medicine. With India’s tremendous genetic diversity due to a series of large migrations historically, this initiative adds greatly to the current information about the human species.
Why In News
The Genome India Project aims to completely sequence 10,000 genomes by the end of 2023, marking a significant milestone in India’s genomics research. This project will create a rich dataset of genetic information that will help researchers better understand the genetic basis of diseases and develop more effective treatments.
MCQs about Genome Sequencing in India
-
What is the expected number of completely sequenced genomes under the Genome India Project?
A. 5,000
B. 7,500
C. 10,000
D. 12,500
-
What is the primary aim of the Genome India Project?
A. To create a database of genetic information specific to the Indian population.
B. To identify potential genetic markers for diseases prevalent in India.
C. To develop gene therapy for genetic disorders in India.
D. To establish India as a leader in genetic research.
-
Which technology is being used for the sequencing of genomes under the Genome India Project?
A. Sanger sequencing
B. Nanopore sequencing
C. Illumina sequencing
D. Pyrosequencing
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


