Daily Current Affairs : 1-November-2023
The Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) stands as a critical tool in the battle against air pollution in the Delhi-NCR region. Envisioned as a set of emergency measures, GRAP aims to prevent further deterioration of air quality when it reaches specific thresholds. Approved by the Supreme Court of India in 2016 and officially notified in 2017, GRAP emerged through extensive consultations between the Environment Pollution (Prevention and Control) Authority, state government representatives, and experts. Its fundamental purpose lies in addressing and mitigating air pollution, especially during severe pollution periods, prioritizing public health and environmental protection.
Understanding the GRAP Stages: A Tiered Approach to Air Quality Management
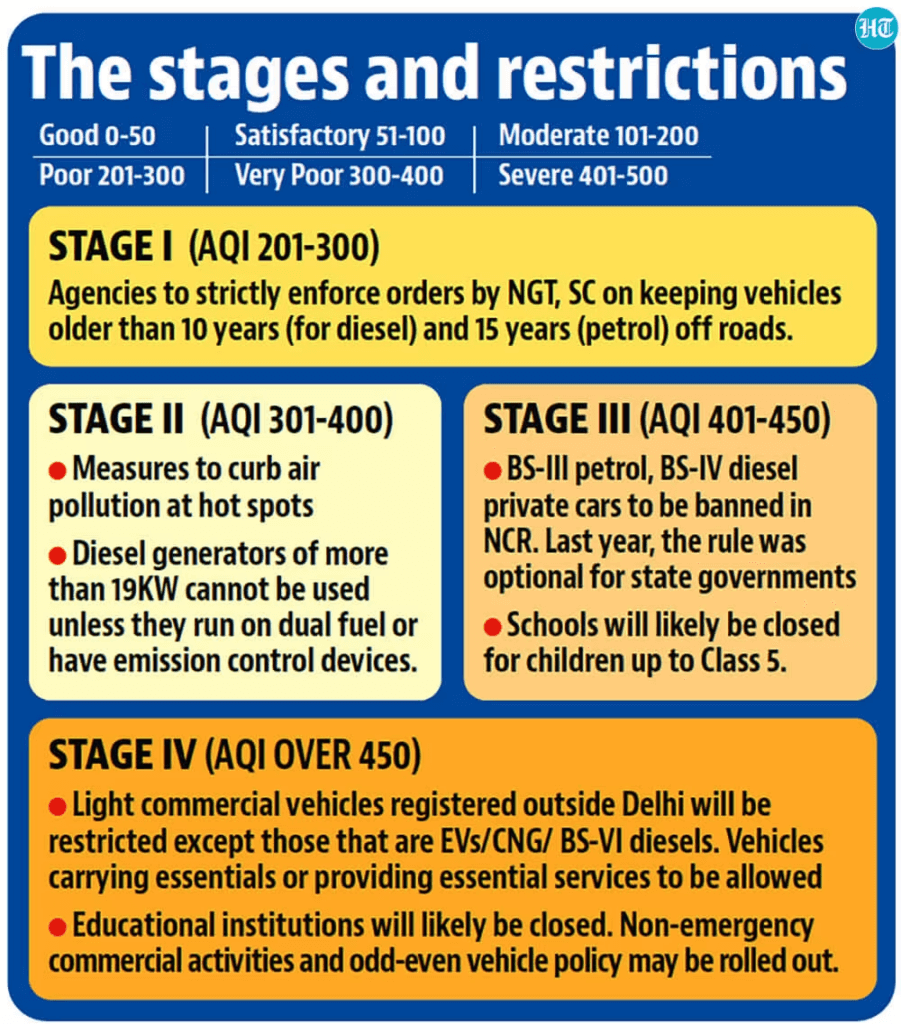
GRAP operates through four distinct stages, each triggered by specific Air Quality Index (AQI) categories:
- Stage 1: Activated when AQI falls within the ‘poor’ category (201-300).
- Stage 2: Activated when AQI enters the ‘very poor’ category (301-400).
- Stage 3: Activated when AQI reaches the ‘severe’ category (401-450).
- Stage 4: Activated when AQI exceeds the ‘severe+’ category (above 450).
Current Measures Under Stage 4: A Swift Response to Escalating Pollution
Recent circumstances in Delhi-NCR have compelled the activation of Stage 4 of GRAP. This stage enforces several crucial measures:
- Ban on Diesel Four-Wheelers: Strict prohibition on non-BS-VI compliant diesel four-wheelers.
- Entry Restrictions on Trucks: Limitations imposed on the entry of trucks in the region.
- Closure of Certain Industries: Temporary closure of specific industries contributing significantly to pollution.
- School Closures and Activity Discontinuation: Closure of all Delhi schools for students up to class five and suspension of outdoor activities.
Evolution of GRAP: A Proactive Approach in 2023
This year, GRAP has taken a proactive turn, incorporating preemptive measures based on forecasts. Collaborating with esteemed organizations like the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology and the India Meteorological Department, GRAP relies on air quality and meteorological forecasts to anticipate deteriorating air quality. Unlike previous implementations, the enforcement this year considers a comprehensive Air Quality Index (AQI), encompassing various pollutants beyond PM2.5 and PM10.
Important Points:
- GRAP Stages:
- Four stages based on specific Air Quality Index (AQI) categories:
- Stage 1: AQI ‘poor’ category (201-300).
- Stage 2: AQI ‘very poor’ category (301-400).
- Stage 3: AQI ‘severe’ category (401-450).
- Stage 4: AQI ‘severe+’ category (above 450).
- Four stages based on specific Air Quality Index (AQI) categories:
- Current Measures Under Stage 4:
- Ban on non-BS-VI compliant diesel four-wheelers.
- Entry restrictions on trucks.
- Closure of specific industries contributing to pollution.
- Closure of Delhi schools for students up to class five and suspension of outdoor activities.
- Evolution of GRAP in 2023:
- Proactive approach based on air quality and meteorological forecasts.
- Collaboration with organizations like the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology and the India Meteorological Department.
- Comprehensive AQI calculation considering various pollutants beyond PM2.5 and PM10.
MCQs about GRAP: Mitigating Air Pollution in Delhi-NCR
-
What does GRAP stand for?
A. Global Response Action Plan
B. Graded Response Action Plan
C. Green Revolution Action Protocol
D. General Reforms Assessment Program
-
When was Stage 4 of GRAP activated in response to deteriorating air quality?
A. When AQI was in the ‘poor’ category (201-300)
B. When AQI was in the ‘very poor’ category (301-400)
C. When AQI was in the ‘severe’ category (401-450)
D. When AQI exceeded the ‘severe+’ category (above 450)
-
What is the primary goal of GRAP?
A. Economic Development
B. Public Health and Environmental Protection
C. Traffic Management
D. Agricultural Advancement
-
How does GRAP determine the implementation of measures in 2023?
A. Based on political decisions
B. Based on public opinion polls
C. Based on air quality and meteorological forecasts
D. Based on historical data
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


