Scientists, including Indian astrophysicist Dr Surhud More, have used gravitational lensing to map the distribution of dark matter in the universe. This phenomenon occurs when a massive object generates a gravitational field that distorts and magnifies the light from objects behind it. The team utilized the Hyper Suprime-Cam (HSC) present on top of the 8.2m diameter Subaru Telescope on Mauna Kea in Hawai’i to carry out one of the most powerful gravitational lensing experiments currently underway.
Understanding Gravitational Lensing
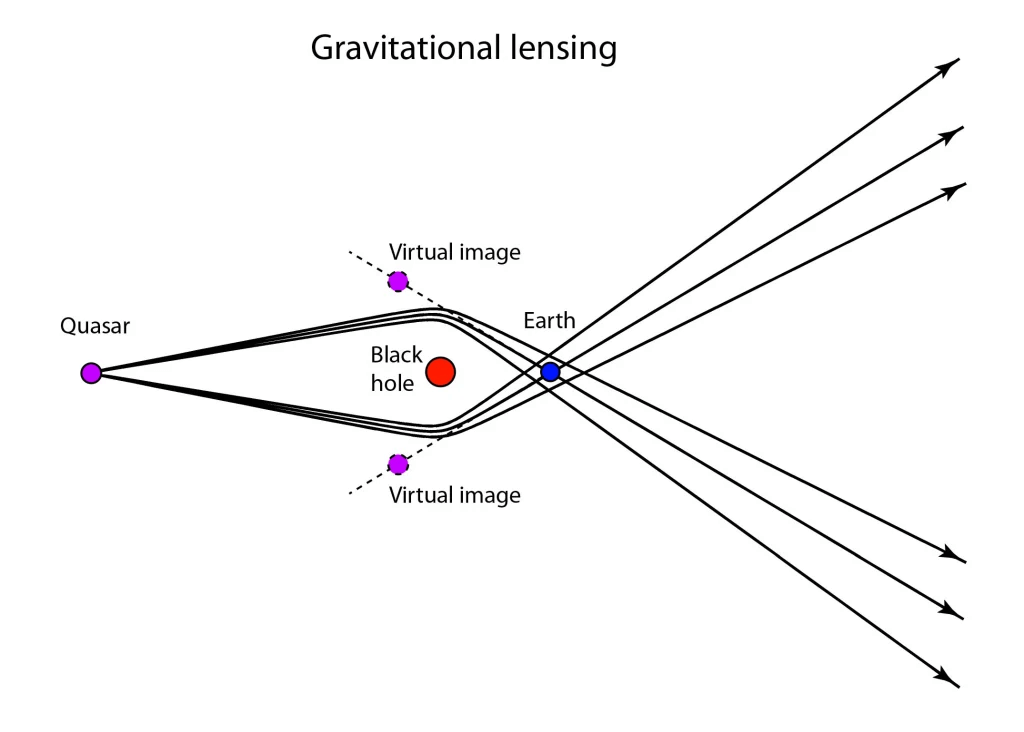
Gravitational lensing is based on Einstein’s theory of general relativity, which suggests that mass bends light. This phenomenon helps astronomers understand black holes, dark matter, and more. In contrast, common camera lenses in a magnifying glass work by bending light rays that pass through them in a process known as refraction, to focus the light elsewhere.
Dark Matter and the Universe
Dark matter makes up 95% of the universe, yet little is known about its structure or evolution. By mapping out dark matter in a tomographic manner (in 3D), the team was able to characterize the structure of dark matter, demonstrating that it is distributed around galaxies in multiple tomographic pieces of distances away. This method is similar to a medical CT scan, allowing scientists to create a detailed map of dark matter distribution in the universe.
The Experiment and Findings
The team utilized images taken from the Subaru telescope to measure a value for the ‘clumpiness,’ known as S8, of 0.76. This value is consistent with values found by other gravitational lensing surveys. However, it doesn’t match the value of 0.83 predicted by the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) when the universe was about 380,000 years old, which dates back to the origin of the universe.
Significance for the Cosmological Model
The density of dark matter and the amount of ‘clumpiness’ are crucial to understanding how the structure in the universe evolves with time. Mapping out dark matter distribution in a tomographic manner allows scientists to carry out a rigorous test of the cosmological model. This finding could help to refine our understanding of the universe’s evolution and structure.
Why In News
Using the effect of gravitational lensing, a team of scientists that included Indian researchers, created a detailed map of the distribution of dark matter in the universe. They found that the dark matter is spread around galaxies in multiple tomographic pieces at varying distances, akin to the sections of a medical CT scan.
MCQs about Gravitational Lensing and its Role in Astrophysics
-
What is gravitational lensing?
A. The phenomenon where light bends due to the presence of a gravitational field.
B. The phenomenon where light is reflected off the surface of a mirror.
C. The phenomenon where light passes through a prism and is separated into its component colors.
D. The phenomenon where light is scattered by particles in the atmosphere.
-
What is the purpose of the Hyper Suprime-Cam (HSC) Survey?
A. To study the effect of gravitational lensing on dark matter.
B. To study the formation of black holes.
C. To study the distribution of visible matter in the universe.
D. To study the formation of stars in galaxies.
-
What did the team of astrophysicists and cosmologists discover about dark matter?
A. It is evenly distributed throughout the universe.
B. It is only found in galaxies.
C. It is distributed around galaxies, in multiple tomographic pieces of distances away.
D. It is only found in clusters of galaxies.
-
Why is mapping out the distribution of dark matter significant?
A. It helps astronomers understand black holes.
B. It helps astronomers understand the evolution of the universe.
C. It helps astronomers understand the distribution of visible matter.
D. It helps astronomers understand the formation of stars.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


