The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) recently achieved a significant milestone with the successful launch of the first second-generation satellite for its navigation constellation, NavIC. This essay explores the details of the launch, the features of the NVS-01 satellite, and the practical purposes served by the NavIC constellation for its users.
Launching the Heaviest Satellite in the NavIC Constellation:
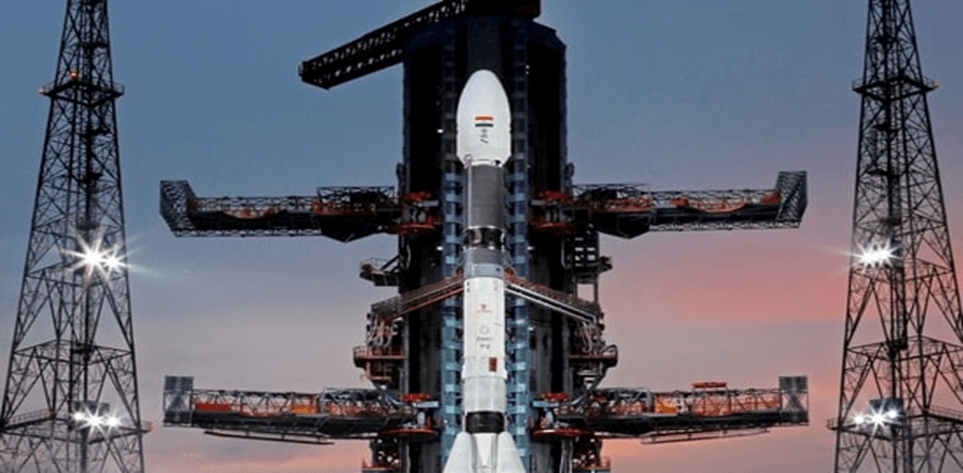
The recently launched NavIC satellite, known as NVS-01, weighs a remarkable 2,232 kg, making it the heaviest among all the satellites in the NavIC constellation. This milestone was achieved through the launch of a Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) rocket from Sriharikota. In comparison, the seven satellites currently in the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) constellation weighed approximately 1,425 kg each and were launched using the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV).
Introducing the NVS-01 Satellite:
The NVS-01 satellite represents the first of India’s second-generation NavIC satellites. It incorporates several notable features that enhance its capabilities and interoperability:
- Space-Qualified Rubidium Atomic Clock: The NVS-01 satellite boasts an indigenous Rubidium atomic clock developed by the Space Application Centre in Ahmedabad. This advanced technology is possessed by only a handful of countries, underscoring India’s prowess in space exploration.
- Expanded Frequency Signals: Unlike the existing satellites in the NavIC constellation, the second-generation satellites, including NVS-01, transmit signals in three frequencies: L1, L5, and S. The addition of the L1 frequency allows for increased interoperability with other satellite-based navigation systems, expanding the range of compatible devices and applications.
- Increased Mission Lifespan: The second-generation satellites offer an extended mission life of over 12 years, surpassing the 10-year lifespan of the existing satellites. This longevity ensures that NavIC can continue to provide reliable navigation services for an extended period.
Practical Applications of the NavIC Constellation:
The NavIC constellation plays a crucial role in various practical applications, benefitting users in several sectors. Some notable applications include:
- Public Vehicle Safety: NavIC aids in enhancing public vehicle safety by providing accurate real-time navigation and positioning information. This technology helps drivers and commuters navigate unfamiliar routes, reducing the likelihood of accidents and improving overall road safety.
- Power Grid Synchronization: The synchronization of power grids is critical for efficient and reliable electricity distribution. NavIC assists in precisely aligning power grids, ensuring better management of power distribution networks and minimizing disruptions.
- Real-time Train Information Systems: NavIC enables real-time train information systems, allowing passengers to access accurate information about train schedules, delays, and arrivals. This feature enhances the overall efficiency and reliability of train travel.
- Fishermen’s Safety: For fishermen, NavIC provides vital information about weather conditions, sea surface temperature, and potential fishing zones. This data helps fishermen make informed decisions, ensuring their safety and increasing their chances of a successful catch.
Important Points:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) launched the first second-generation satellite for its navigation constellation, NavIC. 🚀
- The NVS-01 satellite is the heaviest in the NavIC constellation, weighing 2,232 kg. 🛰️
- NVS-01 incorporates a space-qualified Rubidium atomic clock, a technology possessed by only a few countries. ⏰
- The second-generation satellites in the NavIC constellation transmit signals in three frequencies: L1, L5, and S, increasing interoperability. 📡
- The L1 frequency allows for greater use of the regional navigation system in wearable devices and personal trackers. ⌚
- The second-generation satellites have a longer mission life of over 12 years compared to the existing 10-year lifespan. ⏳
- NavIC serves practical purposes such as public vehicle safety, power grid synchronization, real-time train information systems, and fishermen’s safety. 🚗⚡🚂🎣
- Future initiatives for NavIC include common alert protocol-based emergency warning, time dissemination, and geodetic network establishment. 🚨⌛🗺️
Why In News
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) achieved yet another milestone as it successfully launched the first of the second-generation satellites for its advanced navigation constellation, marking a significant step forward in India’s space exploration endeavors. The newly deployed satellite promises enhanced accuracy and coverage, empowering India to provide more precise navigation services and bolster its position as a global space power.
MCQs about India Launches Second-Generation NavIC Satellite
-
Which frequency signals are transmitted by the second-generation satellites in the NavIC constellation?
A. L1 and L2
B. L2 and L3
C. L1 and L5
D. L4 and L5
-
What is one practical purpose served by the NavIC constellation?
A. Real-time train information systems
B. Weather forecasting for agriculture
C. Space exploration for Mars missions
D. Underwater communication for submarines
-
What additional feature do the second-generation satellites offer compared to the existing satellites in the NavIC constellation?
A. Longer mission lifespan
B. Higher transmission power
C. Smaller physical size
D. Advanced imaging capabilities
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


