Daily Current Affairs : 4-January-2025
India has raised concerns with China over the establishment of two new counties—He’an and Hekang—in the Hotan Prefecture, a region that includes parts of the Aksai Chin area. This area is a point of dispute between India and China, with India claiming it as part of its Ladakh region. Here’s a deeper look at the situation and the region involved.
Hotan Prefecture: An Overview
What is Hotan Prefecture?
- Hotan Prefecture is an administrative division in southwestern Xinjiang, China. It covers a large area, including the disputed region of Aksai Chin.
- The prefecture is located in the Tarim Basin, which borders Tibet to the south and Ladakh and Gilgit-Baltistan to the west.
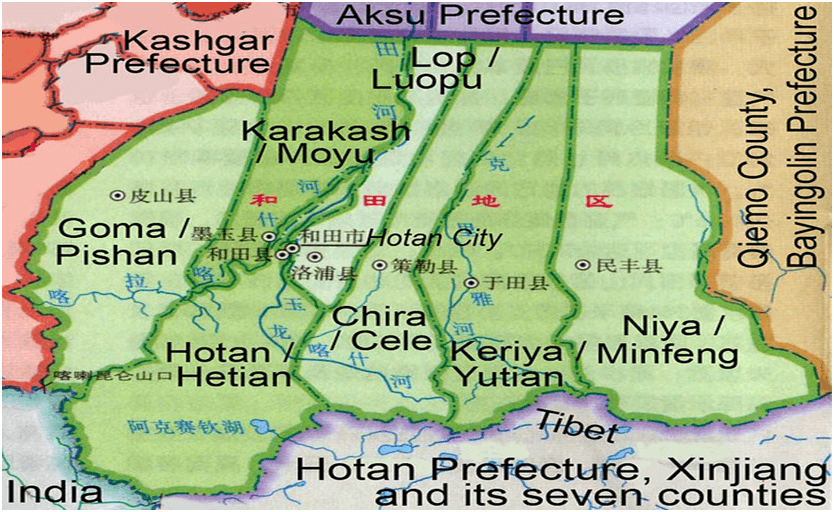
Geography and Features
- Taklamakan Desert: The northern part of Hotan Prefecture is dominated by the Taklamakan Desert, one of the largest deserts in the world.
- Kunlun Mountains: These mountains form the natural southern border, separating Hotan from Tibet.
- Oases: Despite the desert, areas like Hotan city thrive in oases, supporting agriculture and trade.
Historical Context
Sino-Indian Disputes
- The Aksai Chin region became a major point of contention during the Sino-Indian War of 1962, when China gained control over the area.
- Since then, China has administered Aksai Chin, but India continues to claim it as part of its Ladakh region.
China’s Administration
- Hotan Prefecture was established in 1971, and Aksai Chin has been under Chinese control since the early 1960s.
Demographics
The population of Hotan Prefecture mainly consists of Uyghur Muslims. These people live in the oases scattered between the Taklamakan Desert and Kunlun Mountains, where agriculture is possible.
Important Points:
- India’s Protest: India has protested China’s creation of two new counties—He’an and Hekang—in the Hotan Prefecture, part of the disputed Aksai Chin region.
- Aksai Chin Dispute: Aksai Chin is claimed by India as part of its Ladakh region, but China administers it.
- Location of Hotan Prefecture:
- Located in southwestern Xinjiang, China, within the Tarim Basin.
- Borders Tibet to the south and Ladakh and Gilgit-Baltistan to the west.
- Geographical Features:
- Taklamakan Desert: Covers the northern part of Hotan Prefecture.
- Kunlun Mountains: Form the natural southern border of the region, separating it from Tibet.
- Oases: Hotan city and surrounding settlements thrive in these fertile areas, supporting agriculture and trade.
- Historical Context:
- Aksai Chin became a disputed area after the Sino-Indian War of 1962, when China took control of it.
- Hotan was established as a prefecture in 1971, and China has administered Aksai Chin since the 1960s.
- Demographics: The majority of the population in Hotan Prefecture are Uyghur Muslims, living in oases between the Taklamakan Desert and Kunlun Mountains.
- Ongoing Tension: India views China’s actions in the region as a move to strengthen its claim over the disputed Aksai Chin area.
Why In News
India has lodged a strong protest with China over the establishment of two new counties, He’an and Hekang, in the Hotan Prefecture, a region that includes parts of the disputed Aksai Chin area, which both countries claim as their own. This move has further escalated tensions between the two nations over territorial sovereignty.
MCQs about India Protests China’s New Counties in Disputed Aksai Chin Region
-
What is the main reason behind India’s protest regarding the establishment of two new counties by China?
A. China’s expansion of its territory
B. Creation of new administrative divisions in a disputed region
C. Increased military activity in the region
D. Development of infrastructure in Ladakh
-
Which geographical feature forms the southern border of Hotan Prefecture?
A. Himalayas
B. Taklamakan Desert
C. Kunlun Mountains
D. Karakoram Range
-
Which ethnic group predominantly inhabits the Hotan Prefecture?
A. Tibetans
B. Uyghur Muslims
C. Han Chinese
D. Mongols
-
What event led to Aksai Chin becoming a disputed region between India and China?
A. The establishment of Hotan Prefecture in 1971
B. The Sino-Indian War of 1962
C. The signing of the Sino-Indian Border Agreement
D. The creation of the Kunlun Mountains
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


