This article outlines India’s major export hotspots, including top exporting districts and commodities. Additionally, it suggests potential strategies to boost India’s exports, which is a relevant topic for the IAS exam economy segment.
Top Exporting Districts in India
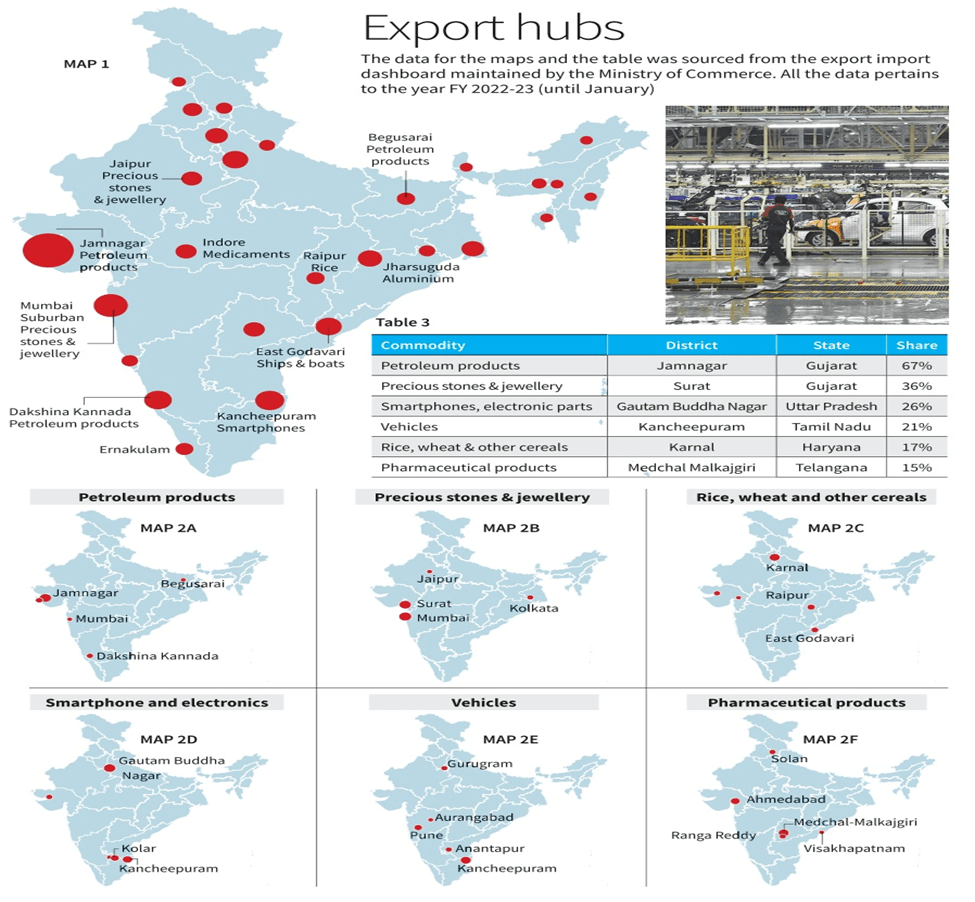
Jamnagar in Gujarat tops the list of India’s exporting districts, accounting for about 24% of the country’s exports in value terms in FY23. Surat in Gujarat and Mumbai Suburban in Maharashtra are the second and third top exporting districts, forming only about 4.5% of the country’s exports in the same period. Other districts in the top 10 include Dakshina Kannada (Karnataka), Devbhumi Dwarka, Bharuch, and Kachchh (Gujarat), Mumbai (Maharashtra), Kancheepuram (Tamil Nadu), and Gautam Buddha Nagar (Uttar Pradesh).
The dominance of Jamnagar is attributed to its contribution to India’s surging petroleum exports, while Kancheepuram’s most exported commodity was smartphones. In the Northeastern States, most top exporting districts formed as much as 90% of a State’s exports.
Top Exported Commodities in India
India exports a wide range of commodities, including petroleum products, precious stones and jewellery, rice, wheat, electronic goods, pharmaceuticals, and automobiles. Some of the top exported commodities in India and their respective top exporting districts are:
- Tea from Kamrup, Assam
- Smartphones from Gautam Buddha Nagar, Uttar Pradesh
- Parboiled rice from Raipur, Chhattisgarh
- Diamonds from Mumbai Suburban, Maharashtra
- Petroleum products from Jamnagar, Dakshina Kannada, and Begusarai
- Precious stones and jewellery from Surat, Mumbai, Mumbai Suburban, Jaipur, and Kolkata
- Rice, wheat, and other cereals from Karnal, Raipur, and East Godavari
- Smartphones and electronic parts from Gautam Buddha Nagar, Kancheepuram, Kolar, Bengaluru Rural, and Kachchh
- Vehicles other than railways from Kancheepuram, Pune, Gurugram, Anantapur, and Aurangabad
- Pharmaceutical products from Medchal Malkajgiri, Ahmedabad, Ranga Reddy, Solan, and Visakhapatnam
Diversification and Infrastructure to Boost India’s Exports
- Diversify export basket by promoting non-traditional items such as electronic goods, pharmaceuticals, and automobiles.
- Improve export infrastructure such as ports, roads, and railways to reduce the cost of exports and improve efficiency.
- Develop regional export hubs that specialize in certain export commodities to create economies of scale, reduce costs, and promote competitiveness.
- Investment in research and development is critical to help Indian exporters produce high-quality goods at lower costs, making them more competitive in the global market.
- Simplify export procedures and reduce red tape to make it easier for Indian exporters to do business with foreign partners.
- Encourage Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) to participate in exports by providing them with easy access to credit, technology, and infrastructure.
- Leverage digital technology to reach out to global customers and promote products, using e-commerce platforms to reach a wider market at a lower cost.
Why In News
It offers valuable insights into India’s export landscape, shedding light on the regions and industries that drive the country’s economic growth. By understanding the key factors that contribute to India’s export success, readers can gain a deeper understanding of the country’s economic potential and the opportunities it presents for businesses and investors.
MCQs about India’s Export Hotspots and Ways to Boost Exports
-
Which district in Gujarat tops the list of India’s exporting districts in FY23?
A. Devbhumi Dwarka
B. Bharuch
C. Kachchh
D. Jamnagar
-
What are the top three commodities exported by India?
A. Gems and jewelry, engineering goods, and chemicals
B. Petroleum products, gems and jewelry, and chemicals
C. Engineering goods, petroleum products, and textiles
D. Textiles, agriculture and allied products, and engineering goods
-
Which of the following is not a potential way suggested to increase India’s exports?
A. Promoting ease of doing business
B. Focusing only on the top 10 exporting districts
C. Encouraging research and development in export-oriented sectors
D. Investing in infrastructure and logistics
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


