Daily Current Affairs : 16-September-2023
In a significant development in the battle against the deadly Nipah virus, India has initiated contact with Australia, seeking to procure monoclonal antibody doses for combating this highly lethal pathogen. This article delves into the details of this development, emphasizing the importance of monoclonal antibodies in fighting Nipah virus infections.
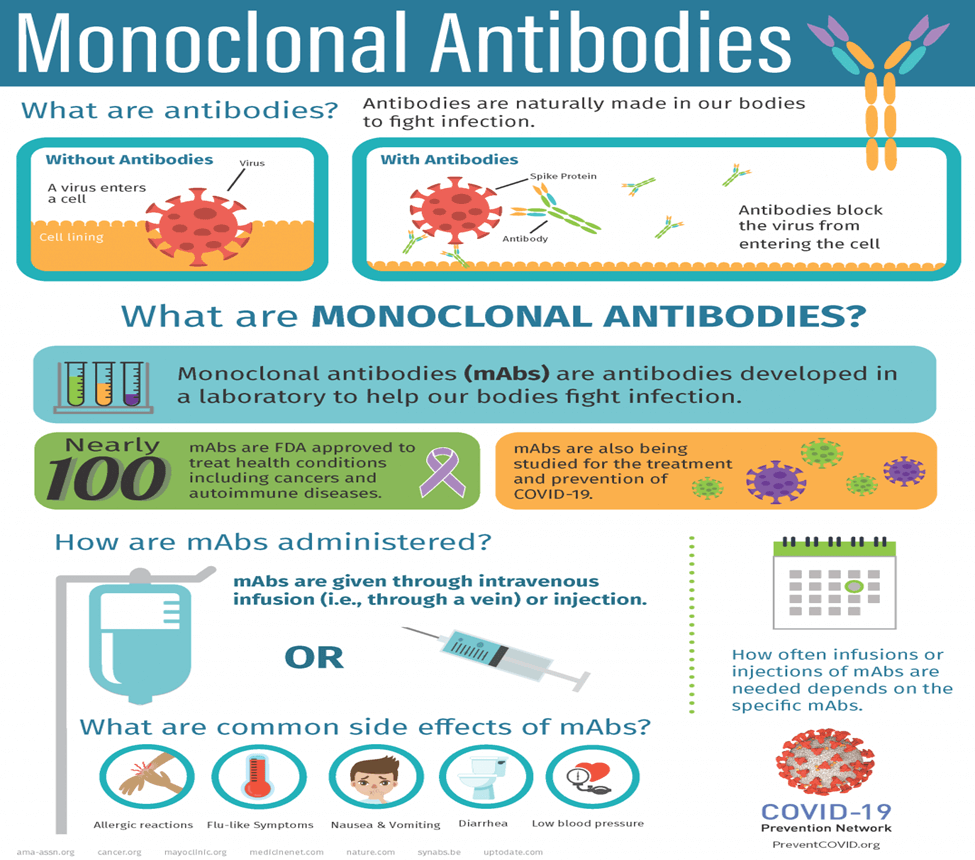
Understanding Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies are specialized proteins meticulously crafted within laboratories to mimic the natural antibodies found in our immune system. These synthetic antibodies play a crucial role in enhancing the body’s immune response. To comprehend their significance in combating Nipah virus, it’s vital to grasp their primary functions:
- Identifying Foreign Invaders: Antibodies are the foot soldiers of our immune system. They possess the remarkable ability to seek out and attach themselves to foreign substances called antigens, facilitating their destruction.
- Immune System Boost: Laboratory-produced monoclonal antibodies serve as a boost to the immune system, aiding it in recognizing and eliminating invading pathogens.
- Cloning Process: The term “monoclonal” stems from the fact that these laboratory-generated antibodies are clones, identical in structure and function, designed to target a specific antigen.
The Role of Monoclonal Antibodies in Nipah Virus Control
Nipah virus poses a grave threat due to its alarmingly high mortality rate, ranging from 40% to a staggering 70%. Given the urgency of containing the virus, monoclonal antibodies are emerging as a potential weapon to curtail the mortality rate. Here’s why they are crucial:
- Limited Treatment Options: Currently, there is no authorized treatment for Nipah virus infections. Monoclonal antibodies offer a glimmer of hope, but their effectiveness in treating Nipah is yet to be fully ascertained.
- Early Intervention: To maximize their impact, monoclonal antibodies need to be administered during the early stages of infection. This underscores the importance of swift action and early diagnosis.
Global Testing and Usage
The monoclonal antibody in question has undergone a phase-one trial and has already been administered to 14 individuals worldwide. Notably, it has been utilized for the treatment of COVID-19, albeit primarily under compassionate use provisions. However, its effectiveness against Nipah virus remains a topic of ongoing research.
Australia’s Experience
Australia has employed monoclonal antibodies to combat the Hendra virus, which is transmitted by bats. In this context, it’s worth noting that two doses of the antibody are typically required per person, emphasizing the need for adequate supplies to tackle Nipah virus effectively.
Important Points:
- India seeks monoclonal antibody doses from Australia to combat Nipah virus.
- Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-made proteins that mimic natural antibodies in the immune system.
- They identify and attach to antigens (foreign materials) to stimulate the immune response.
- Monoclonal antibodies are used for diagnosis, disease treatment, and research.
- Monoclonal antibodies have been tested for COVID-19 but are not yet confirmed for Nipah virus treatment.
- Nipah virus has a high mortality rate (40-70%), making containment a top priority.
- There is currently no authorized treatment for Nipah virus, emphasizing the need for effective interventions.
- Monoclonal antibodies must be administered in the early stages of infection for potential effectiveness.
- The antibody has undergone a phase-one trial and has been given to 14 individuals globally.
- Australia has used monoclonal antibodies to combat the bat-borne Hendra virus.
- Two doses of the antibody are typically required for effective treatment.
Why In News
India has reached out to Australia, urgently requesting additional supplies of monoclonal antibody doses to bolster its efforts in combating the Nipah virus outbreak. The collaborative response aims to enhance India’s preparedness and response capabilities against this deadly virus.
MCQs about India’s Monoclonal Antibody Initiative
-
Why is early intervention with monoclonal antibodies crucial in treating Nipah virus infections?
A) To boost the immune system
B) To maximize antibody effectiveness
C) To reduce mortality rates
D) To treat COVID-19
-
What is the current status of monoclonal antibodies as a treatment for Nipah virus?
A) Confirmed as an authorized treatment
B) Not effective against Nipah virus
C) Still under research and testing
D) Administered only in the late stages of infection
-
In which country has monoclonal antibodies been used to combat the Hendra virus, transmitted by bats?
A) India
B) Australia
C) United States
D) China
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


