Daily Current Affairs : 3-August-2023
India, like many other countries, is increasingly focused on finding sustainable solutions to meet its energy demands while reducing carbon emissions. As part of this endeavor, the country is exploring the potential of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) as a viable option. SMRs are advanced nuclear reactors with a capacity of up to 300 MW(e) per unit, offering about one-third of the generating capacity of traditional nuclear power reactors. This essay explores the concept of SMRs, their benefits, and India’s steps towards indigenous development, with a focus on clean energy transition.
Understanding Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
Size and Capacity
SMRs, as the name suggests, are smaller in size compared to conventional nuclear power reactors. This reduced physical footprint makes them more versatile, allowing them to be deployed in various settings, including remote locations and areas with limited space. Despite their smaller size, SMRs are capable of producing up to 300 MW(e) of electricity per unit, making them suitable for meeting the energy needs of small to medium-sized communities or industrial facilities.
Modularity and Transportability
One of the key advantages of SMRs is their modular design. The components and systems of these reactors can be factory-assembled and transported as a unit to their installation site. This modularity streamlines the construction process, reduces costs, and allows for standardized manufacturing, leading to potential economies of scale. Additionally, since SMRs are pre-fabricated and transported, they have the potential to minimize on-site construction time and disruption.
Efficient Operation and Refueling
SMRs have several features that enhance their efficiency compared to traditional nuclear power plants. One significant advantage is the extended refueling interval. While conventional plants require refueling every 1 to 2 years, some SMRs can operate for up to 30 years without refueling. This extended interval reduces downtime and increases the overall capacity factor, ensuring a more stable power supply.
The Promise of SMRs in Decarbonization
The drive to transition to cleaner energy sources has become a global priority to combat climate change. SMRs play a promising role in industrial decarbonization, particularly in areas where a reliable and continuous supply of power is essential. By generating low-carbon electricity, SMRs can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to India’s commitment to cleaner energy.
India’s Initiatives and Future Prospects
Collaboration and Indigenous Development
India is actively exploring the possibilities of collaborating with other countries to harness the potential of SMRs. In addition, the country is considering indigenous development of SMRs, which could pave the way for self-reliance and technological advancement. To facilitate this, authorities are examining the provisions of the Atomic Energy Act, 1962, to allow the private sector and start-ups to participate in promoting SMR technology within the country.
Advantages of SMRs for India
For a country like India, where energy demand is constantly increasing, SMRs offer several advantages:
- Flexibility: SMRs can be deployed in various locations, including remote areas, providing access to clean and reliable energy where traditional power plants might not be feasible.
- Enhanced Safety: SMRs are designed with enhanced safety features, reducing potential risks associated with nuclear energy production.
- Clean Energy Transition: By adopting SMRs, India can further its commitment to transitioning to cleaner energy sources, reducing carbon emissions, and contributing to global efforts in combating climate change.
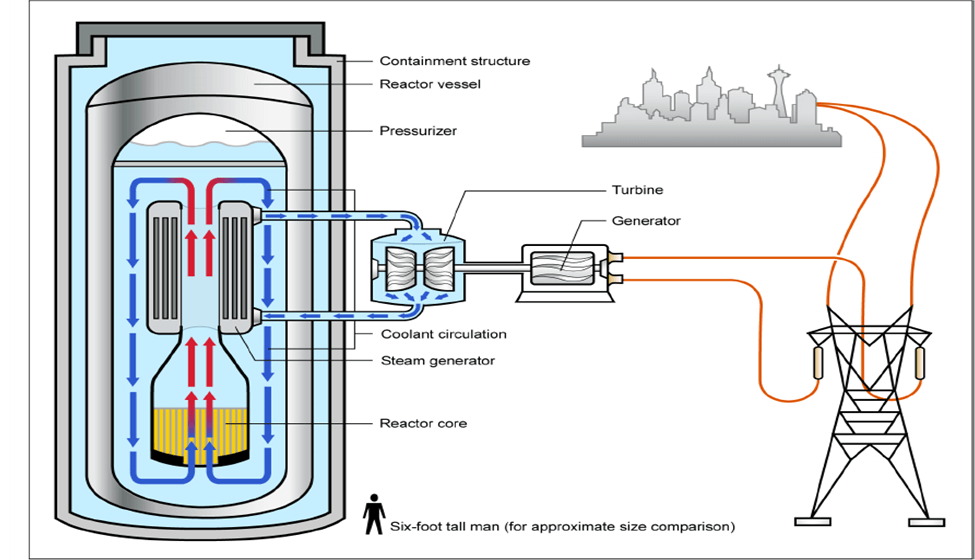
Important Points:
- SMRs are advanced nuclear reactors with a power capacity of up to 300 MW(e) per unit, about one-third of traditional nuclear power reactors.
- SMRs are physically smaller and can be factory-assembled, allowing for easier transportation and installation.
- They may require less frequent refueling, with some designed to operate for up to 30 years without refueling.
- SMRs are a promising technology for industrial decarbonization, providing reliable and continuous clean energy supply.
- India is exploring the options of collaborating with other countries and pursuing indigenous development of SMRs.
- The Atomic Energy Act, 1962 is being examined to allow private sector and start-up participation in promoting SMR technology in India.
- SMRs offer advantages such as flexibility in deployment, enhanced safety features, and supporting India’s clean energy transition.
- Embracing SMRs can help India meet its growing energy demands while contributing to global efforts in combating climate change.
Why In News
India is actively engaging in international partnerships to foster collaboration in the development of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs). Additionally, the government is diligently reviewing the provisions of the Atomic Energy Act, 1962, to facilitate the involvement of private enterprises and start-ups, paving the way for accelerated advancement of SMR technology within the nation.
MCQs about India’s Quest for Small Modular Reactors
-
What is the main advantage of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) compared to traditional nuclear power reactors?
A. Smaller physical size
B. Lower cost of construction
C. Higher power capacity
D. Longer refueling intervals
-
How often do some SMRs operate without requiring refueling?
A. Every 1 to 2 years
B. Every 3 to 7 years
C. Every 10 to 15 years
D. Up to 30 years
-
What role do SMRs play in industrial decarbonization?
A. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions
B. Enhancing nuclear fission technology
C. Increasing power capacity
D. Expanding factory-assembled components
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


