In recent years, the Indian government-owned engineering consultancy firm, Engineers India (EIL), has been conducting a study to assess the feasibility of developing salt cavern-based strategic oil reserves in Rajasthan. This potential endeavor holds significant importance for India, as it could mark the country’s first salt cavern-based oil storage facility. This essay delves into the need for oil reserves, India’s current capacity, a comparison between salt cavern-based and rock cavern-based reserves, and the potential for storing crude and petroleum products in Rajasthan.
The Need for Oil Reserves:
Countries worldwide create strategic crude oil reserves to counterbalance major disruptions in the global supply chain. India, being the third-largest consumer of crude oil globally, heavily relies on imports for more than 85% of its requirements. To ensure energy security and availability during supply shocks and emergencies, India seeks to establish strategic petroleum reserves (SPRs). These stockpiles of crude oil are diligently maintained and released when supply disruptions occur.
India’s Current Capacity:
Currently, India possesses a strategic petroleum reserve (SPR) capacity of 5.33 million tonnes, equivalent to approximately 39 million barrels of crude. This capacity can sustain the country’s demand for around 9.5 days. To further enhance energy security, India is in the process of expanding its SPR capacity by a cumulative 6.5 million tonnes. This expansion will occur at two locations: Chandikhol in Odisha (4 million tonnes) and Padur (2.5 million tonnes). The Indian Strategic Petroleum Reserve (ISPRL), established under the Petroleum Ministry’s special purpose vehicle, oversees these reserves.
Salt Cavern-Based Reserves vs. Rock Cavern-Based Reserves:
Salt cavern-based reserves offer a compelling alternative to the traditional rock cavern-based reserves, which are developed through excavation. The process of creating salt caverns involves solution mining, where water is pumped into geological formations containing extensive salt deposits. This water dissolves the salt, enabling the space to be utilized for crude oil storage. Compared to rock caverns, salt caverns provide several advantages:
- Simplicity and Efficiency:
- Salt cavern development through solution mining is simpler, faster, and less cost-intensive compared to excavation.
- Salt cavern-based oil storage facilities are naturally well-sealed and engineered for rapid injection and extraction of oil.
- Impermeable Barrier:
- The salt linings in the caverns possess low oil absorbency, creating a natural barrier against liquid and gaseous hydrocarbons.
- This impermeable nature makes salt caverns highly suitable for oil storage.
- Surface Operation:
- Unlike rock caverns, salt cavern-based storages can be primarily created and operated from the surface, minimizing complexities.
- Versatility:
- Salt caverns are utilized worldwide for storing liquid fuels, natural gas, compressed air, and hydrogen.
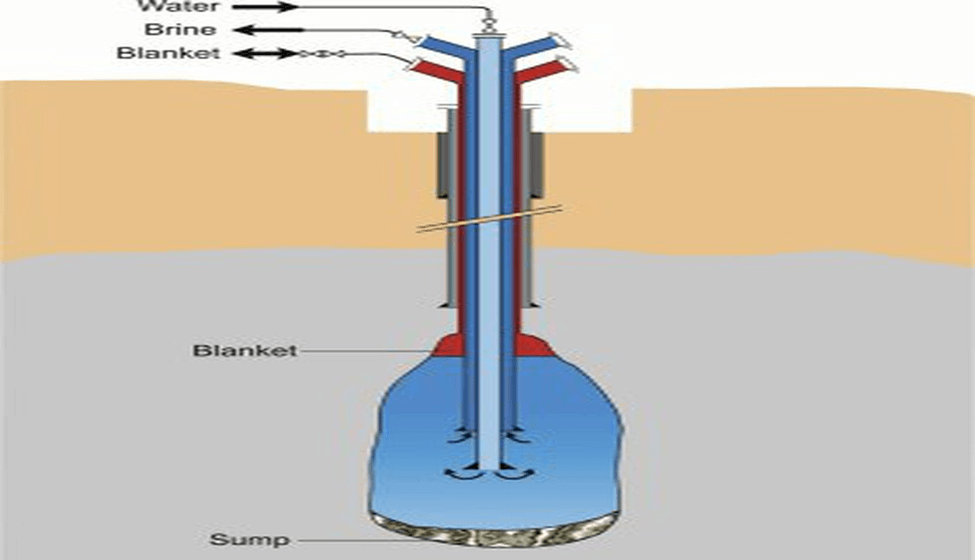
Potential for Storing Crude and Petroleum Products in Rajasthan:
Rajasthan, known for its abundant salt formations, presents a favorable environment for the development of salt cavern-based strategic storage facilities. With the upcoming refinery in Barmer and the existence of crude pipelines, Rajasthan possesses the necessary infrastructure to support the establishment of strategic oil reserves. Prior to EIL’s partnership with Germany’s DEEP, no Indian company possessed the technical expertise required for constructing salt cavern-based hydrocarbon storage. This partnership bridges the technological gap, facilitating the realization of salt cavern-based oil reserves in Rajasthan.
Important Points:
- Importance of oil reserves: 🛢️
- Mitigate supply disruptions in the global supply chain.
- Ensure energy security during emergencies.
- India’s current capacity: ⛽
- SPR capacity of 5.33 million tonnes (39 million barrels).
- Expansion plans of 6.5 million tonnes.
- Indian Strategic Petroleum Reserve (ISPRL) oversight.
- Salt cavern-based vs. rock cavern-based reserves: 🏞️
- Salt caverns developed through solution mining.
- Simpler, faster, and cost-effective process.
- Naturally well-sealed and suitable for rapid oil injection/extraction.
- Impermeable barriers against hydrocarbons.
- Salt caverns operated primarily from the surface.
- Versatile for storing various fuels and gases.
- Salt caverns developed through solution mining.
- Potential in Rajasthan: 🏜️
- Rajasthan favorable for salt cavern-based storage.
- Abundant salt formations.
- Infrastructure support with upcoming refinery and crude pipelines.
- EIL’s partnership with Germany’s DEEP bridging technological gap.
Why In News
Government-owned engineering consultancy firm Engineers India (EIL) is conducting a comprehensive study to assess the potential and viability of establishing salt cavern-based strategic oil reserves in the state of Rajasthan. This initiative aims to enhance India’s energy security by exploring innovative storage solutions and leveraging the natural geological formations available in the region.
MCQs about India’s Salt Cavern-Based Oil Reserves Initiative
-
Which method is used to develop salt caverns for oil storage?
A. Excavation
B. Fracking
C. Solution mining
D. Compression
-
What is the primary advantage of salt cavern-based oil storage facilities over rock cavern-based facilities?
A. Higher storage capacity
B. Lower construction costs
C. Faster oil extraction process
D. Enhanced geological stability
-
Which Indian state is considered most suitable for the development of salt cavern-based strategic oil reserves?
A. Karnataka
B. Andhra Pradesh
C. Odisha
D. Rajasthan
-
Who oversees India’s strategic oil reserves?
A. Ministry of Energy
B. Indian Strategic Petroleum Reserve Limited (ISPRL)
C. Engineers India (EIL)
D. German Energy and Environment Partnership (DEEP)
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


