In order to promote fairness and transparency in the issuance of surety bonds, the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) has introduced guidelines. Surety bonds serve as risk management tools and are governed by the Indian Contract Act of 1872. This essay explores the concept of surety bonds and their significance, focusing on the guidelines issued by IRDAI. Understanding this topic is crucial for the Indian Administrative Services (IAS) exam’s General Studies (GS) Paper III, particularly the Indian Economy segment.
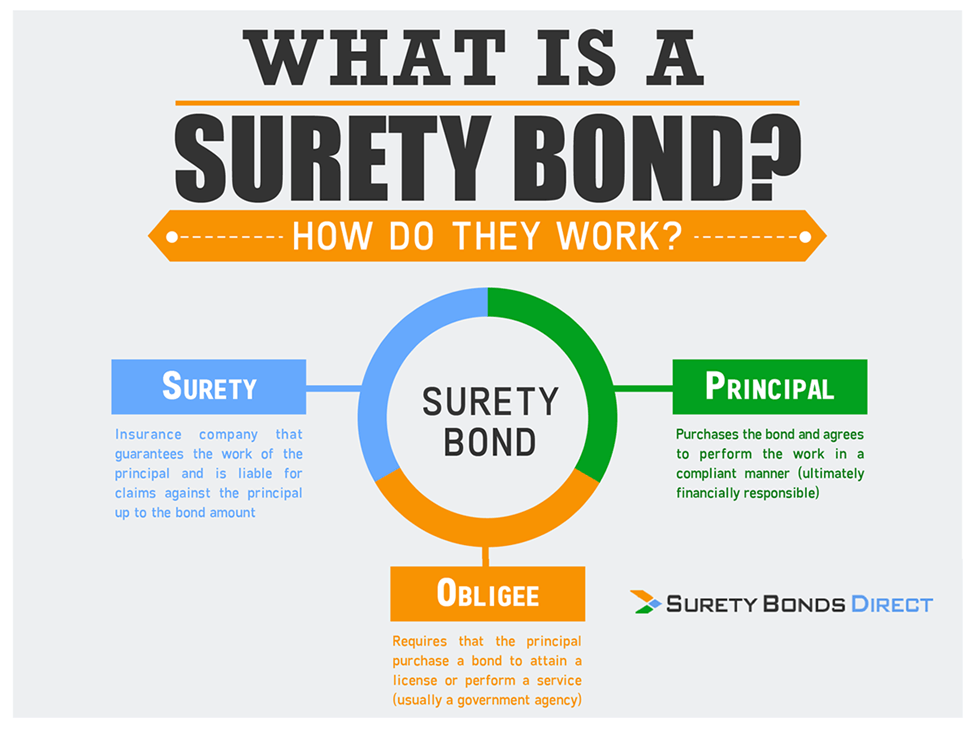
What are Surety Bonds?
Surety bonds are legally binding agreements that ensure economic growth and mitigate risks. They are commonly used in construction and infrastructure projects. These bonds guarantee that the principal, who is obligated to fulfill certain tasks or duties, will meet the commitments stated in the contract. If the principal fails to fulfill these obligations, the obligee (the party protected by the surety bond) is compensated by the surety, reducing financial risk. Key points about surety bonds include:
- Three parties involved: A surety bond involves three parties – the obligee (entity requiring the bond), the principal (party responsible for fulfilling the task or duty), and the surety (party ensuring the principal’s performance).
- Protection against financial risk: The primary objective of obtaining a surety bond is to protect the project owner from financial risk. This includes instances where a contractor fails to complete a project or meet quality standards.
- Types of surety bonds: Various types of surety bonds are issued for different purposes. These include bid bonds, performance bonds, advance payment bonds, and retention money bonds.
- Financial capability: The guarantor (surety) must possess the financial capacity to fulfill the obligations under the bond. The surety bond premium is determined based on the associated risks and must be reasonable.
IRDAI Guidelines on Surety Bonds
The IRDAI guidelines aim to promote and regulate the sustainable growth of India’s surety insurance sector. These guidelines address several aspects of surety bonds, including:
- Types of surety bonds: The guidelines specify the types of surety bonds that can be issued, ensuring clarity and standardization in the market.
- Terms and conditions: They provide a framework for establishing terms and conditions for surety bonds, ensuring uniformity and transparency.
- Underwriting criteria: The guidelines outline underwriting criteria that must be followed by surety providers, preventing variations in standards and procedures.
- Pricing: The guidelines help establish fair and reasonable pricing for surety bonds, taking into account the associated risks and ensuring affordability for contractors.
Challenges in the Surety Bond Market
Despite the introduction of guidelines by IRDAI, there are challenges that need to be addressed in the surety bond market:
- Limited market penetration: The lack of a deep and well-established surety bond market in India poses difficulties for contractors, particularly small and medium-sized organizations (SMEs), in obtaining bonds.
- Lack of uniform standards: Different surety providers following varying standards and procedures create confusion for contractors, hindering their understanding of the system.
- Complex enforcement process: Surety bond enforcement can be lengthy, time-consuming, and complex, often involving legal conflicts. Streamlining this process would benefit all parties involved.
Important Points:
- Definition and Purpose of Surety Bonds:
- Surety bonds are risk management tools that guarantee economic growth. They are governed by the Indian Contract Act of 1872. 💼🔒
- They are primarily issued for construction and infrastructure projects to ensure that the principal fulfills their contractual obligations. 💪📜
- In case of failure by the principal, the obligee (protected party) is compensated by the surety, reducing financial risk. 💸🛡️
- Three Parties Involved:
- Obligee: The entity requiring the bond. 🏢
- Principal: The party responsible for fulfilling a task or duty. 🙋♂️
- Surety: The party ensuring the principal’s performance. 🤝💼
- Types of Surety Bonds:
- Bid Bonds: Ensures that the bidder fulfills their obligations if awarded the contract. 💼📜
- Performance Bonds: Ensures completion of the project and adherence to quality standards. 🏗️✅
- Advance Payment Bonds: Protects the obligee if the principal fails to utilize the advance payment as agreed. 💰⚠️
- Retention Money Bonds: Covers the obligee against the principal’s failure to repay retention money. 💸💔
- IRDAI Guidelines on Surety Bonds:
- Objective: Promote and control sustainable growth in India’s surety insurance sector. 📝🚀
- Topics Covered: Types of bonds, terms and conditions, underwriting criteria, and pricing. 📋💲
- Framework for Issuance: Provides a standardized approach for issuing surety bonds. 📈🔏
- Challenges in the Surety Bond Market:
- Limited Market Penetration: Difficulty for contractors, especially SMEs, in obtaining bonds due to a shallow market. 🛑🔍
- Lack of Uniform Standards: Varying standards and procedures among surety providers create confusion for contractors. ❓🔀
- Complex Enforcement Process: Lengthy, time-consuming, and legally involved process for surety bond enforcement. 🕒⚖️
- Importance for IAS Exam GS Paper III:
- Understanding surety bonds and IRDAI guidelines is crucial for the Indian Economy segment of the IAS exam. 📚🏛️
Why In News
To promote fairness and transparency in the issuance of surety bonds, the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) took a crucial step by issuing comprehensive guidelines. Surety bonds, which serve as a guarantee for the performance of contractual obligations, are vital in various sectors such as construction, finance, and government projects, providing assurance to stakeholders and mitigating financial risks.
MCQs about IRDAI Guidelines for Surety Bonds
-
What is the purpose of obtaining a surety bond in construction projects?
A. To protect the project owner from financial risk.
B. To ensure timely completion of the project.
C. To guarantee quality standards.
D. To secure advance payments from the project owner.
-
Which party is responsible for ensuring the principal’s performance in a surety bond?
A. Obligee
B. Principal
C. Surety
D. Contractor
-
What types of surety bonds are issued for various purposes?
A. Payment bonds, retention bonds, performance bonds, bid bonds
B. Advance payment bonds, completion bonds, bid bonds, indemnity bonds
C. Performance bonds, payment bonds, bid bonds, advance payment bonds
D. Completion bonds, advance payment bonds, indemnity bonds, retention bonds
-
What is one of the challenges in the surety bond market discussed in the essay?
A. High premiums for surety bonds
B. Limited availability of surety bonds for large organizations
C. Varying standards and procedures among surety providers
D. Lack of clarity in IRDAI guidelines for surety bonds
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


