The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) are collaborating on a new earth-observing mission called the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) satellite. This satellite will be equipped with Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) technology to create high-resolution images of the earth’s surface, which can penetrate clouds and vegetation to generate accurate data. The mission will map the most earthquake-prone regions in the Himalayas with unprecedented regularity.
What is NISAR Satellite?
The NISAR satellite is a joint collaboration between NASA and ISRO, designed for all-weather, earth-observing purposes. SAR technology will be used to capture high-resolution images of the earth’s surface, providing valuable insights into various phenomena such as natural disasters, changes in permafrost, forest resources, agriculture, and food security. The NISAR satellite is expected to cost approximately $900 million, with ISRO contributing about one-tenth of the total cost.
How will NISAR Satellite work?
The NISAR satellite will use two frequency bands, L-band (1-2 GHz, commonly used for satellite communication and remote sensing) and S-band (2-4 GHz, commonly used for satellite communication and weather monitoring). NASA requires the L-band radar for its global science operations for at least three years, while ISRO will utilize the S-band radar for a minimum of five years. The satellite will image the seismically active Himalayan region, creating a deformation map every 12 days. The map can be used to determine how strain is building up in various parts of the Himalayas.
Applications of NISAR Satellite
NISAR Satellite will have several applications, including:
- Disaster Mapping: Pre-disaster images collected by the satellite will be used to better understand natural disasters and inform official policy on the best courses of action in the future. Satellite observations will also be uninterrupted by weather, providing quick and reliable information for rescue operations and loss estimates.
- Changes in Permafrost: The NISAR satellite will be programmed to observe global changes in permafrost at regular intervals, updating scientists about its degradation, with implications for global water resources, aquatic ecosystems, coastal water levels, and more.
- Forests: NISAR will monitor global forest resources, their extent, and quality, and provide information for their sustainable development and management.
- Agriculture and Food Security: SAR imaging of crop rotation, growth, and harvest can be used to streamline planned agricultural output and monitor the health of crops.
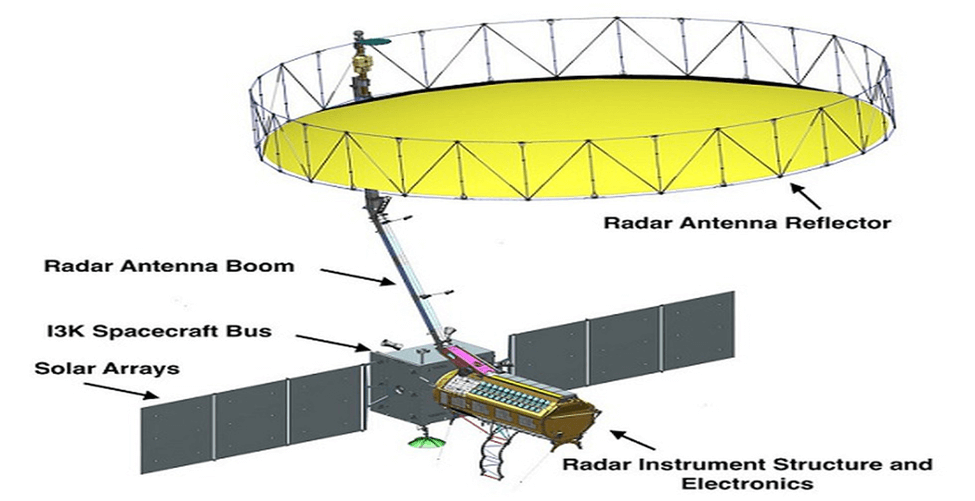
Date of Launch and Duration
The NISAR satellite is expected to be launched in January 2024 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre into a near-polar orbit. The satellite will operate for a minimum of three years.
Why In News
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) of the U.S. have jointly developed the NISAR satellite mission, which will use synthetic aperture radar technology to map the most earthquake-prone regions in the Himalayas with unprecedented regularity.
MCQs about Launch and Cost Details of the NISAR Satellite Mission
-
What is the NISAR satellite?
A. A weather-observing mission
B. A radar-imaging satellite
C. A manned spacecraft
D. A communication satellite
-
How much will the NISAR satellite cost?
A. Approximately $9 million
B. Approximately $90 million
C. Approximately $900 million
D. Approximately $9 billion
-
What are the applications of the NISAR satellite?
A. Disaster mapping
B. Changes in permafrost
C. Monitoring of global forest resources
D. All of the above
-
When is the NISAR satellite expected to be launched?
A. January 2021
B. January 2022
C. January 2023
D. January 2024
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


