Daily Current Affairs : 5-July-2023
Leptospirosis, a potentially fatal zoonotic bacterial disease, has emerged as a significant infectious disease worldwide. This essay will explore the various aspects of leptospirosis, including its causes, transmission, prevalence, challenges, and potential solutions. By adopting a ‘One Health’ approach, which recognizes the interconnections between the health of humans, animals, plants, and their shared environment, we can effectively combat this disease.
Understanding Leptospirosis
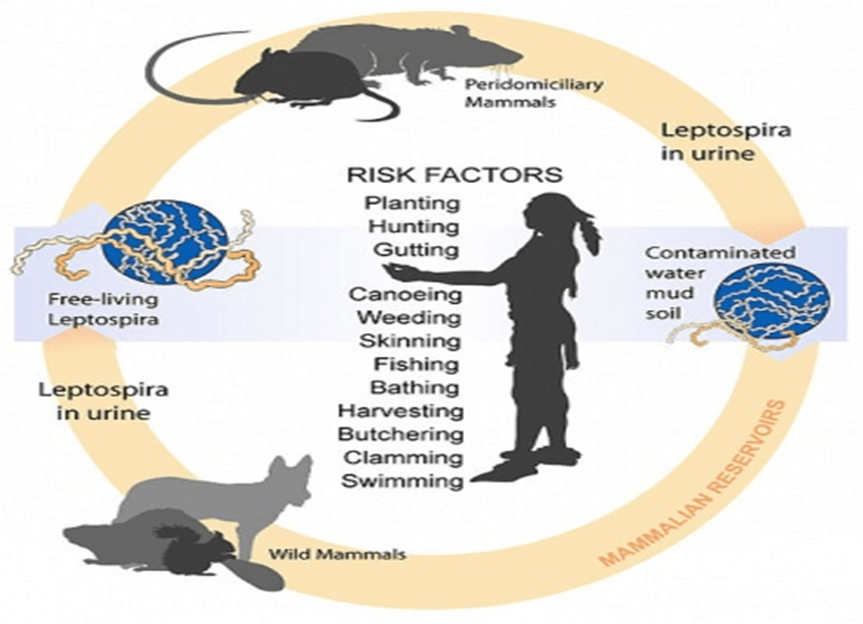
Leptospirosis is caused by a bacterium called Leptospira interrogans, or leptospira. It tends to have large outbreaks following heavy rain or flooding, making it a disease of concern in flood-prone regions. The disease is primarily contagious in animals, but humans can be infected under certain environmental conditions. In Kannada and Malayalam, it is known as “ili jwara” and “eli pani,” respectively, both meaning “rat fever.”
Hosts and Climate
Leptospirosis carriers include wild and domestic animals such as rodents, cattle, pigs, and dogs. The disease thrives in warm and humid climates, affecting both urban and rural areas. As a result, it is more prevalent in tropical regions. In India, leptospirosis affects thousands of people every year, with studies suggesting a higher incidence in the southern part of the country due to better healthcare and disease detection capabilities.
Magnitude of the Disease
Leptospirosis poses a significant burden on public health, impacting approximately 1.03 million individuals annually and causing around 60,000 deaths. Unfortunately, the disease’s prevalence is expected to rise in the future, particularly among the urban poor in tropical countries where sanitary infrastructure is lacking. This emphasizes the urgency of addressing leptospirosis to prevent further suffering and loss of life.
Challenges Faced
Several challenges hinder effective leptospirosis control. Firstly, the disease’s symptoms mimic those of dengue, malaria, and hepatitis, leading to misdiagnosis. Limited access to reliable diagnostic tools further complicates early detection and treatment. Additionally, many treating physicians lack awareness of leptospirosis, contributing to delayed or incorrect diagnoses. Lastly, there is a lack of comprehensive environmental surveillance to monitor the disease’s spread and implement preventive measures.
The Way Forward: A ‘One Health’ Approach
To tackle leptospirosis effectively, a ‘One Health’ approach is crucial. This interdisciplinary strategy recognizes the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health. Several key measures can be implemented:
- Increased Awareness: Public health professionals must collaborate closely with animal husbandry departments to raise awareness about the dangers of leptospirosis. Educational campaigns targeting individuals who frequently interact with animals, such as farmers and pet owners, can help promote preventive measures.
- Sanitary Animal-Keeping Conditions: Preventing animals from getting infected is essential to reduce the risk of leptospirosis transmission. This requires maintaining sanitary conditions for animals, which not only safeguards their health but also prevents the spread of various diseases. By improving animal welfare, we can protect both animals and humans from leptospirosis.
- Strengthened Surveillance: Implementing robust environmental surveillance systems is crucial for monitoring leptospirosis outbreaks. This includes collecting data on animal infections, identifying high-risk areas, and implementing timely interventions to prevent further transmission.
Important Points:
- Leptospirosis is a potentially fatal zoonotic bacterial disease caused by Leptospira interrogans.
- It tends to have large outbreaks after heavy rain or flooding.
- The disease affects both animals and humans, with rodents, cattle, pigs, and dogs being carriers.
- Leptospirosis is more prevalent in warm, humid countries and in both urban and rural areas.
- It affects an estimated 1.03 million people annually, causing around 60,000 deaths.
- The burden of leptospirosis is expected to increase as the urban poor population in tropical countries grows, and sanitary infrastructure falls short.
- Misdiagnosis, limited access to reliable diagnostics, lack of awareness among physicians, and lack of environmental surveillance are major challenges.
- A ‘One Health’ approach, considering the interconnectedness of humans, animals, plants, and the environment, is crucial for leptospirosis control.
- Increased awareness campaigns should target individuals who frequently interact with animals.
- Maintaining sanitary animal-keeping conditions is important to prevent the spread of leptospirosis and other diseases.
- Strengthened surveillance systems are necessary for monitoring and timely intervention.
- Collaboration between public health professionals and animal husbandry departments is vital to familiarize people with leptospirosis dangers and develop effective countermeasures.
- Implementation of these measures can help mitigate the impact of leptospirosis and protect human and animal health.
Why In News
Leptospirosis, a once overlooked infectious disease, has now garnered significant attention due to its growing prevalence and impact worldwide. As the global health community recognizes its importance, research and preventive measures have intensified to mitigate the spread and consequences of leptospirosis.
MCQs about Leptospirosis
-
What is the primary cause of leptospirosis?
A. Leptospira interrogans
B. Heavy rain and flooding
C. Dengue virus
D. Malaria parasite
-
In which areas is leptospirosis more prevalent?
A. Cold and dry regions
B. Urban areas only
C. Warm and humid regions
D. Coastal regions
-
What is a major challenge in diagnosing leptospirosis?
A. Limited access to reliable diagnostics
B. Lack of awareness among physicians
C. Misdiagnosis due to similarity with other diseases
D. All of the above
-
What is the recommended approach for leptospirosis control?
A. Isolating infected individuals
B. Vaccinating animals against leptospirosis
C. Implementing a ‘One Health’ approach
D. Increasing public health funding
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


