Daily Current Affairs : 11-July-2024
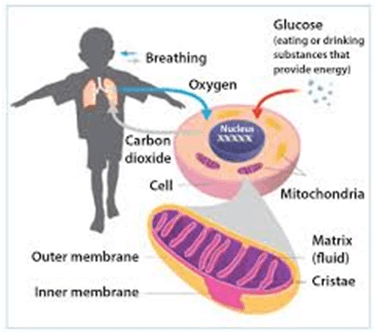
Mitochondrial disease (Mito) is a set of disorders that occur when the mitochondria, which are the energy-producing structures in our cells, do not function properly. Mitochondria are vital for generating the energy that organs need to carry out their tasks. When mitochondria fail, organs that require significant energy, such as the heart, brain, and muscles, may begin to malfunction. This can lead to severe health problems, and in some cases, organ failure.
Types of Mitochondrial Disease
Mitochondrial diseases can be caused by issues in two types of DNA:
- Nuclear DNA: These faulty genes are inherited from both parents and affect the overall function of mitochondria.
- Mitochondrial DNA: This type of DNA is passed down from the mother, as mitochondria are inherited from the egg cell. Mutations in mitochondrial DNA can also lead to mitochondrial disorders.
It is estimated that 1 in every 5,000 people is affected by some form of mitochondrial disease. The disease can cause a wide range of symptoms, particularly in energy-demanding organs. This leads to problems such as muscle weakness, neurological issues, and heart problems.
Mitochondrial Donation: A Potential Cure
One promising new development in treating mitochondrial disease is a procedure called mitochondrial donation. This procedure offers a way for families with mitochondrial disorders to have healthy children without passing on faulty mitochondrial DNA.
How Mitochondrial Donation Works
Mitochondrial donation is based on an in vitro fertilization (IVF) technique. Here’s how it works:
- Step 1: The nuclear DNA (which carries the genetic information) is removed from an egg with faulty mitochondria from the mother.
- Step 2: This nuclear DNA is then transferred into a donor egg that has healthy mitochondria.
- Step 3: The resulting embryo will inherit the nuclear DNA from the parents, but the mitochondrial DNA will come from the donor egg, ensuring that the child does not inherit the mitochondrial disorder.
Benefits of Mitochondrial Donation
- It allows parents with mitochondrial disorders to have children who are genetically related to them.
- It helps prevent the transmission of mitochondrial diseases to future generations.
- It offers hope for families affected by severe, life-threatening mitochondrial conditions.
Mitochondrial donation could be a groundbreaking solution for families dealing with the challenges of mitochondrial disease, enabling them to avoid passing on life-threatening conditions to their children.
Important Points:
Mitochondrial Disease (Mito)
- Definition: A group of disorders where mitochondria (energy-producing structures in cells) do not function properly.
- Cause: Can be caused by faulty nuclear DNA (inherited from both parents) or mitochondrial DNA (inherited from the mother).
- Impact: Affects energy-demanding organs such as the heart, brain, and muscles, potentially leading to organ failure.
- Prevalence: Affects 1 in 5,000 people globally.
Types of Mitochondrial Disease
- Nuclear DNA: Faulty genes inherited from both parents, affecting overall mitochondrial function.
- Mitochondrial DNA: Mutations passed down from the mother, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction.
Mitochondrial Donation: A Potential Cure
- Definition: A new procedure offering a way to have children without passing on faulty mitochondrial DNA.
- Technique: Involves using IVF to transfer nuclear DNA from the mother’s egg to a donor egg with healthy mitochondria.
- Outcome: The child inherits nuclear DNA from the parents and mitochondrial DNA from the donor egg.
Benefits of Mitochondrial Donation
- Genetic Relation: Parents can have children who are genetically related to them, without passing on mitochondrial disorders.
- Prevention: Helps prevent the transmission of mitochondrial diseases to future generations.
- Hope for Families: Provides a potential solution for families affected by severe mitochondrial diseases, offering a healthier future for their children.
Why In News
Mitochondrial disease (Mito) encompasses a group of disorders that impair mitochondria’s ability to produce the energy necessary for organs to function, potentially leading to organ failure. These diseases can affect various systems in the body, causing a wide range of symptoms, particularly in energy-demanding organs such as the heart, brain, and muscles, which are most vulnerable to mitochondrial dysfunction.
MCQs about Mitochondrial Disease
-
What is mitochondrial disease (Mito)?
A. A genetic disorder that affects only the heart
B. A group of disorders that impair mitochondria’s ability to produce energy
C. A disease caused by infections affecting mitochondria
D. A disorder that only affects the muscles
-
Which organs are most affected by mitochondrial disease?
A. Liver and kidneys
B. Heart, brain, and muscles
C. Lungs and stomach
D. Eyes and ears
-
How does mitochondrial donation work?
A. It involves using nuclear DNA from both parents and mitochondrial DNA from the father
B. It uses a donor egg with healthy mitochondria and transfers the mother’s nuclear DNA
C. It only involves the transfer of mitochondrial DNA
D. It is a form of gene therapy that directly corrects faulty DNA
-
What is one key benefit of mitochondrial donation?
A. It cures all types of mitochondrial diseases
B. It prevents the transmission of mitochondrial diseases to future generations
C. It eliminates the need for IVF procedures
D. It guarantees a perfect health outcome for the child
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


