Daily Current Affairs : 16-August-2023
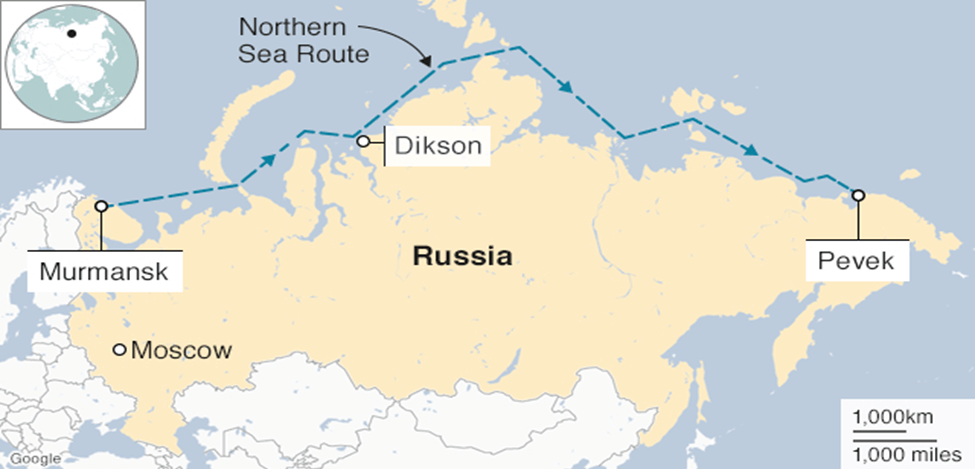
India’s connection with Russia’s Arctic region has been rapidly intensifying, highlighted by the fact that India-bound goods have dominated the cargo handled at Russia’s Arctic Murmansk port in the first half of 2023. This essay delves into the significance of this engagement, the unique attributes of the Murmansk port, and India’s involvement in the Northern Sea Route (NSR) as an alternative trade route.
Murmansk Port: A Gateway to the Arctic
Situated approximately 2,000 km northwest of Moscow, Murmansk port boasts a significant role in Russia’s maritime activities. Accounting for 35% of the cargo handled by the port, India has emerged as a prominent partner in this region. Some key points about the Murmansk port include:
- Location and Uniqueness: The Murmansk port holds the distinction of being the world’s largest port located north of the polar circle. Nestled on the Kola peninsula along the Barents Sea coast, it remains operational throughout the year due to its non-freezing status.
- Strategic Importance: This port has evolved into the focal point of Russia’s icebreaker fleet, crucial for facilitating oil and gas transportation from the North-West Russian Arctic fields. Additionally, the port encompasses auxiliary road handling terminals and anchorage and repair terminals beyond Kola Bay.
Navigating the Northern Sea Route (NSR)
The NSR, a shorter maritime passage connecting the Asia-Pacific region and the western part of Eurasia, has garnered India’s attention. This route presents significant advantages, but navigating its 5,600-km expanse poses challenges due to the presence of icebound seas such as Kara, Laptev, East Siberian, and Chukchi. FSUE Atomflot, a unit of Rosatom, takes on the crucial task of icebreaking, utilizing nuclear-powered icebreakers to ensure safe passage.
The NSR as an Alternative to the Suez Canal
The NSR holds great potential as a viable alternative to the Suez Canal. The shorter distance it offers between Europe and Asia-Pacific countries can lead to substantial time and cost savings. For instance:
- Comparing Distances: A journey across the Arctic Ocean from Murmansk to Yokohama in Japan covers approximately 6,000 nautical miles. In contrast, the distance via traditional southern shipping routes amounts to around 13,000 nautical miles.
Important Points:
Murmansk Port: A Gateway to the Arctic
- India-bound goods dominate cargo handled at Russia’s Arctic Murmansk port in 2023 (35% share).
- Murmansk port located 2,000 km northwest of Moscow.
- World’s largest port north of the polar circle, operational year-round due to non-freezing status.
- Key hub for Russia’s icebreaker fleet and crucial for oil and gas transport from North-West Russian Arctic fields.
- Includes auxiliary road handling terminals and repair terminals beyond Kola Bay.
Navigating the Northern Sea Route (NSR)
- NSR: Short shipping route linking Asia-Pacific and western Eurasia.
- Challenges in navigating the 5,600-km-long NSR due to icebound seas (Kara, Laptev, East Siberian, Chukchi).
- FSUE Atomflot, part of Rosatom, uses nuclear-powered icebreakers for safe passage.
The NSR as an Alternative to the Suez Canal
- NSR proposed as an alternative to the Suez Canal, potentially reducing distance between Europe and Asia-Pacific.
- Murmansk to Yokohama distance via NSR: ~6,000 nautical miles; southern shipping routes: ~13,000 nautical miles.
Why In News
In the first half of 2023, India’s significant presence becomes evident as it contributes to a remarkable 35% share of the cargo handled through Russia’s Arctic Murmansk port. This pivotal port, serving as Russia’s primary northern gateway and a pivotal transshipment hub, underscores the strengthening economic ties between the two nations and their thriving trade relations.
MCQs about Murmansk Port
-
What unique characteristic allows Murmansk port to remain operational throughout the year?
A. Non-freezing status
B. Icebreaker escorts
C. Nuclear power
D. Its proximity to Moscow
-
Which organization is responsible for performing icebreaking tasks along the Northern Sea Route?
A. FSUE Atomflot, a unit of Rosatom
B. International Maritime Organization (IMO)
C. United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
D. International Maritime Bureau (IMB)
-
How does the Northern Sea Route (NSR) compare to the traditional southern shipping routes in terms of distance between Murmansk and Yokohama in Japan?
A. NSR is about half the distance of southern routes.
B. NSR is three times longer than southern routes.
C. NSR and southern routes have similar distances.
D. NSR is slightly shorter than southern routes.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


