Hindu Editorial Analysis : 28-December-2023
The recent armed drone attack on the MV Chem Pluto in the Arabian Sea highlights the escalating threats to maritime security. This incident underscores the critical importance of addressing challenges faced by India in safeguarding its extensive coastline and strategic position in the Indian Ocean.
Maritime Security Landscape of India
Significance of the Region
India, with its vast 7,500 km coastline and a strategic location in the Indian Ocean, grapples with diverse maritime security challenges. The Indian Ocean, covering over 19.8% of the Earth’s surface, is a pivotal area connecting Africa, Asia, and Australia through vital sea lanes and trade routes.
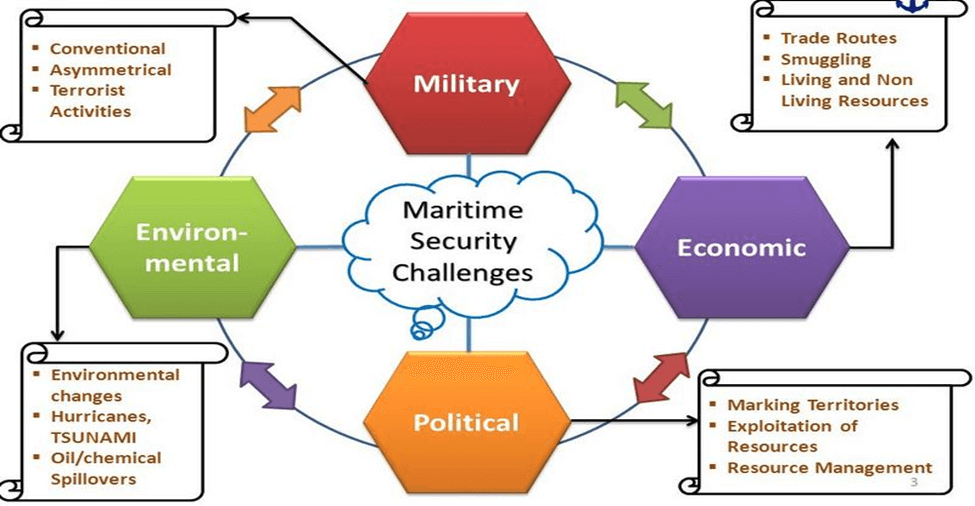
Threats and Challenges
- Traditional Threats: Issues like restricted freedom of navigation and China’s expanding influence pose conventional challenges.
- Non-Traditional Threats: Terrorism, piracy, drug trafficking, smuggling, illegal migration, and climate change-related threats complicate the security scenario.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Limited coastal surveillance infrastructure, communication systems, and logistical capabilities create vulnerabilities.
- Manpower Shortage: The shortage of personnel in the Indian Navy and Coast Guard necessitates efficient recruitment and training programs.
- Technological Advancements: Adopting emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and unmanned vehicles is crucial for effective security measures.
Measures to Enhance Maritime Security
Collaboration and Cooperation
- Regional and International Initiatives: India actively engages in maritime security collaborations with countries like the US, Japan, and France.
- Intelligence Sharing: Strengthening international cooperation and intelligence sharing are vital for proactive threat detection.
Investments and Infrastructure
- Technology Adoption: Investments in advanced technologies, including drones, satellites, and artificial intelligence, enhance surveillance and response capabilities.
- Infrastructure Development: Upgrading coastal infrastructure, ports, harbors, and communication networks is essential for effective maritime security operations.
- Capacity Building: Training programs for personnel involved in maritime security, including fishermen and coastal communities, are crucial for raising awareness and preparedness.
Steps Taken by India
Strategic Initiatives
- Modernization of the Indian Navy: A growing fleet of modern warships, submarines, and aircraft strengthens the Indian Navy.
- Indian Coast Guard: Vital in coastal security, patrolling territorial waters, and combating smuggling, piracy, and illegal fishing.
- Information Fusion Centre-Indian Ocean Region (IFC-IOR): Enhances maritime domain awareness through information exchange.
- Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) and Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS): Collaborative initiatives for regional cooperation and sustainable development.
Why In News
On December 23, an armed drone struck a merchant ship, the MV Chem Pluto, with a crew of 20 Indians in the Arabian Sea. This alarming incident underscores the growing threat of unconventional attacks on commercial shipping, posing serious challenges to marine security and necessitating a heightened focus on innovative security measures.
MCQs about Navigating Challenges: India’s Maritime Security Roadmap
-
What recent incident underscores the escalating threats to maritime security in the Indian Ocean?
A. Piracy off the coast of Somalia
B. Armed drone attack on MV Chem Pluto
C. Climate change-related threats
D. Illegal fishing in the Indian Ocean
-
What percentage of the Earth’s surface does the Indian Ocean cover?
A. 12.3%
B. 19.8%
C. 25.5%
D. 30.2%
-
Which of the following is NOT listed as a non-traditional threat to maritime security in the Indian Ocean?
A. Terrorism
B. Piracy
C. Climate change-related threats
D. String of pearls policy
-
What initiative aims to increase maritime cooperation among navies of the littoral states in the Indian Ocean Region?
A. Indian Coast Guard
B. Information Fusion Centre-Indian Ocean Region (IFC-IOR)
C. Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA)
D. Maritime Security Collaboration (MSC)
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


