Daily Current Affairs : 6-December-2023
India’s vast coastline, spanning over one-third of the country’s perimeter, faces a growing threat from coastal erosion, according to a study by the National Centre for Coastal Research (NCCR). Coastal erosion, the gradual wearing away of coastal land, presents a significant environmental challenge globally, affecting sandy shorelines and leading to the formation of various landforms.
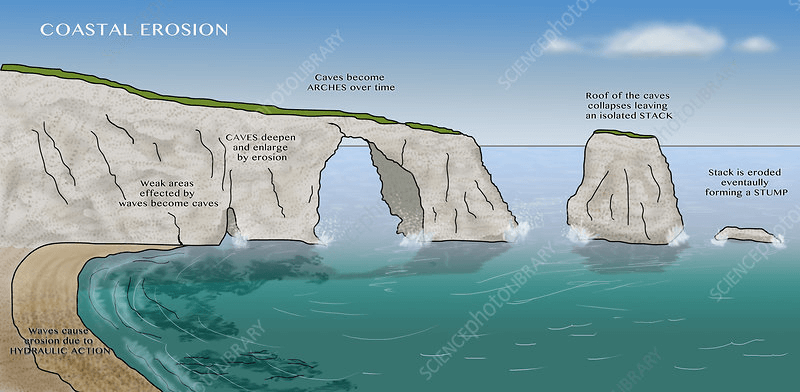
Coastal Erosion: A Global Phenomenon
- Extent: Globally, an estimated 70% of sandy shorelines are eroding, with regional variations, such as 27% in Europe and 86% on the US East coast barrier beaches.
- Processes: Four main processes contribute to coastal erosion: corrasion, abrasion, hydraulic action, and attrition.
- Landforms: The type of material forming the cliffs influences the landforms created, such as arches, caves, stacks, and stumps.
Causes of Coastal Erosion
- Sea Level Rise: Rising sea levels result in the inland movement of shorelines, causing erosion.
- Storm Surges: Large waves generated by storms, like hurricanes, lead to extensive coastal damage.
- Wave Action: Constant pounding of waves against the shoreline contributes to land erosion.
- Longshore Currents: Currents flowing parallel to the shoreline can carry away sediments, accelerating erosion.
- Human Activities: Dam construction, sand mining, and coastal development disrupt natural processes that protect coastlines.
Mitigation Measures
- Beach Nourishment: Adding sand to restore natural beach shape and size.
- Seawalls and Revetments: Structures built along the shoreline to protect against erosion.
- Breakwaters: Offshore structures to break waves and reduce their energy.
- Vegetative Buffers: Planting vegetation along the shoreline to bind soil and reduce wave impact.
- Artificial Reefs: Creating coral reefs to dissipate wave energy and enhance marine life.
Government Initiatives for Coastal Conservation
- Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) Notification, 2019: Aims to conserve coastal stretches, marine areas, and ensure livelihood security for local communities.
- Coastal Zone Management Plan (CZMP): Includes mapping erosion-prone areas and developing a shoreline management plan.
- Hazard Line Delineation: The Ministry of Environment defines the hazard line for the entire coast, guiding conservation efforts.
- Coastal Vulnerability Index (CVI): Estimated by INCOIS to assess vulnerability along the Indian coastline.
- 15th Finance Commission: Allocates Rs. 1000 crore from the National Disaster Response Fund for resettlement of people affected by erosion.
Important Points:
- Coastal Erosion in India: Key Facts
- Over one-third of India’s coastline vulnerable to erosion (NCCR study).
- Global erosion estimate: 70% of sandy shorelines worldwide.
- Regional variations: Europe (27%), US East coast barrier beaches (86%).
- Causes of Coastal Erosion
- Sea level rise: Inland movement of shorelines.
- Storm surges: Large waves from hurricanes and storms.
- Wave action: Constant pounding of waves.
- Longshore currents: Parallel currents eroding shorelines.
- Human activities: Dam construction, sand mining, and coastal development.
- Mitigation Measures
- Beach nourishment: Adding sand to restore natural shape and size.
- Seawalls and revetments: Shoreline structures for erosion protection.
- Breakwaters: Offshore structures to break waves and reduce energy.
- Vegetative buffers: Planting vegetation along the shoreline.
- Artificial reefs: Creating reefs to dissipate wave energy and enhance marine life.
- Government Initiatives for Coastal Conservation
- Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) Notification, 2019: Conservation of coastal stretches and marine areas.
- Coastal Zone Management Plan (CZMP): Mapping erosion-prone areas and developing management plans.
- Hazard Line Delineation: Ministry of Environment defines hazard line for entire coast.
- Coastal Vulnerability Index (CVI): INCOIS assesses vulnerability along the Indian coastline.
- 15th Finance Commission: Allocates Rs. 1000 crore for resettlement from National Disaster Response Fund.
Why In News
Over one-third of India’s coastline is vulnerable to erosion, as per a study by the National Centre for Coastal Research (NCCR), highlighting the urgent need for sustainable coastal management practices to mitigate the environmental impact and protect coastal communities.
MCQs about Navigating Coastal Erosion
-
Which human activity is mentioned as a contributor to coastal erosion?
A. Fishing
B. Dam construction
C. Agriculture
D. Tourism
-
What is the purpose of Beach Nourishment as a mitigation measure?
A. Building resorts
B. Adding sand to restore natural shape and size
C. Planting trees along the shoreline
D. Constructing seawalls
-
Which government initiative allocates funds for the resettlement of people affected by erosion?
A. Swachh Bharat Abhiyan
B. National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme
C. Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) Notification, 2019
D. Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


