Daily Current Affairs : 9-November-2023
In the current climate crisis, the terms “adaptation” and “loss and damage” (L&D) have gained prominence as crucial elements in addressing the challenges posed by climate change.
Adaptation vs. Loss and Damage:
Adaptation:
- Proactive response to climate change.
- Involves deliberate choices to prepare for and cope with climate-related challenges.
Loss and Damage:
- Represents irreversible consequences of climate change.
- Encompasses real losses beyond monetary value, affecting human rights and well-being.
- Includes economic losses, human casualties, and degradation of ecosystems and cultural heritage.
The Loss and Damage Fund:
Historic Pollution:
- Call for affluent nations to acknowledge accountability for historic pollution.
- Historic pollution has raised global average surface temperature by over 1 degree Celsius.
Creation of L&D Fund:
- Established at COP 19 in 2013 in Warsaw, Poland.
- Intended to provide financial and technical assistance to economically developing nations facing L&D due to climate change.
Subsequent COPs and Status:
- COP 25 set up the Santiago Network for L&D, but no commitment of funds.
- COP 26 established the Glasgow Dialogue on finance for L&D.
- COP 27 in 2022 agreed to set up the L&D fund and a Transitional Committee (TC).
TC5 Meeting and Aftereffects:
- TC5 meeting in Abu Dhabi led to recommendations for COP 28.
- Developing nations agreed to host the fund at the World Bank Financial Intermediary Fund for an interim period.
- Developed nations, especially the U.S., remain non-committal about primary donor status.
Implications of Outcome:
- Threatens climate justice and worsens the suffering of vulnerable communities.
- Increases the risk of humanitarian crises, food shortages, people displacement, and conflicts.
- Economic consequences for both developing and developed nations.
- Security implications as climate-change-induced instability may lead to conflicts.
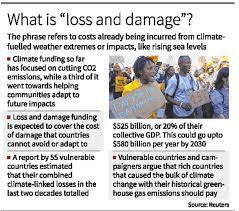
Important Points:
- Adaptation vs. Loss and Damage:
- Adaptation is a proactive response to climate change.
- Loss and Damage (L&D) represents irreversible consequences.
- L&D includes economic losses, human casualties, and ecosystem degradation.
- The Loss and Damage Fund:
- Historic pollution raised global temperature by over 1 degree Celsius.
- L&D fund established at COP 19 in 2013.
- Intended to assist economically developing nations facing L&D.
- Subsequent COPs and Status:
- COP 25 set up Santiago Network for L&D but no funding commitment.
- COP 26 established Glasgow Dialogue on finance for L&D.
- COP 27 in 2022 agreed to set up L&D fund and Transitional Committee.
- TC5 Meeting and Aftereffects:
- TC5 meeting led to recommendations for COP 28.
- Developing nations agreed to host the fund at World Bank for an interim period.
- Developed nations, especially the U.S., remain non-committal about primary donor status.
- Implications of Outcome:
- Threatens climate justice and worsens the suffering of vulnerable communities.
- Increases risk of humanitarian crises, including food shortages and conflicts.
- Economic consequences for both developing and developed nations.
- Security implications as climate-change-induced instability may lead to conflicts.
Why In News
As the climate crisis intensifies, two terms are in sharp focus — adaptation and ‘loss and damage’ (L&D), highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive strategies to address the escalating impacts on vulnerable communities and ecosystems.
MCQs about Navigating Loss & Damage Funding Challenges
-
What is the primary difference between adaptation and loss & damage in the context of climate change?
A. Adaptation is reactive, while loss & damage is proactive.
B. Adaptation involves deliberate choices, while loss & damage represents irreversible consequences.
C. Adaptation is solely financial, while loss & damage is related to human casualties.
D. Adaptation efforts can mitigate loss & damage.
-
When was the Loss & Damage fund established, and what is its primary purpose?
A. Established at COP 25 in 2013 to address economic losses.
B. Established at COP 19 in 2013 to provide financial and technical assistance for L&D due to climate change.
C. Established at COP 27 in 2022 to support developing nations.
D. Established at COP 26 in 2013 to mitigate historic pollution.
-
What was the outcome of the TC5 meeting regarding the Loss & Damage fund?
A. Developed nations committed substantial funds to the World Bank Financial Intermediary Fund.
B. Developing nations rejected the fund hosted by the World Bank.
C. Recommendations were drafted and forwarded to COP 28.
D. The World Bank confirmed its willingness to host the fund without any overhead fee.
-
What are the implications of the watering down of the Loss & Damage fund?
A. It strengthens climate justice and supports vulnerable communities.
B. It has no impact on humanitarian crises.
C. It threatens climate justice and exacerbates suffering in vulnerable communities.
D. It leads to increased financial support from developed nations.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


