Daily Current Affairs : 24-June-2023
In recent news, a Delhi-based hospital has come under scrutiny for its negligent and unethical practices during an in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedure. The hospital has been instructed by the National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC) to pay a fine of ₹1.5 crore for their misconduct. This essay aims to shed light on the NCDRC’s role, the significance of the Consumer Protection Act, and the basics of IVF.
- The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC)
1.1 Purpose and Establishment:
- The NCDRC is a quasi-judicial commission set up in 1988 under the Consumer Protection Act of 1986.
- Its main objective is to resolve consumer disputes and provide justice to affected individuals.
1.2 Composition and Jurisdiction:
- The Commission is headed by a sitting or retired Judge of the Supreme Court or a Chief Justice of a High Court.
- It has jurisdiction over complaints valued at more than two crore rupees.
- It also has appellate and revisional jurisdiction over the orders of State Commissions and District Forums.
- Individuals dissatisfied with NCDRC’s order can file an appeal to the Supreme Court within 30 days.
- The Consumer Protection Act
2.1 Rights and Protection:
- The Consumer Protection Act lays down the rights of consumers and ensures their promotion and protection.
- It is the first and only Act in India that empowers consumers to seek affordable and expedient redressal for their grievances.
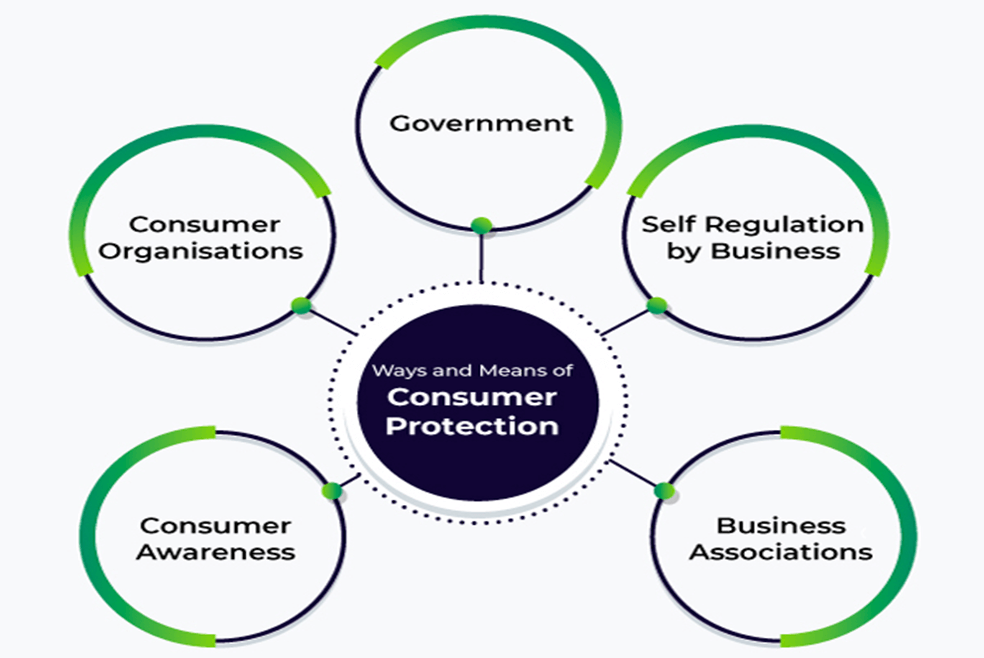
2.2 Consumer Protection Councils:
- The Act mandates the establishment of Consumer Protection Councils at the Centre, State, and District levels to enhance consumer awareness.
- The Central Council, headed by the Minister In-charge of the Department of Consumer Affairs, plays a crucial role in overseeing consumer welfare.
2.3 3-Tier Structure:
- The Act establishes a 3-tier structure for addressing consumer complaints: a) The National Commission, b) The State Commissions, and c) The District Commissions.
- These commissions handle grievances related to both goods and services.
- Understanding IVF (In Vitro Fertilization)
3.1 Definition and Purpose:
- IVF stands for in vitro fertilization and is a well-known type of assisted reproductive technology (ART).
- It involves the use of medications and surgical procedures to facilitate the fertilization of an egg by sperm in a laboratory setting.
- IVF is utilized by individuals or couples facing fertility challenges to conceive a child.
3.2 Process and Importance:
- The process of IVF involves: a) Stimulating the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, b) Retrieving the eggs from the ovaries, c) Combining the eggs with sperm in a laboratory dish, d) Cultivating the embryos for a few days, and e) Transferring the developed embryos into the uterus.
- IVF has revolutionized reproductive medicine and has been a source of hope for many individuals or couples struggling with infertility.
Important Points:
- A Delhi-based hospital has been fined ₹1.5 crore by the NCDRC for negligence and unethical practices during an IVF procedure.
- The NCDRC is a quasi-judicial commission established in 1988 under the Consumer Protection Act of 1986.
- The Commission is headed by a sitting or retired Judge of the Supreme Court or a Chief Justice of a High Court.
- The NCDRC has jurisdiction over complaints valued at more than two crore rupees and handles appeals and revisions from State Commissions and District Forums.
- The Consumer Protection Act protects the rights of consumers and provides avenues for redressal of grievances.
- Consumer Protection Councils at the Centre, State, and District levels are established to promote consumer awareness.
- The Act’s 3-tier structure includes the National Commission, State Commissions, and District Commissions to handle consumer complaints.
- IVF, or in vitro fertilization, is a well-known assisted reproductive technology (ART).
- IVF involves using medications and surgical procedures to fertilize an egg with sperm in a laboratory setting.
- The process includes stimulating the ovaries, retrieving the eggs, fertilizing them in a laboratory dish, cultivating the embryos, and transferring them into the uterus.
- IVF offers hope for individuals or couples facing fertility challenges.
- Medical professionals must adhere to ethical standards and prioritize patient well-being during IVF procedures.
Why In News
Recently, a Delhi-based hospital that committed grave errors during an in vitro fertilization procedure (IVF) has faced the consequences, as the National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC) mandated the hospital to pay a significant fine of ₹1.5 crore. This ruling not only holds the hospital accountable for its negligence but also sends a strong message against engaging in unethical practices in the field of reproductive medicine. The decision aims to safeguard the rights and well-being of patients, ensuring that medical professionals adhere to the highest standards of care and ethics in fertility treatments.
MCQs about NCDRC’s Response to Unethical IVF Procedures
-
What is the purpose of the National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC)?
A. To regulate IVF procedures in Delhi
B. To promote consumer awareness
C. To provide financial assistance to consumers
D. To oversee the functioning of hospitals in India
-
Which jurisdiction does the NCDRC have?
A. Complaints valued at less than two crore rupees
B. Appeals from the Supreme Court
C. Consumer cases related to goods only
D. Appeals and revisions from State Commissions and District Forums
-
What does the Consumer Protection Act aim to do?
A. Ensure the rights and protection of consumers
B. Regulate the pricing of medical treatments
C. Establish hospitals across the country
D. Provide financial assistance to hospitals
-
What is the purpose of IVF?
A. To stimulate egg production in women
B. To assist in the fertilization of eggs by sperm in a laboratory setting
C. To prevent infertility in men
D. To promote consumer awareness about reproductive technologies
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


