Daily Current Affairs : 20-November-2023
Isotopes, variations of a chemical element, play a pivotal role in our comprehension of atomic structures. They possess the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons, leading to distinctive atomic masses. For instance, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon, showcasing how this variation occurs in nature.
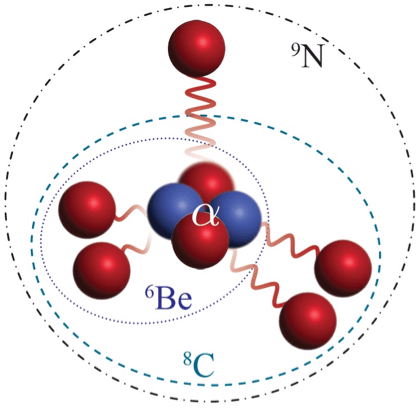
Demystifying Nitrogen-9: An Unusual Isotope
Nitrogen-9 emerges as a focal point of recent scientific discovery. Unlike its more common counterpart with an atomic mass of 14, consisting of seven protons and seven neutrons, Nitrogen-9 is marked by a distinctive composition of seven protons and merely two neutrons. This unusual arrangement challenges the conventional wisdom about isotopes and prompts a reevaluation of stability in subatomic particles.
Unprecedented Proton-Neutron Ratio: A Puzzling Anomaly
The crux of Nitrogen-9’s peculiarity lies in its remarkably high ratio of protons to neutrons. Typically, elements maintain a balanced ratio for stability. However, Nitrogen-9 defies this norm, boasting an imbalance that challenges established stability thresholds. The heightened proton content introduces an element of instability, prompting scientists to question the mechanisms that allow Nitrogen-9 to exist in this state and maintain stability.
Questioning Stability Thresholds: Nitrogen-9’s Enigmatic Existence
The discovery of Nitrogen-9 prompts a fundamental reexamination of stability in atomic nuclei. Its unconventional composition raises intriguing questions about the factors influencing stability and introduces a layer of complexity to our understanding of subatomic structures. As scientists delve deeper into the mysteries of Nitrogen-9, they aim to unravel the intricacies of its existence and contribute to a paradigm shift in our comprehension of the fundamental building blocks of matter.
Important Points:
- Isotopes Overview:
- Variants of chemical elements with the same protons but different neutrons in the nucleus.
- Result in distinct atomic masses, exemplified by carbon-12 and carbon-14.
- Nitrogen-9 Characteristics:
- Uncommon isotope with seven protons and two neutrons.
- Deviates from the standard nitrogen atom with an atomic mass of 14 (7 protons and 7 neutrons).
- Unusual Proton-Neutron Ratio:
- Nitrogen-9 exhibits a significantly high ratio of protons to neutrons.
- Challenges the typical balanced ratio observed in stable elements.
- Puzzling Anomaly and Stability:
- The abnormal composition of Nitrogen-9 questions established stability thresholds.
- Its heightened proton content introduces instability, defying conventional norms.
- Enigmatic Existence and Scientific Inquiry:
- Scientists question how Nitrogen-9 maintains stability with its unusual composition.
- The discovery prompts a fundamental reexamination of stability in atomic nuclei.
- Complexity in Subatomic Structures:
- Nitrogen-9’s unique characteristics introduce complexity to our understanding of atomic nuclei.
- The scientific community aims to unravel the mysteries surrounding Nitrogen-9, contributing to a paradigm shift in our comprehension of subatomic structures.
Why In News
Scientists have discovered “strong evidence” for the existence of the unusual nitrogen-9 isotope, challenging previous interpretations and offering a new perspective on subatomic structures. This groundbreaking finding opens up avenues for further research, potentially reshaping our understanding of fundamental particles and their interactions.
MCQs about Nitrogen-9
-
Nitrogen-9 distinguishes itself from a standard Nitrogen atom by:
A. It has more protons.
B. It has fewer neutrons.
C. It has a higher atomic mass.
D. It has an unusual proton-neutron ratio.
-
What makes Nitrogen-9 unusual?
A. It has a lower proton count.
B. It has a higher neutron count.
C. It maintains a balanced proton-neutron ratio.
D. It possesses an unusually high proton-neutron ratio.
-
How does Nitrogen-9 challenge stability norms?
A. It has a lower atomic mass.
B. It maintains conventional proton-neutron ratios.
C. It defies typical stability thresholds with its high proton content.
D. It undergoes rapid decay over time.
-
What impact does Nitrogen-9’s discovery have on our understanding of subatomic structures?
A. It simplifies existing models.
B. It introduces complexity and prompts a reevaluation.
C. It confirms established stability thresholds.
D. It has no significant implications for subatomic studies.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


