Daily Current Affairs : 1-August-2023
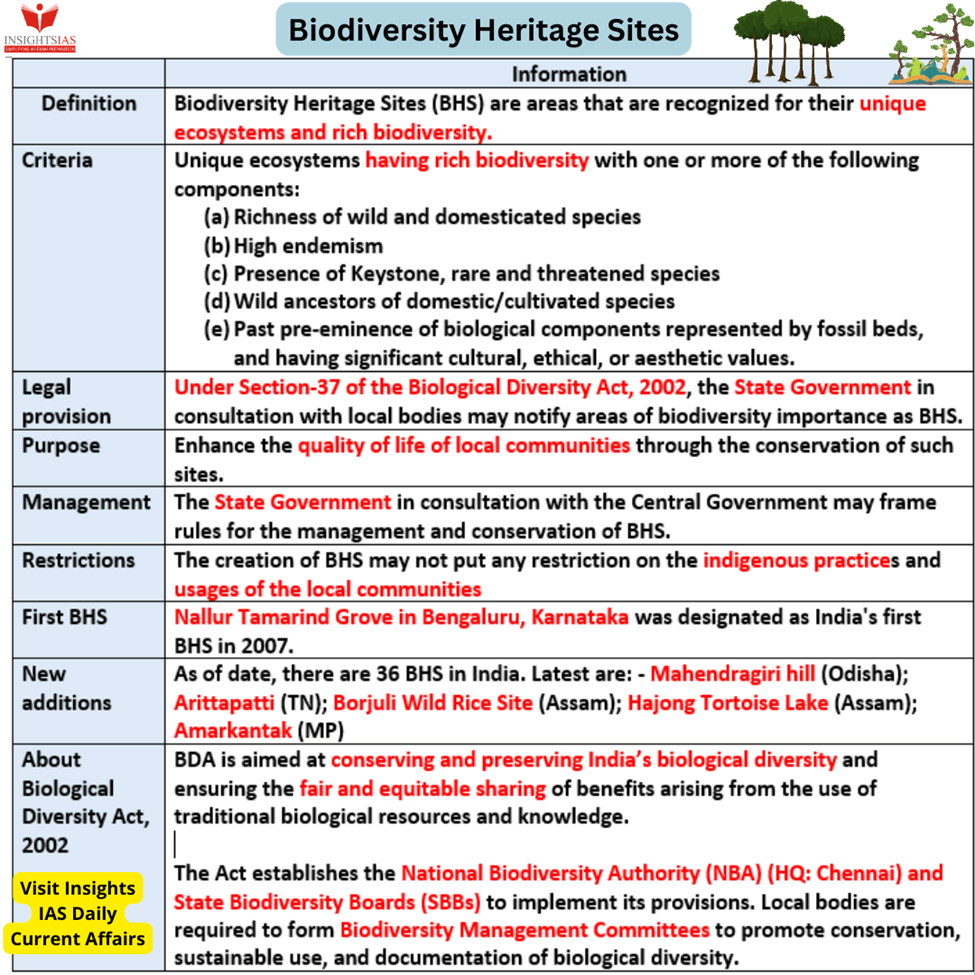
The Government of Odisha has recently taken a significant step towards preserving its natural treasures by notifying three Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS). These sites, namely Mandasaru Hills, Mahendragiri Hills, and Gandhamardan Hills, are deemed unique and ecologically fragile ecosystems that require special protection. In this essay, we will explore the concept of Biodiversity Heritage Sites, the criteria for their identification, and the positive implications of such a declaration in Odisha.
Understanding Biodiversity Heritage Sites
Biodiversity Heritage Sites are areas that possess exceptional biodiversity, encompassing various factors such as species richness, high endemism, the presence of rare and threatened species, keystone species, and species of evolutionary significance. These sites also include areas with wild ancestors of domestic or cultivated species, fossil beds representing past pre-eminence of biological components, and areas with significant cultural, ethical, or aesthetic values that contribute to the preservation of cultural diversity.
Criteria for Identification of Biodiversity Heritage Sites
The identification and declaration of Biodiversity Heritage Sites are regulated by the Biological Diversity Act of 2002. According to this act, the State Government, in consultation with local bodies, has the authority to notify areas as BHS. The process involves a careful assessment of the ecological significance of the site and its contribution to biodiversity conservation. The following are the key criteria considered for designating an area as a BHS:
- Rich Biodiversity: The site must exhibit a remarkable diversity of plant and animal species, indicating a healthy and thriving ecosystem.
- Endangered Species: The presence of rare and threatened species within the area is an essential factor in determining its importance for conservation.
- Keystone Species: The presence of keystone species, which have a significant impact on the ecosystem’s structure and function, enhances the ecological value of the site.
- Evolutionary Significance: Sites harboring species of evolutionary significance, contributing to our understanding of evolution and adaptation, are given special consideration.
- Wild Ancestors of Domestic/Cultivated Species: The existence of wild ancestors of domestic or cultivated species demonstrates the site’s historical and ecological importance.
- Fossil Beds: Areas representing past pre-eminence of biological components through fossil beds contribute to the scientific understanding of Earth’s history and evolution.
- Cultural, Ethical, and Aesthetic Values: Sites with cultural importance, having links to local traditions, customs, and practices, are recognized as essential for cultural diversity.
Implications of Notifying Biodiversity Heritage Sites in Odisha
The notification of Biodiversity Heritage Sites in Odisha carries numerous benefits and positive implications:
- Conservation and Restoration: The declaration ensures that these ecologically sensitive areas receive heightened protection and conservation efforts, safeguarding their unique biodiversity for future generations.
- Sustainable Development: While the designation of BHS protects the sites, it does not impose restrictions on the practices and usages of local communities. This allows for sustainable development that considers both conservation and the welfare of local inhabitants.
- Tourism and Awareness: Notified BHS sites can attract eco-tourists and nature enthusiasts, generating revenue for local communities while raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation.
- Scientific Research: Biodiversity Heritage Sites offer valuable opportunities for scientific research and discovery, aiding our understanding of the natural world and promoting innovative conservation strategies.
Important Points:
- The Government of Odisha has notified three Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS): Mandasaru Hills, Mahendragiri Hills, and Gandhamardan Hills.
- Biodiversity Heritage Sites are areas with unique and ecologically fragile ecosystems, encompassing factors like species richness, high endemism, presence of rare and threatened species, and more.
- Declaration of BHS does not impose restrictions on local communities’ practices and usages, allowing for sustainable development.
- The Biological Diversity Act, 2002, empowers the State Government to designate areas as BHS in consultation with local bodies.
- Criteria for identifying BHS include rich biodiversity, presence of endangered and keystone species, evolutionary significance, wild ancestors of domestic/cultivated species, fossil beds, and cultural, ethical, and aesthetic values.
- Notifying BHS leads to heightened protection, conservation, and restoration efforts for these ecologically sensitive areas.
- Sustainable development is encouraged, balancing conservation goals with the well-being of local communities.
- BHS designation attracts eco-tourists and promotes biodiversity awareness, benefiting local economies.
- Scientific research opportunities arise from studying BHS, advancing our understanding of the natural world and fostering innovative conservation strategies.
- Odisha’s decision to protect Biodiversity Heritage Sites sets an example for prioritizing biodiversity conservation and cultural heritage preservation for present and future generations.
Why In News
The Government of Odisha, recognizing the invaluable importance of biodiversity conservation, has recently taken a significant step by notifying three new Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS). These designated sites are set to receive enhanced protection and preservation measures to safeguard their unique ecosystems for future generations.
MCQs about Odisha’s Notified Biodiversity Heritage Sites
-
What are Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS)?
A. Sites designated for exclusive tourist purposes
B. Areas with high cultural significance and historical importance
C. Unique and ecologically fragile ecosystems with rich biodiversity
D. Locations reserved for scientific research and exploration
-
Who has the authority to notify areas as Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS) in Odisha?
A. The local communities residing in the areas
B. Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) working for biodiversity conservation
C. The State Government in consultation with local bodies
D. The Central Government’s Ministry of Environment and Forests
-
What is the main implication of declaring an area as a Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS)?
A. Complete ban on any human activity within the designated area
B. Restrictions imposed on the prevailing practices and usages of local communities
C. Increased tourism activities leading to ecological degradation
D. Mandatory relocation of the local communities from the area
-
How do Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS) contribute to scientific research?
A. They promote historical studies of ancient civilizations and artifacts.
B. They offer opportunities for archaeological excavations.
C. They provide valuable opportunities for scientific research and discovery.
D. They allow for the examination of geological formations and minerals.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


