Daily Current Affairs : 26-October-2023
Recently, the art world commemorated the 142nd birth anniversary of Pablo Picasso, the iconic Spanish artist (1881-1973), who left an indelible mark on the world of art through his mastery of Cubism.
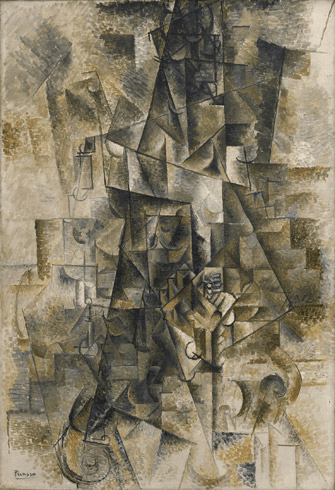
Understanding Cubism: More Than Just Cubes
Cubism, despite its name, is not about cubes. It was a revolutionary approach to art in the early 20th century that profoundly influenced the artistic landscape. Unlike traditional art, where objects were depicted from a single viewpoint, Cubism allowed artists to portray objects from every imaginable angle. It rejected the conventional methods of creating art, steering away from mere copies of nature.
Instead, it compelled artists to explore the two-dimensional nature of the canvas, emphasizing the importance of everyday objects that often went unnoticed.
The Evolution of Cubism: Analytical and Synthetic Phases
Cubism’s evolution can be understood through its two distinct phases:
Analytical Cubism (1907-1912): During this period, artists depicted objects from multiple viewpoints, utilizing muted tones of blacks, greys, and ochres. This phase challenged the traditional norms of representation, encouraging viewers to perceive objects in a new light.
Synthetic Cubism (1912-1914): In this later phase, Cubism embraced simpler shapes, vibrant colors, and a groundbreaking element—real-life objects were incorporated into artworks. This innovation marked a departure from the confines of traditional art, pushing boundaries and redefining creativity.
Cubism’s Influence and Legacy: Beyond the Canvas
Cubism, although short-lived, paved the way for non-representational art movements like Surrealism. Its impact was not confined to the canvas; it encouraged people to view the world differently. By challenging established artistic norms, Cubism inspired a fresh perspective on everyday objects, fostering a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of the mundane.
Important Points:
- Cubism is Not About Cubes:
- Cubism, despite its name, is not about cubes; it is a groundbreaking art movement from the early 20th century.
- Artists depicted objects from multiple angles, challenging the traditional single-viewpoint approach.
- Pablo Picasso’s Contribution:
- Picasso, the renowned Spanish artist, played a pivotal role in shaping Cubism.
- His mastery of Cubism revolutionized the art world and left a lasting impact on artistic expression.
- Analytical Cubism (1907-1912):
- In this phase, artists portrayed objects from various viewpoints.
- Muted tones of blacks, greys, and ochres were used, deviating from traditional vibrant colors.
- Synthetic Cubism (1912-1914):
- This phase introduced simpler shapes, brighter colors, and a significant innovation – real-life objects were incorporated into artworks.
- Synthetic Cubism marked a departure from traditional art, pushing boundaries and embracing creativity.
- Cubism’s Influence and Legacy:
- Cubism influenced non-representational art movements like Surrealism.
- It encouraged viewers to perceive everyday objects in a new light, fostering a deeper appreciation for the mundane.
- Cubism’s impact extended beyond the canvas, transforming how people viewed the world and inspiring fresh perspectives.
- Challenging Traditional Norms:
- Cubism rejected the conventional approach of art as a mere copy of nature.
- Artists explored the two-dimensional nature of the canvas, emphasizing overlooked everyday objects.
- Picasso’s Enduring Legacy:
- Picasso’s contribution to Cubism transformed the art world, inspiring artists and art enthusiasts globally.
- Cubism continues to influence contemporary art, encouraging exploration and innovation.
Why In News
Recently, the 142nd birth anniversary of the renowned Spanish artist Pablo Picasso (1881-1973), a master of cubism art, was celebrated worldwide, honoring his enduring influence on the art world and inspiring generations of artists with his innovative techniques and creative vision.
MCQs about Picasso’s Cubism
-
What is Cubism primarily known for?
A. Depicting objects from a single viewpoint
B. Using only cubes as artistic elements
C. Portraying objects from multiple angles
D. Emphasizing three-dimensional illusions
-
Which phase of Cubism involved the use of real-life objects in artworks?
A. Analytical Cubism
B. Synthetic Cubism
C. Monochromatic Cubism
D. Geometric Cubism
-
Who was the renowned artist associated with the development of Cubism?
A. Vincent van Gogh
B. Pablo Picasso
C. Leonardo da Vinci
D. Claude Monet
-
What did Cubism encourage viewers to appreciate?
A. Vibrant colors
B. Three-dimensional illusions
C. Mundane everyday objects
D. Classical art techniques
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


