Daily Current Affairs : 14-December-2024
The European Space Agency (ESA) recently launched the Proba-3 mission from India to conduct a unique and groundbreaking study of the Sun. This mission aims to create artificial solar eclipses, providing scientists with the opportunity to study the Sun’s corona in unprecedented detail. Let’s explore the concept of artificial solar eclipses, how they work, and their significance.
What is an Artificial Solar Eclipse?
An artificial solar eclipse is a man-made simulation of a natural solar eclipse. In a natural eclipse, the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, blocking sunlight and allowing scientists to study the Sun’s outer atmosphere, called the corona. However, these natural eclipses are brief, lasting only a few minutes.
In an artificial solar eclipse, two satellites are used to create a controlled shadow, mimicking the Moon’s role. This setup allows for detailed and extended observations of the Sun’s corona. The primary aim is to understand why the corona is much hotter than the Sun’s surface, a mystery that has puzzled scientists for years.
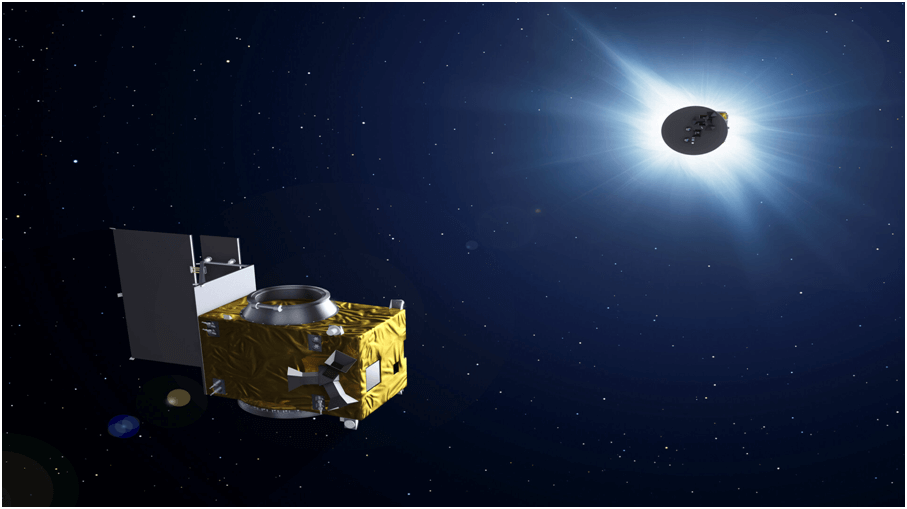
How the Artificial Solar Eclipse Works
The Proba-3 mission uses two satellites: the Coronagraph Spacecraft (CSC) and the Occulter Spacecraft (OSC). These satellites work together to simulate an eclipse by blocking the Sun’s light.
- Satellite Alignment: The two satellites maintain precise alignment, staying just 150 meters apart.
- Shadow Creation: The OSC spacecraft casts a shadow onto the CSC, just like the Moon does during a natural eclipse.
- Precision: The satellites maintain millimetre-level accuracy, ensuring the artificial eclipse lasts for up to six hours per orbit.
This precision is crucial because it allows for long-duration observations, far surpassing the few minutes offered by natural solar eclipses.
Significance of Artificial Solar Eclipses
Artificial solar eclipses offer several scientific benefits:
- Extended Observation Time: Unlike natural eclipses, which last only a few minutes, Proba-3 enables hours of continuous observation of the Sun’s corona.
- Space Weather Predictions: The data collected can help predict geomagnetic storms, which can affect satellites, power grids, and other Earth-based systems.
- Scientific Insights: Proba-3 will also help scientists study solar phenomena such as solar flares and coronal heating, which are essential for understanding the Sun’s behavior and its impact on space weather.
What is Precise Formation Flying (PFF) Technology?
To achieve this remarkable feat, Proba-3 uses a technology called Precise Formation Flying (PFF). PFF allows satellites to maintain a specific position and orientation relative to each other in orbit.
- Mechanism: The satellites use GPS, inter-satellite radio links, and automated control systems to stay aligned with millimetre-level accuracy.
- Proba-3 Implementation: The satellites in Proba-3 remain 150 meters apart, maintaining the perfect alignment required for simulating an eclipse.
- Benefits: This technology ensures the accuracy of the mission and provides a platform for advanced observational techniques, making Proba-3 an essential mission for space science.
Important Points:
- Proba-3 Mission: Launched by the European Space Agency (ESA) to create artificial solar eclipses for extended study of the Sun’s corona.
- Artificial Solar Eclipse: A controlled eclipse created by two satellites, mimicking the natural eclipse where the Moon blocks sunlight.
- Satellite Pair: The mission uses two satellites — Coronagraph Spacecraft (CSC) and Occulter Spacecraft (OSC) — to block sunlight and simulate an eclipse.
- Precision Alignment: The satellites remain 150 meters apart, maintaining millimetre-level precision for up to six hours per orbit.
- Extended Observation: Unlike natural eclipses, which last only minutes, Proba-3 allows hours of continuous observation of the Sun’s corona.
- Scientific Benefits:
- Helps study solar phenomena like coronal heating and solar flares.
- Aids in predicting geomagnetic storms, which impact satellites and Earth-based systems.
- Provides insights into why the Sun’s corona is hotter than its surface.
- Precise Formation Flying (PFF): Technology that ensures satellites stay in perfect alignment using GPS, inter-satellite links, and automated control systems.
- Impact of PFF: Enables accurate, long-duration observations, crucial for advanced space science and observational techniques.
- Significance for Space Weather: Data from Proba-3 can help predict and mitigate space weather events, ensuring the safety of space infrastructure.
Why In News
The European Space Agency (ESA) launched the Proba-3 mission from India to create artificial solar eclipses, enabling extended studies of the Sun’s corona using cutting-edge precise formation flying technology, which allows for highly accurate and prolonged observations of solar phenomena that were previously impossible to capture.
MCQs about Proba-3: Unlocking the Mysteries of the Sun with Artificial Eclipses
-
What is the main purpose of the Proba-3 mission?
A. To study the Earth’s atmosphere
B. To create artificial solar eclipses for studying the Sun’s corona
C. To observe other planets
D. To track asteroids
-
How do the Proba-3 satellites maintain their alignment?
A. By using a manual control system
B. Through GPS, inter-satellite communication, and automated control systems
C. By using mirrors
D. By following the Moon’s orbit
-
What phenomenon does the Proba-3 mission aim to study in the Sun?
A. Sunspots
B. The Sun’s corona, including its temperature and solar flares
C. Solar wind
D. Solar eclipses
-
What technology is used to simulate the eclipse in the Proba-3 mission?
A. Inter-satellite laser technology
B. Precise Formation Flying (PFF) technology
C. Optical alignment
D. Solar-powered tracking
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


