China has emerged as a major player in the Blue Economy, which refers to the sustainable development of ocean resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods and jobs, and the preservation of the ocean ecosystem. India can learn from China’s success in developing its blue economy, particularly in the fisheries sector, which is critical to both countries’ food security.
China’s Rise as a Fishery Superpower
China’s fishing industry has grown rapidly due to a shortage of farmland and the need to meet the demand for protein in the Chinese diet. China is now a leading “fishery superpower,” with a deep-water fishing fleet that engages in distant deepwater fishing in Asia and Africa. China also uses part of its fishing fleet as a maritime militia to support its navy and coast guard.
India and its Fisheries Sector
Fish is a great source of protein for India to combat hunger and malnutrition as it is affordable and a rich source. India’s fisheries sector has become a major contributor to foreign exchange and provides livelihood to about 15 million fishers. However, the sector faces several challenges, including the depletion of fish populations, competition from neighboring countries, and illegal, unregulated, and unreported fishing.
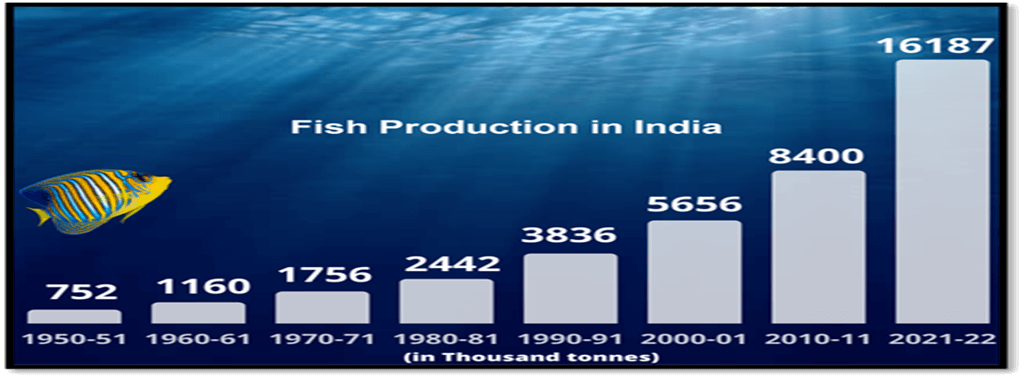
Reform Needed in the Indian Fisheries Sector
To improve the industry, India needs to focus on four areas: modernizing fishing vessels with electronic fish detection devices and providing funding for artisanal fishers, developing deep-sea fishing fleets with larger trawlers equipped with refrigeration facilities, building a deep-water fishing fleet around the “mothership” concept, and developing modern fishing harbors with proper facilities for storing, preserving, and packaging fish.
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana
Launched in 2020, this scheme aims to develop India’s fisheries sector sustainably with an estimated investment of Rs 20,000 crores over the next five years. One proposal is to form an “Indo-Sri Lankan Fishing Corporation” to benefit both countries’ fishing industries and improve bilateral relations. This initiative aligns with the principle of SAGAR, which stands for “Security and Growth for All in the Region.”
Why In News
The World Bank defines the Blue Economy as the sustainable use of ocean resources to promote economic growth, create job opportunities, and enhance livelihoods while preserving the health of the marine ecosystem. China has made significant progress in developing its blue economy and there are valuable insights that India can learn from.
MCQs about Reforming India’s Fisheries Sector
-
What is the Blue Economy according to the World Bank?
A. The sustainable development of ocean resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and jobs while preserving the health of the ocean ecosystem.
B. The sustainable development of land resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and jobs while preserving the health of the land ecosystem.
C. The sustainable development of forest resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and jobs while preserving the health of the forest ecosystem.
D. The sustainable development of air resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and jobs while preserving the health of the air ecosystem.
-
Why did China develop its fishing industry?
A. To meet the demand for protein in the Chinese diet.
B. To mitigate hunger in African countries.
C. To reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
D. To increase the country’s GDP.
-
What is IUU fishing?
A. Illegal, unregulated, and unreported fishing.
B. Industrial underwater unearthing.
C. Illegal underwater unearthing.
D. Invasive underwater unearthing.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


