Daily Current Affairs : 8-February-2024
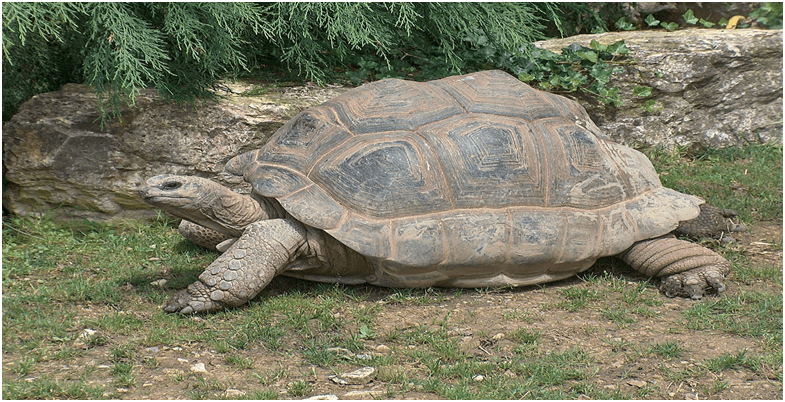
A widespread venture spanning six years has successfully reintroduced Aldabra large tortoises to Madagascar. This marks a hopeful second for the island, as those tortoises should thrive and repopulate for the first time in six hundred years. The initiative aims to restore the island’s ecosystems, that have suffered because of the absence of these megaherbivores.
The Role of Aldabra Giant Tortoises
The Aldabra giant tortoise, scientifically called Aldabrachelys gigantea, is native to the Seychelles. Here are a few key data approximately this tremendous species:
- Size: They are amongst the biggest land tortoises, with males weighing as much as 550 pounds and measuring around four feet lengthy.
- Longevity: Aldabra tortoises can stay for over a hundred and fifty years, making them one of the longest-living animals on earth.
Ecological Benefits
Reintroducing those tortoises to Madagascar gives numerous ecological benefits:
- Ecosystem Restoration: Giant tortoises play a vital role in keeping wholesome ecosystems. They assist form the surroundings by way of eating plant life and dispersing seeds.
- Biodiversity Support: Their presence can help restore various habitats, consisting of forests, grasslands, and shrublands, contributing to more biodiversity.
- Habitat Mosaics: Tortoises can useful resource in re-establishing habitat mosaics, which are crucial for many species to thrive.
Economic and Environmental Impact
The successful reintroduction of Aldabra massive tortoises is likewise anticipated to have superb influences on the local financial system and environment:
- Tourism Boost: Increased biodiversity can attract tourists, presenting economic blessings to neighborhood groups.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Healthy ecosystems can help combat the effects of climate trade by using sequestering carbon and supplying crucial services.
Important Points:
Project Overview:
- Six-year initiative to reintroduce Aldabra giant tortoises to Madagascar.
- First repopulation in 600 years.
Significance of Aldabra Giant Tortoises:
- Native to the Seychelles.
- Size: Up to 550 pounds and four feet long.
- Longevity: Can live over 150 years.
Ecological Benefits:
- Ecosystem Restoration: Help maintain healthy ecosystems by eating plants and dispersing seeds.
- Biodiversity Support: Restore habitats like forests, grasslands, and shrublands.
- Habitat Mosaics: Aid in re-establishing important habitat mosaics for various species.
Economic and Environmental Impact:
- Tourism Boost: Increased biodiversity attracts tourists, benefiting local economies.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Healthy ecosystems sequester carbon and provide essential services.
Why In News
A project spanning six years has successfully reintroduced Aldabra giant tortoises to Madagascar, potentially leading to thousands of these megaherbivores repopulating the island for the first time in 600 years. This remarkable achievement not only promises to restore the island’s ecological balance but also brings hope for a vibrant future for its diverse wildlife.
MCQs about Reintroducing Aldabra Giant Tortoises to Madagascar
-
What is the primary goal of the project that reintroduced Aldabra giant tortoises to Madagascar?
A. To increase tourism
B. To restore the island’s ecosystems
C. To study tortoise behavior
D. To export tortoises to other regions
-
How long can Aldabra giant tortoises live?
A. 50 years
B. 100 years
C. 150 years
D. Over 150 years
-
Which of the following is NOT an ecological benefit of reintroducing Aldabra giant tortoises to Madagascar?
A. Ecosystem restoration
B. Increased biodiversity
C. Creation of artificial habitats
D. Habitat mosaics
-
What potential economic impact could result from the increased biodiversity following the reintroduction of the tortoises?
A. Decreased agricultural output
B. Enhanced tourism
C. Increased deforestation
D. Higher import costs
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


