Daily Current Affairs : 9-September-2023
In recent news, the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) released its 2023 Air Quality and Climate Bulletin, shedding light on a concerning environmental issue. This report is the third in an annual series and highlights a critical connection between climate change-induced heatwaves and the rise in ozone pollution. This essay delves into the key details of the report, elucidates the link between heatwaves and ozone pollution, and discusses the far-reaching impacts of this environmental concern.
Understanding Heatwaves
Before we delve into the specifics of the WMO report, let’s clarify what a heatwave is. A heatwave is a period marked by abnormally high temperatures, surpassing the region’s typical maximum temperature during the summer season. In North-Western parts of India, where heatwaves are common, they generally occur between March and June, occasionally extending into July. These extreme temperatures can be life-threatening, causing physiological stress and even fatalities.
The Criteria for Identifying a Heatwave
The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) has laid out criteria for recognizing heatwaves. They stipulate that a heatwave should not be declared until the maximum temperature reaches at least 40°C in plains and 30°C in hilly regions. Additionally, when the actual maximum temperature remains at 45°C or higher, regardless of the normal maximum temperature, it qualifies as a heatwave.
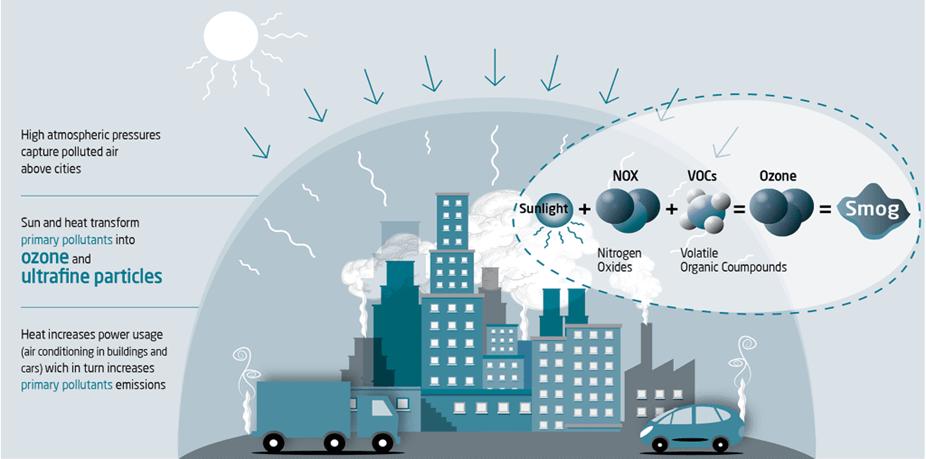
The Link Between Heatwaves and Ozone Pollution
The WMO report underscores the profound connection between climate change-induced heatwaves and the surge in ozone pollution. Here’s how this relationship works:
- Wildfires and Carbon Emissions: Heatwaves intensify the frequency and severity of wildfires. These blazes release a multitude of chemicals, leading to increased carbon emissions and greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Reactive Gases and Ozone Production: Short-lived reactive gases like nitrogen oxides and biogenic volatile organic compounds, released during wildfires and other combustion processes, contribute to the production of ozone and particulate matter (PM). This results in a surge of ozone in the atmosphere.
Impacts of Increased Ozone Pollution
The repercussions of heightened ozone pollution are substantial and multifaceted:
- Agricultural Impact: Globally, the increase in ozone levels has adversely affected agriculture. Ozone-induced crop losses have been estimated at an average of 4.4% to 12.4% for staple crops. In key agricultural regions of India and China, losses for wheat and soybean have soared as high as 15% to 30%.
- Air Quality and Health: Heatwaves exacerbate air quality, leading to detrimental effects on human health and ecosystems. Ozone pollution can cause respiratory problems and other health issues, posing a significant threat to vulnerable populations.
- Ecosystem Disruption: Ozone pollution also disrupts ecosystems, affecting plants and wildlife. This imbalance can have far-reaching consequences on biodiversity.
- Agriculture and Food Security: The impact on agriculture not only affects crop yields but also jeopardizes food security, as staple crops become more susceptible to ozone-related damage.
In conclusion, the recent WMO report underscores the critical link between increasing heatwaves and rising ozone pollution. As climate change continues to escalate the frequency and intensity of heatwaves, addressing this issue becomes paramount. The repercussions extend beyond the environment, affecting agriculture, human health, ecosystems, and food security. Mitigating the impact of heatwaves and ozone pollution requires collective global efforts to combat climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
About the World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations dedicated to promoting international cooperation in atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology, and geophysics. With 193 member countries, it fosters the exchange of data, information, and research among meteorological and hydrological institutions worldwide. The WMO’s headquarters are located in Geneva, Switzerland, and it is governed by the World Meteorological Congress, which sets policies and priorities every four years. The organization publishes an annual statement on the status of the world’s climate, providing vital information on global temperatures, extreme weather events, and long-term climate change indicators.
Important Points:
Understanding Heatwaves
- Heatwaves are periods of abnormally high temperatures during summer.
- Common in North-Western India between March and June, occasionally extending into July.
- Indian Meteorological Department’s criteria for identifying heatwaves.
Link Between Heatwaves and Ozone Pollution
- Heatwaves intensify wildfires, leading to increased carbon emissions.
- Wildfires release short-lived reactive gases that contribute to ozone production.
- Ozone pollution surges as a result.
Impacts of Increased Ozone Pollution
- Ozone pollution negatively affects agriculture globally.
- Crop losses average 4.4% to 12.4% for staple crops.
- Wheat and soybean losses reach 15% to 30% in key agricultural areas of India and China.
- Heatwaves worsen air quality, affecting human health, ecosystems, and agriculture.
- Ozone pollution disrupts ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Threatens food security due to crop damage.
About the World Meteorological Organization (WMO)
- Specialized UN agency for atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology, and geophysics.
- Composed of 193 member countries.
- Facilitates global exchange of data, information, and research.
- Headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland.
- Governed by the World Meteorological Congress, which sets policies and priorities.
- Publishes the annual WMO Statement on the status of the world’s climate, including key climate indicators.
Why In News
According to a recent report from the World Meteorological Organization, the rising frequency of heatwaves has not only exacerbated ozone pollution but also posed significant threats to public health and the environment. These findings underscore the urgent need for global efforts to mitigate climate change and curb the detrimental impacts of extreme heat events on our atmosphere.
MCQs about Rising Heatwaves Fuel Ozone Pollution
-
What is the primary connection between heatwaves and ozone pollution?
A. Heatwaves reduce ozone levels due to increased rainfall.
B. Heatwaves lead to a decrease in reactive gases.
C. Heatwaves intensify wildfires, leading to increased ozone pollution.
D. Heatwaves have no impact on ozone pollution.
-
What is the impact of increased ozone levels on agriculture?
A. Increased ozone levels have no effect on agriculture.
B. Ozone pollution leads to higher crop yields.
C. Ozone-induced crop losses average 4.4% to 12.4% for staples.
D. Ozone pollution only affects non-staple crops.
-
What is the role of short-lived reactive gases in ozone production during heatwaves?
A. Short-lived reactive gases have no impact on ozone production.
B. They decrease ozone levels by trapping pollutants.
C. They contribute to the production of ozone.
D. They primarily lead to the formation of carbon dioxide.
-
What is the mission of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO)?
A. The WMO conducts research on space exploration.
B. The WMO focuses on international cooperation in climate change adaptation.
C. The WMO facilitates the exchange of data, information, and research in atmospheric science.
D. The WMO is primarily responsible for global water resource management.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


