The pandemic accord, also known as the pandemic treaty, is an international agreement developed by countries worldwide to prevent and effectively respond to pandemics and health emergencies. However, there is a risk of removing measures related to addressing antimicrobial resistance (AMR) from the treaty. This essay explores the importance of including AMR in the pandemic accord and highlights the potential consequences of its exclusion.
Understanding the Pandemic Accord:
The pandemic accord is an international agreement aimed at establishing rules and norms for preventing and responding to pandemics. It serves as a crucial mechanism for holding countries accountable and addressing global challenges that transcend borders. Similar to the success of the Montreal Protocol in eliminating ozone-depleting substances, the pandemic accord has the potential to prevent pandemics, save lives, and protect the global economy.
Significance of Addressing Antimicrobial Resistance:
Including measures to address AMR in the pandemic accord holds several significant advantages, including:
- Improved transparency and early warning: Efforts to combat AMR can enhance early detection and warning systems for potential outbreaks, allowing for timely responses.
- Enhanced protection for health workers: Addressing AMR ensures that healthcare professionals have access to necessary tools and protection, reducing the risk of infections and improving patient care.
- Accelerated development and deployment of vaccines and medicines: The inclusion of AMR measures can facilitate the rapid development and global distribution of vaccines and medicines, supporting effective pandemic response.
- Strengthened laboratory and surveillance capabilities: By prioritizing AMR, the pandemic accord can bolster laboratory capacities and surveillance systems worldwide, aiding in the identification and containment of infectious diseases.
- Cooperative response to health crises: Integrating AMR measures enables a faster, more effective, and collaborative response to future health emergencies, promoting international cooperation and coordination.
- Protection of human rights: The inclusion of AMR in the accord emphasizes the respect and protection of human rights, ensuring equitable access to healthcare and addressing health disparities.
Decision-making Process and Sovereignty:
The pandemic accord is determined through a negotiation process involving leaders from 194 countries, facilitated by the World Health Organization (WHO). Each country can decide whether to become a party to the final agreement. Importantly, the accord does not hand over control of domestic public health policies to the WHO or any other international body. Implementation of the accord depends on individual countries’ domestic laws and policies, safeguarding their sovereignty.
Understanding Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR):
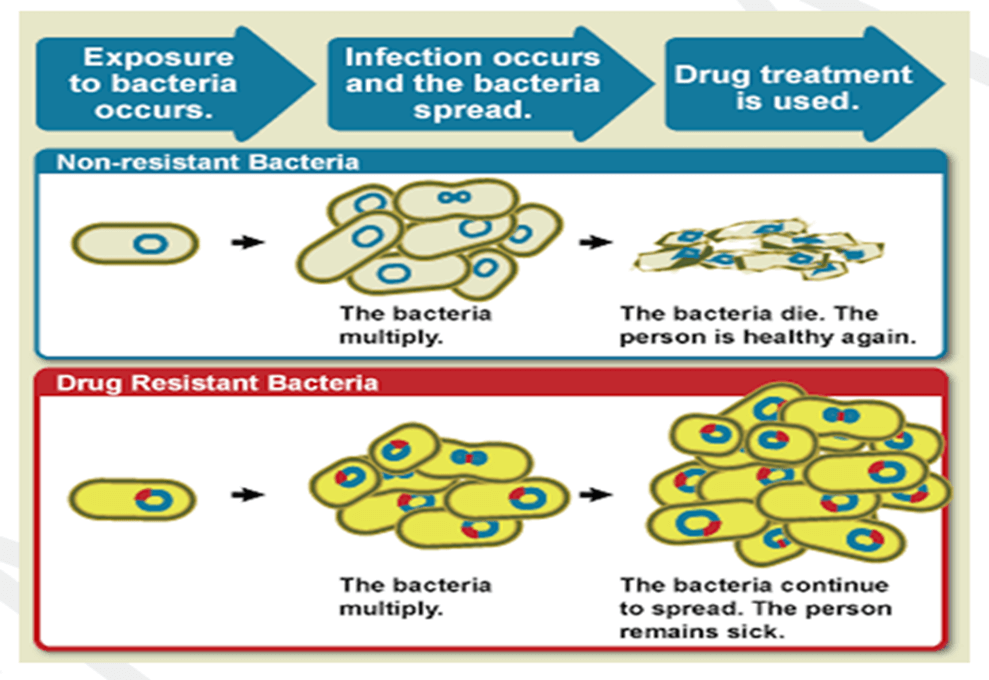
AMR refers to the process where microbes, including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites, develop resistance to the medicines designed to treat them. It has become a leading cause of death globally, with drug-resistant infections such as tuberculosis, pneumonia, and MRSA posing significant threats.
The Importance of Addressing AMR in the Pandemic Treaty:
Considering the uncertainty of future pandemics, the pandemic treaty must plan and prepare for a wide range of pandemic threats, including secondary bacterial infections. During the COVID-19 pandemic, many hospitalized patients required treatment for such infections, necessitating effective antibiotics. However, with the rise of AMR, these antibiotics are becoming scarce. Therefore, removing measures from the pandemic treaty that address AMR and safeguard antimicrobial effectiveness would hinder efforts to protect against future pandemics.
Important Points:
- The pandemic accord, or pandemic treaty, is an international agreement 🌍
- It aims to prevent and respond to pandemics and health emergencies 💉
- AMR (antimicrobial resistance) measures are at risk of being removed from the treaty ⚠️
- AMR refers to the resistance of microbes to medicines 🦠
- Including AMR in the treaty is crucial for better pandemic preparedness and response 🛡️
- AMR measures can improve transparency and early warning systems ⏰
- Health workers’ tools and protection can be ensured with AMR inclusion 🏥
- Faster development and deployment of vaccines and medicines worldwide can be facilitated with AMR measures 💨
- Laboratory and surveillance capabilities can be improved globally with AMR focus 🔬
- Cooperative response to health crises is enhanced by addressing AMR 🤝
- Human rights can be respected and protected by including AMR in the treaty ✊
- The pandemic accord is being determined by leaders from 194 countries 🌐
- Countries retain sovereignty over their own public health policies within the accord 🏛️
- AMR is a leading cause of death worldwide, requiring urgent attention ❗️
- Secondary bacterial infections in pandemics necessitate effective antibiotics 🩺
- Removal of AMR measures would hinder efforts to protect against future pandemics ⛔️
- The pandemic accord should prioritize addressing AMR to safeguard antimicrobials 💪
- Global political action is needed to mitigate AMR and support equitable distribution of antimicrobials 🌍
- Neglecting AMR in the accord undermines its broader goals of pandemic protection 🚫
- Member States must recognize the importance of antimicrobials in pandemic response and strengthen relevant measures 👥
Why In News
During the World Health Assembly, the draft Pandemic Instrument, commonly known as the “pandemic treaty,” was presented to Member States in its most recent iteration. However, concerns arose as it became evident that all references to combating antimicrobial resistance within the Pandemic Instrument were in danger of being eliminated. Consequently, urgent efforts were initiated to safeguard the crucial inclusion of measures against antimicrobial resistance within the treaty.
MCQs about Pandemic Accord
-
What is the purpose of the pandemic accord?
A. To develop international trade agreements
B. To address climate change issues
C. To prevent and respond to pandemics and health emergencies
D. To establish rules for international travel
-
Why is addressing antimicrobial resistance (AMR) important in the pandemic accord?
A. To strengthen international borders
B. To control population growth
C. To improve transparency and early warning systems
D. To enforce strict quarantine measures
-
Who is responsible for determining the content of the pandemic accord?
A. World Health Organization (WHO)
B. United Nations (UN)
C. G20 leaders
D. Member States from 194 countries
-
What potential consequence could arise from the exclusion of AMR measures in the pandemic accord?
A. Improved collaboration among healthcare professionals
B. Enhanced laboratory capabilities worldwide
C. Hindered efforts to protect against future pandemics
D. Strengthened international travel restrictions
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


