The Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has been tasked with regulating the practices of market index providers, which are companies responsible for designing and calculating indexes. These indexes are used by passive investors who invest in funds linked to these indexes, which may include stocks from companies such as the Adani group.
What are Market Index Providers?
Market index providers set the rules that determine what securities are included in an index, how it will be managed, and how securities will be added or removed from the index over time. They play an important role in the financial markets by providing benchmarks against which the performance of funds can be measured.
Need for Regulation
SEBI has stressed the need for greater oversight of index providers, given their growing dominance due to the “proliferation” of index funds. The market watchdog has raised concerns about possible conflicts of interest that could arise in their governance, as these firms have the power to make decisions that can impact the volumes, liquidity, and price of stocks, as well as investors’ returns from index funds.
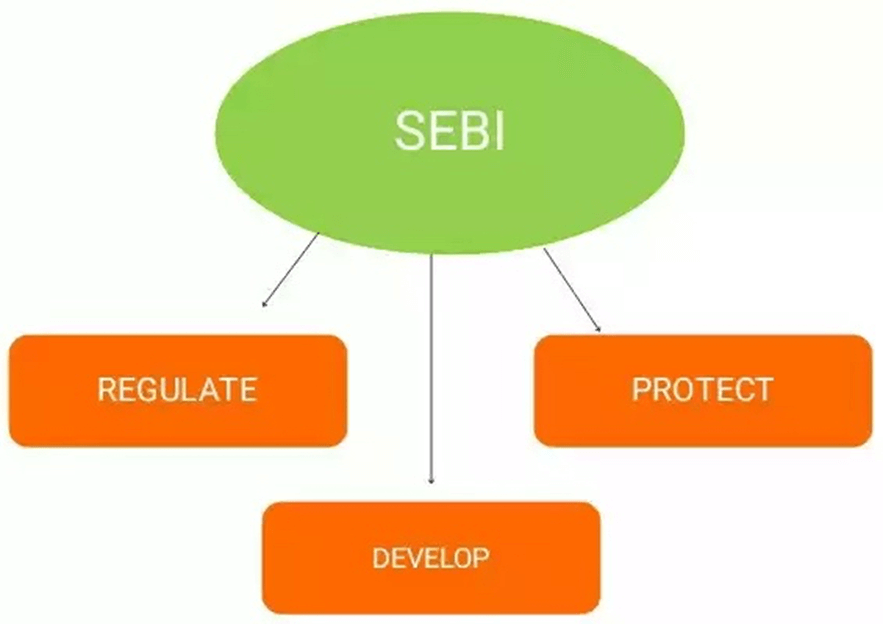
SEBI’s Role in Regulating Market Index Providers
SEBI is a statutory body established in 1992 to protect the interests of investors in securities and to promote the development of, and regulate the securities market. Before SEBI, the Controller of Capital Issues was the regulatory authority for the capital markets in India.
SEBI has the power to draft regulations, conduct inquiries, pass rulings, and impose penalties. Its aim is to promote the development and hassle-free functioning of the securities market, to regulate the business operations of the securities market, and to serve as a platform for portfolio managers, bankers, stockbrokers, investment advisers, merchant bankers, registrars, share transfer agents, and other people.
SEBI’s draft regulatory framework for index providers, which was proposed in December, aims to address concerns about possible conflicts of interest that could arise in their governance. The framework seeks to ensure that index providers are transparent in their decision-making processes and that they take into account the interests of all stakeholders.
Why In News
In response to worries about the security of passive investors’ savings held in funds linked to indexes that have included or kept several Adani group stocks, the Indian government has placed the responsibility for regulating market index providers on the Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI). As SEBI has been entrusted by Parliament with safeguarding investor interests, it is taking steps to regulate index providers to fulfill its mandate.
MCQs on SEBI’s Role in Protecting Investor Interests
-
What are index providers?
A. Companies that design and calculate indexes
B. Mutual fund companies
C. Companies that regulate the stock market
D. Companies that invest in the stock market
-
Why is SEBI moving to regulate index providers?
A. To protect investor interests
B. To increase the profits of mutual fund companies
C. To decrease the number of index funds available in the market
D. To support the growth of Adani group stocks
-
Which companies have been cited as examples of unregulated index providers by SEBI?
A. National Stock Exchange and Dow Jones
B. Adani and Reliance
C. Bombay Stock Exchange and NASDAQ
D. Goldman Sachs and JPMorgan
-
What are the functions of SEBI?
A. Draft regulations, conduct inquiries, pass rulings and impose penalties
B. Promote the interests of mutual fund companies
C. Regulate the prices of stocks
D. Promote the growth of specific industries in India
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


