India and Japan are collaborating on a High-Speed Rail Track system for the Mumbai Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail corridor (MAHSR), also known as the bullet train project. As part of the collaboration, Japan will train 1,000 Indian engineers in the construction and maintenance of the J Slab Track system used in the Japanese Shinkansen high-speed railways.
What is the J Slab Track System?
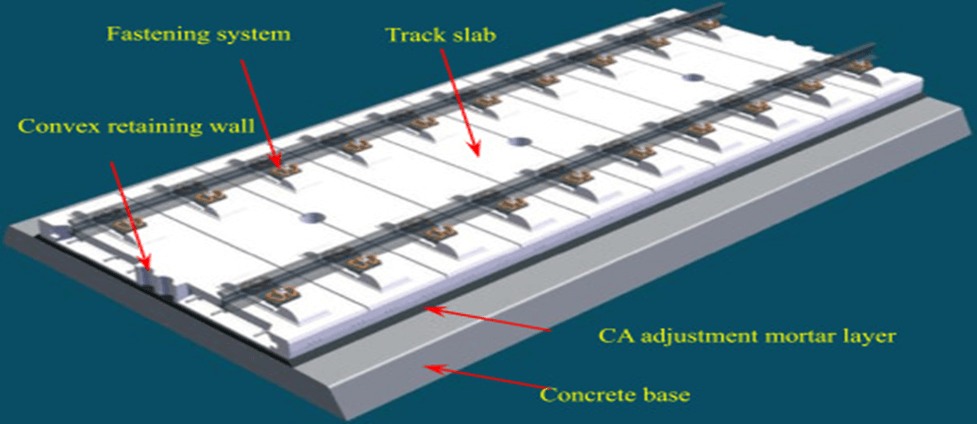
The J Slab Track system, also known as a ballastless track or slab track, is a type of railway track infrastructure. Instead of the traditional elastic combination of ties/sleepers and ballast, a rigid construction of concrete is used. The system was invented and developed in Japan and has evolved to become synonymous with high-speed railway tracks.
How did the J Slab Track System come into use?
The first high-speed railway in Japan, the Tokaido Shinkansen, began operation in 1964 between Tokyo and Shin-Osaka. A conventional ballasted track structure was used in this railway. However, with the increase in traffic density, the track geometry of conventional ballasted tracks used to frequently disturb. This, coupled with a reduction in time available for maintenance and labor shortage, led to the introduction of a low maintenance track. This need gave rise to the development of the J Slab Track system.
Significance of the J Slab Track System
The J Slab Track system offers better performance for high-speed railways compared to ballasted tracks due to its higher flexural stiffness. The forces in the Slab Track are distributed over a larger area, and deflections are considerably less compared to ballasted tracks. This results in lesser maintenance requirements for the Slab Track structure. Although the initial construction cost of Slab Track is higher than ballasted tracks, the difference is compensated within a few years of operation due to less maintenance and labor requirements.
The Slab Track structure is particularly advantageous in the case of viaducts and tunnels due to its lighter and sleek structure.
Important Points:
- Japan will train 1,000 Indian engineers on the J Slab Track system used in Japanese high-speed railways 🚄👨🔧
- The J Slab Track system is a type of ballastless track infrastructure that uses a rigid construction of concrete instead of traditional ties/sleepers and ballast 💼🚧
- The system was invented and developed in Japan and is now synonymous with high-speed railway tracks 🇯🇵🔬
- The J Slab Track system offers better performance for high-speed railways compared to ballasted tracks due to its higher flexural stiffness and lower maintenance requirements 💪💰
- The initial construction cost of Slab Track is higher compared to ballasted track, but the difference is compensated within a few years of operation due to less maintenance and labor requirements 💵👷♂️
- The Slab Track structure is particularly advantageous in the case of viaducts and tunnels due to its lighter and sleek structure 🏗️🚇
- The collaboration between Japan and India for the Mumbai Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail corridor will bring the latest technology and infrastructure to India and create job opportunities for engineers 👷♀️💻
- The training of 1,000 Indian engineers by Japanese experts will be an important step in technology transfer and help India build world-class infrastructure 🌎🤝
- The J Slab Track system is an important innovation in railway track infrastructure and has the potential to revolutionize high-speed railways globally 🌟🚀
Why In News
Japan and India are collaborating on the Mumbai-Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail Corridor, and Japan will be training 1,000 Indian engineers on the J Slab Track system used in Japanese high-speed railways. This training will not only facilitate the transfer of bullet train technology to India, but also create job opportunities for Indian engineers and bring the latest technology and infrastructure to the country.
MCQs about Significance of the J Slab Track System
-
What is the J Slab Track System?
A. A type of railway track infrastructure with traditional elastic combination of ties and ballast replaced by a rigid construction of concrete.
B. A type of railway track infrastructure with traditional wooden sleepers and gravel ballast.
C. A type of railway track infrastructure with no concrete or ballast.
D. A type of railway track infrastructure with flexible combination of ties and ballast.
-
Why is the Slab Track structure particularly advantageous in case of viaduct and tunnel?
A. Because it requires more maintenance and labor requirements.
B. Because it has a heavier and bulkier structure.
C. Because it has a lighter and sleek structure.
D. Because it has a higher maintenance cost.
-
What is the significance of using Slab Track for High Speed Railway?
A. It has a higher maintenance cost compared to ballasted track.
B. It has lower flexural stiffness compared to ballasted track.
C. It requires less maintenance requirements compared to ballasted track.
D. It has more deflections compared to ballasted track.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


