Daily Current Affairs : 27-October-2023
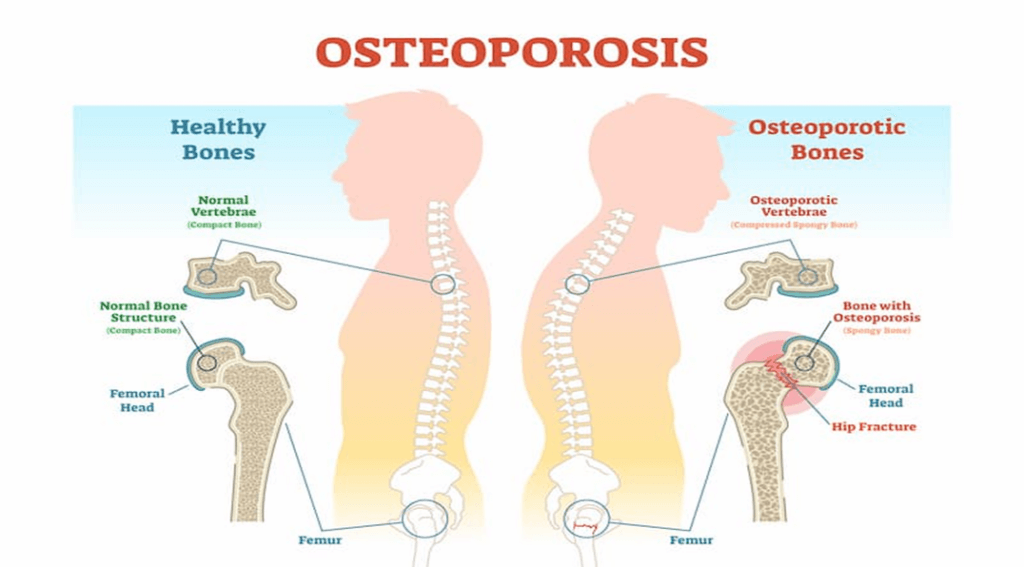
Osteoporosis, a debilitating bone disease characterized by decreased bone mass and density, poses a significant threat to the health of millions. While it often remains unnoticed until a bone is fractured, its prevalence in India demands urgent attention.
Understanding Osteoporosis:
- Osteoporosis weakens bones, increasing the risk of fractures, especially in postmenopausal women and older men.
- Fractures commonly occur in hip bones, spine vertebrae, and wrists, affecting mobility and overall well-being.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Sex and Age: Women, especially postmenopausal, are more susceptible due to hormonal changes. Aging accelerates bone loss.
- Body Size and Race: Slender individuals, especially white and Asian women, face higher risks.
- Genetics and Hormonal Imbalances: Family history and low hormone levels contribute.
- Diet and Medications: Low calcium, vitamin D intake, and certain medications amplify risks.
- Lifestyle Factors: Lack of physical activity and prolonged inactivity increase bone loss rates.
The Alarming Indian Scenario:
- High Mortality Rates: India ranks highest globally in osteoporosis-related deaths/disabilities, highlighting its severity.
- Micronutrient Deficiencies: Indian women’s poor diets worsen the situation, escalating susceptibility.
- Limited Access to Diagnostic Tools: Scarce availability of DEXA machines (gold standard for osteoporosis diagnosis) hampers early detection.
- Need for Suspicion in Patient Assessment: Due to deficiencies and sedentary lifestyles, healthcare providers must be vigilant in suspecting osteoporosis.
Important Points:
Key Points on Osteoporosis in India:
- Osteoporosis is a bone disease characterized by decreased bone mass and density, increasing the risk of fractures, especially in postmenopausal women and older men.
- Fractures typically occur in hip bones, spine vertebrae, and wrists, leading to mobility issues and reduced well-being.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Women, particularly postmenopausal, are more vulnerable to osteoporosis due to hormonal changes, and aging accelerates bone loss.
- Slender individuals, especially white and Asian women, face higher risks.
- Family history and low hormone levels can contribute to osteoporosis.
- Low calcium and vitamin D intake, along with certain medications, amplify risks.
- Lack of physical activity and prolonged inactivity increase the rate of bone loss.
The Alarming Indian Scenario:
- India ranks highest globally in osteoporosis-related deaths/disabilities.
- Micronutrient deficiencies in Indian women worsen the situation and increase susceptibility.
- Limited access to DEXA machines, the gold standard for osteoporosis diagnosis, hampers early detection.
- Healthcare providers need to be vigilant in suspecting osteoporosis due to deficiencies and sedentary lifestyles.
Why In News
Although large-scale studies on osteoporosis in India are lacking, projected data reveals that approximately 46 million women in the country are currently affected by post-menopausal osteoporosis, which represents just one form of this condition. It is crucial for further research efforts to encompass various types of osteoporosis, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of this widespread health concern in the Indian population.
MCQs about Osteoporosis Challenges in India
-
What is the primary cause of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and older men?
A. Lack of physical activity
B. Genetic factors
C. Hormonal changes and aging
D. Low calcium intake
-
Which of the following bones is most susceptible to fractures in individuals with osteoporosis?
A. Arm bones
B. Hip bones
C. Skull bones
D. Rib bones
-
What factor significantly increases the risk of osteoporosis in women?
A. High body mass index
B. Regular exercise routine
C. Postmenopausal hormonal changes
D. Adequate calcium intake
-
Why is osteoporosis often referred to as a “silent disease”?
A. It affects older adults
B. It doesn’t cause pain or noticeable symptoms until a fracture occurs
C. It primarily affects women
D. It is a hereditary condition
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


