Daily Current Affairs : 8-Novembe-2023
As the global community grapples with the urgent need to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change, scientists are increasingly turning to unconventional solutions. One such proposal gaining attention is Solar Radiation Management (SRM), a technique aimed at reflecting the sun’s rays back into space to limit warming and avert climate catastrophe.
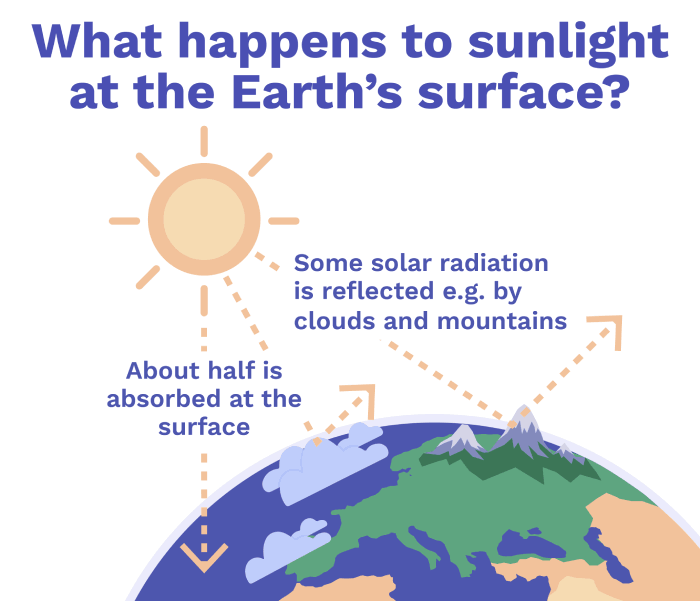
Solar Radiation Management (SRM):
Solar Radiation Management involves various strategies, with the most prominent being the injection of sulphur dioxide (SO2) into the higher atmosphere. The concept dates back to 1992 when the U.S. National Academy of Sciences first proposed the idea. Volcanic eruptions, which naturally release large amounts of SO2, have been observed to have a cooling effect on the planet, providing a basis for exploring this method.
Challenges of SRM:
Despite its potential, SRM comes with significant challenges and risks that must be carefully considered:
- Side Effects:
- While cooling the planet, the injection of sulphate aerosols may have destructive side effects.
- Potential impacts on weather patterns, agriculture, and the availability of food and water.
- Disruption of Monsoons:
- SRM interventions could disrupt monsoons, leading to droughts in critical regions such as Africa and Asia.
- Effect on the Ozone Layer:
- Concerns about the potential slowing of the ozone layer’s recovery and an increased risk of acid rain.
- Weaponisation of Technology:
- The risk of the technology being weaponised, raising geopolitical and security threats as highlighted by the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP).
- Delay in Climate Targets:
- The possibility that SRM could be used as an excuse to postpone the necessary shift towards achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions.
- Short-Term Impact:
- SRM’s effectiveness is limited to the short term, necessitating continued deployment for centuries to maintain desired temperature levels.
Important Points:
- Solar Radiation Management (SRM):
- Involves reflecting the sun’s rays back into space to mitigate global warming.
- Primary method involves injecting sulphur dioxide (SO2) into the higher atmosphere.
- Concept proposed by the U.S. National Academy of Sciences in 1992.
- Challenges of SRM:
- Side Effects:
- Cooling the planet may have destructive consequences.
- Potential impacts on weather patterns, agriculture, and food and water availability.
- Disruption of Monsoons:
- SRM interventions could lead to disrupted monsoons and droughts in Africa and Asia.
- Effect on the Ozone Layer:
- Concerns about slowing the recovery of the ozone layer and an increased risk of acid rain.
- Weaponisation of Technology:
- Risk of SRM technology being weaponised by “rogue states” or private companies.
- Poses new geopolitical and security threats (UNEP warning).
- Delay in Climate Targets:
- SRM may serve as an excuse to postpone the necessary shift towards net-zero greenhouse gas emissions.
- Short-Term Impact:
- SRM’s effectiveness is limited to the short term, raising the possibility of continued deployment for centuries.
- Side Effects:
Why In News
As the world struggles to renounce its burning of fossil fuels, scientists are studying whether atmospheric geoengineering could help limit warming and avert climate catastrophe, exploring innovative strategies to address the urgent need for sustainable solutions.
MCQs about Solar Radiation Management (SRM)
-
What is the primary method of Solar Radiation Management (SRM)?
A. Carbon capture
B. Injection of sulphur dioxide (SO2)
C. Wind energy harnessing
D. Ocean acidification
-
What potential impact does SRM have on weather patterns, agriculture, and basic needs?
A. Enhanced productivity
B. Destructive consequences
C. No impact
D. Positive effects on water availability
-
According to the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP), what is a potential risk associated with SRM?
A. Accelerated ozone layer recovery
B. Decreased geopolitical threats
C. Weaponisation by “rogue states” or private companies
D. Positive impact on climate targets
-
What is a limitation of the short-term impact of SRM interventions?
A. Immediate and permanent cooling
B. Potential for centuries-long deployment
C. Continuous greenhouse gas reduction
D. Effective solution for ocean acidification
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


