Daily Current Affairs : 16-August-2023
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) recently unveiled images from its Aditya-L1 mission, marking a significant step in the realm of solar exploration. This mission holds the promise of shedding light on the enigmatic Sun and unraveling its secrets.
Aditya-L1 Mission Overview
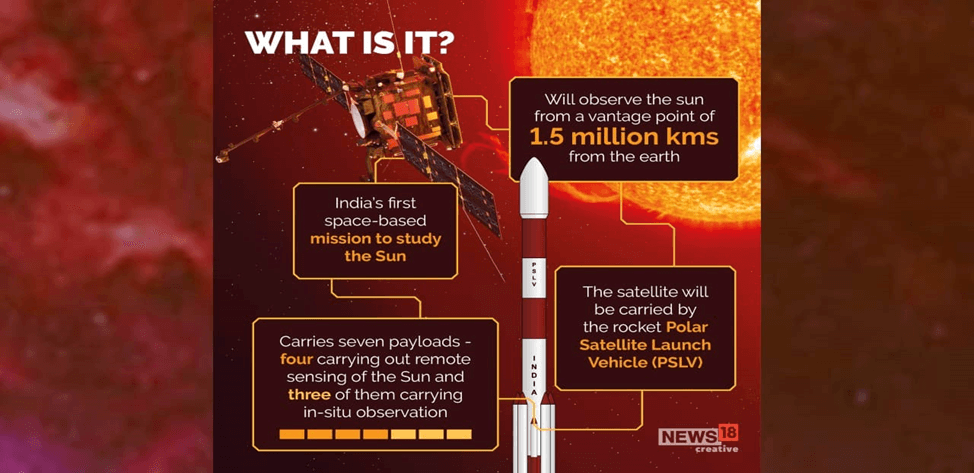
The Aditya-L1 mission is designed with a distinct purpose: to closely observe the Sun and gather crucial insights into its atmosphere and magnetic field. This remarkable endeavor is outfitted with seven specialized instruments, each playing a vital role in comprehending various aspects of the Sun’s behavior. These payloads are geared towards studying the Sun’s corona, solar emissions, solar winds, flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs). A standout feature of the mission is its continuous, round-the-clock imaging of the Sun.
Significance of Solar Study
1. Solar Weather’s Global Influence
The Sun’s influence extends far beyond its immediate surroundings. Solar weather significantly impacts the entire solar system, including our home planet. Understanding the dynamics of the Sun’s behavior is paramount, as it has a cascading effect on various phenomena.
2. Impact on Spacecraft and Satellites
Variations in solar weather can substantially alter the trajectories of satellites, leading to shifts in their orbits or reduced operational lifespans. Furthermore, these fluctuations can interfere with onboard electronics, potentially causing malfunctions and even damage.
3. Earthly Disruptions and Space Weather Prediction
The effects of solar activity are not confined to outer space. On Earth, solar events can trigger power blackouts and disrupt communication systems. Accurate prediction of such events is contingent on a comprehensive understanding of space weather, enabling us to mitigate potential disruptions.
4. Aditya-L1’s Strategic Location
Aditya-L1’s positioning holds immense value in solar observation. As solar storms emanate from the Sun and travel towards Earth, they pass through a critical point known as Lagrangian Point 1 (L1). Placing a satellite in the halo orbit around L1 offers a unique advantage: uninterrupted views of the Sun without any hindrance from occultations or eclipses.
5. Lagrange Points: The Orbital Dance
Lagrangian Points, a concept devised by the Italian-French mathematician Joseph-Louis Lagrange, are locations in space where gravitational forces of a two-body system produce regions of enhanced attraction and repulsion. These points provide an energy-efficient means for spacecraft to maintain their positions.
6. SOHO: L1’s Celestial Tenant
The L1 point is home to the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory Satellite (SOHO), a collaborative effort between NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA). This satellite plays a pivotal role in solar observation, making the L1 point a hub for solar research.
Important Points:
Aditya-L1 Mission Overview:
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) released images from the Aditya-L1 mission.
- Mission aims to observe the Sun up close and gather information about its atmosphere and magnetic field.
- Equipped with seven specialized instruments to study corona, solar emissions, solar winds, flares, and CMEs.
- Prominent feature: Continuous round-the-clock imaging of the Sun.
Significance of Solar Study:
- Solar weather impacts the entire solar system, including Earth.
- Solar variations affect satellite orbits, operational lifespans, and onboard electronics.
- Solar events cause disruptions on Earth such as power blackouts and communication glitches.
- Understanding space weather is crucial for accurate prediction and mitigation of disruptions.
Aditya-L1’s Strategic Location:
- Aditya-L1 observes the Sun’s events as they travel toward Earth.
- Positioned at Lagrangian Point 1 (L1), where solar storms pass through.
- Satellite in halo orbit around L1 provides uninterrupted views of the Sun, no hindrance from occultations/eclipses.
Lagrangian Points and L1:
- Lagrangian Points are locations in space with enhanced gravitational forces.
- Joseph-Louis Lagrange introduced the concept.
- Spacecraft use these points for energy-efficient positioning.
- L1 is home to Solar and Heliospheric Observatory Satellite (SOHO), a collaboration between NASA and ESA.
Why In News
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has unveiled captivating images showcasing the remarkable progress of the Aditya-L1 mission. These images provide a captivating glimpse into ISRO’s innovative strides towards understanding and exploring the dynamics of our Sun’s outermost layer.
MCQs about The Aditya-L1 Mission’s Exploration of the Sun
-
What is the primary objective of the Aditya-L1 mission?
A. To study Earth’s atmosphere
B. To explore Mars’ magnetic field
C. To observe the Sun and gather information about its atmosphere and magnetic field
D. To search for extraterrestrial life
-
Why is the positioning of Aditya-L1 at Lagrangian Point 1 (L1) significant?
A. It provides a view of Earth’s surface.
B. It allows for uninterrupted views of the Sun without any hindrance.
C. It’s a point of interest for observing distant galaxies.
D. It helps in studying the Moon’s craters.
-
What is the purpose of the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory Satellite (SOHO)?
A. To monitor Earth’s weather patterns
B. To observe distant stars and galaxies
C. To study the Moon’s surface
D. To conduct solar observation and research at Lagrangian Point 1 (L1)
-
Why is understanding space weather important for Earth?
A. It helps in predicting volcanic eruptions.
B. It aids in predicting earthquakes.
C. It enables accurate prediction and mitigation of disruptions caused by solar activity.
D. It helps in forecasting hurricanes.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


