Hindu Editorial Analysis : 25-May-2023
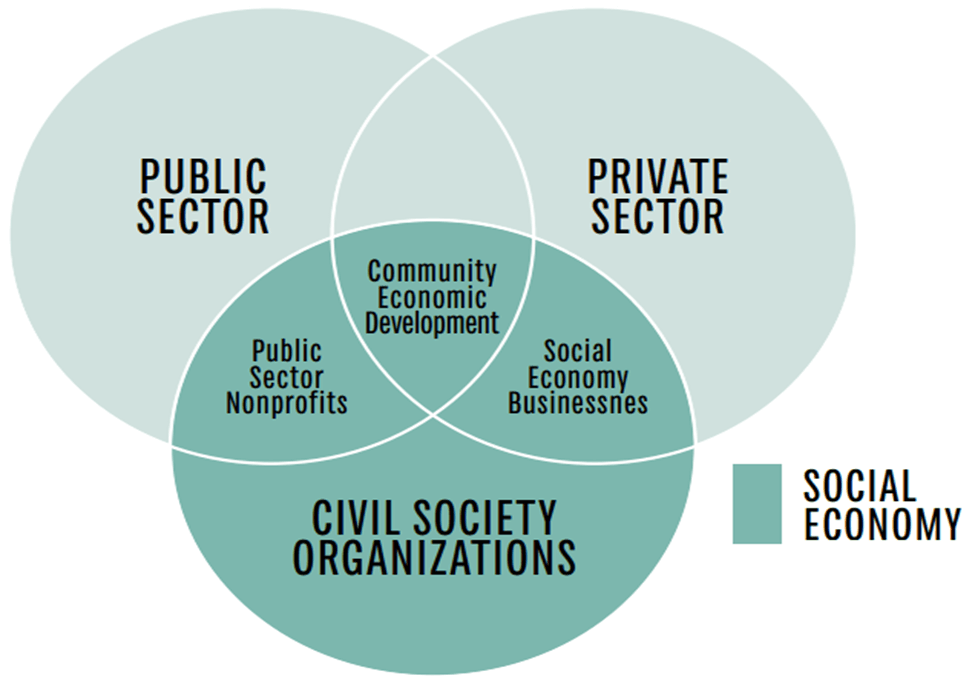
Civil society organizations (CSOs) or non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play a vital role in Indian society, rooted in the concepts of daana (giving) and seva (service). These organizations operate voluntarily and focus on various areas such as cultural promotion, education, health, and disaster relief. In India, there are approximately 1.5 million NGOs, which are nonprofit groups organized at the local, national, or international level. Let’s delve deeper into the significance of civil society and the challenges it faces.
The Values and Role of Civil Society:
- Political Participation and State Accountability: Civil society embodies the values of political participation and state accountability, providing a basis for engagement with formal political institutions. It promotes pluralism and opposes totalitarianism, ensuring that the authority of an authoritarian state is challenged.
- Enforceable Rights and Democracy: Within civil society, individuals enjoy rights of free expression, association, opinion formulation, and dissent. These rights are essential preconditions for the existence of a functioning democracy.
Criticisms of Civil Society:
- Credibility Concerns: While civil society organizations worldwide are gaining influence, there are concerns about their credibility. Critics argue that NGOs are self-appointed rather than elected, leading to a lack of representation of the popular will. They also claim that NGOs receiving foreign funding may be more accountable to external constituencies, advancing foreign agendas rather than local ones. Additionally, some view civil society groups as elite actors out of touch with ordinary citizens, working to perpetuate their privileged lifestyles.
Challenges Faced by Civil Society:
- Shrinking Voice: Civil society’s ability to shape policy and public discourse has been significantly curtailed due to perceived threats from war and foreign interference.
- Financial Crunch: CSOs face financial and structural constraints that make it difficult to attract conscientious young individuals who need financial sustenance. This has resulted in resource starvation and joblessness for many working in grassroots organizations.
- Limited Tangible Contribution: Without sustained support and recognition, CSOs cannot effectively influence public discourse or have a tangible impact on the nation. Governments avoiding engagement with civil society diminishes their ability to shape policies, leading to reduced organizational morale.
Suggestions for Strengthening Civil Society:
- Government Support: The government should recognize that a strong civil society is crucial for the relevance and monitoring of laws such as the Right to Information Act and the National Food Security Act. Measures to disturb civil society could dilute the effectiveness of these laws and hinder the implementation of government schemes.
- Alternate Funding Sources for NGOs: NGOs should explore alternative funding options such as local resource mobilization (LRM) and corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. Encouraging collective giving, where groups pool donations to address social issues, can also be beneficial.
- Technological Advancements: Utilizing data and digital technology can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of NGOs. Embracing technological tools and solutions can help organizations better serve their communities.
- Engagement of Young Activists: There is potential for young activists to join political parties and contribute to institutionalized moral forces within these parties. This would create a balanced approach that considers ethical and human rights aspects alongside electoral considerations.
Why In News
It is imperative to continuously re-emphasize the indispensable and life-sustaining role that civil society plays in our communities. By recognizing its critical nature, we can ensure the support and nurturing of civil society, empowering it to thrive and make a profound impact on our society’s well-being.
MCQs about The Crucial Role of Civil Society Organizations in India
-
Which values do civil society organizations in India embody?
A. Economic growth and profit-making
B. Political participation and state accountability
C. Technological advancements and digitalization
D. Cultural promotion and religious activities
-
What is one of the criticisms often raised against civil society organizations?
A. Lack of representation of the popular will
B. Overreliance on domestic funding
C. Excessive engagement with foreign agendas
D. Strong connection with grassroots organizations
-
What is one of the challenges faced by civil society organizations in India?
A. Overwhelming financial resources
B. Unrestricted access to government schemes
C. Limited impact on public discourse and policy shaping
D. Excessive engagement with local communities
-
Which suggestion is provided for strengthening civil society organizations?
A. Decreasing reliance on corporate funding
B. Avoiding technological advancements
C. Discouraging young activists’ involvement
D. Exploring alternative funding options and embracing technology
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


