Daily Current Affairs : 2-January-2025
India’s data centre sector is experiencing rapid growth, and its capacity is projected to double by FY27. This growth is largely driven by digitalization, the rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI), the rollout of 5G networks, and data localization laws. However, several challenges remain, including infrastructure gaps, sustainability concerns, and intense competition from global players.
What Are Data Centres?
Data centres are specialized facilities designed to store, manage, and process vast amounts of data. These centres play a crucial role in supporting IT infrastructure, including servers, storage devices, and networking equipment. They also house cooling systems, power supply networks, and security measures, ensuring data is processed efficiently and securely.
Key Components of a Data Centre:
- Servers and Storage Systems: These handle tasks like hosting websites, running applications, and managing cloud storage.
- Networking Equipment: Includes routers, switches, and firewalls for communication between servers and external networks.
- Power Supply Systems: Uninterrupted power supplies and backup generators ensure continuous operation.
- Cooling Systems: Prevent overheating by using air conditioning or liquid cooling.
- Security Infrastructure: Includes both physical and cybersecurity measures to protect data from breaches.
Key Drivers of Data Centre Growth in India
Several factors contribute to the expansion of India’s data centre industry:
- Digitalization: With more people adopting digital technologies, there is an increasing demand for data storage and processing capabilities.
- AI and 5G: The adoption of AI and the rollout of 5G networks are expected to significantly increase data consumption.
- RBI Mandate on Data Storage: The Reserve Bank of India’s data localization law mandates that financial data be stored within the country, driving the need for local data centres.
- Data Localization Laws: Acts like the Public Records Act, 1993, and the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, further push for local storage and processing of sensitive data.
Economic Significance of Data Centres
Data centres are essential for India’s digital economy, offering services that power cloud computing, AI, and data analytics. They support sectors such as e-commerce, banking, healthcare, and entertainment.
- Economic Growth: The expansion of data centres can boost employment, infrastructure development, and digital economy growth.
- Global Cloud Services: Major cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud rely on data centres to provide scalable services.
- Reduced Latency: Edge computing, which processes data closer to users, is becoming more popular, especially with the advent of 5G networks.
Key Challenges Facing India’s Data Centre Sector
Despite the promising growth, there are several challenges that could hinder the development of India’s data centre industry:
- Infrastructure Constraints: Limited infrastructure, unreliable power supply, and high capital investment needs are significant barriers, especially in non-metro areas.
- Environmental Sustainability: Data centres are energy-intensive and need to adopt greener technologies to reduce their carbon footprint.
- Skill Shortages: The sector faces a shortage of skilled professionals, hindering growth and innovation.
- Regional Disparities: While major cities like Mumbai are well-equipped, smaller towns and cities lack the necessary infrastructure, leading to uneven distribution of data centres.
- Competition: Countries like China, with more advanced infrastructure, present strong competition in the global market.
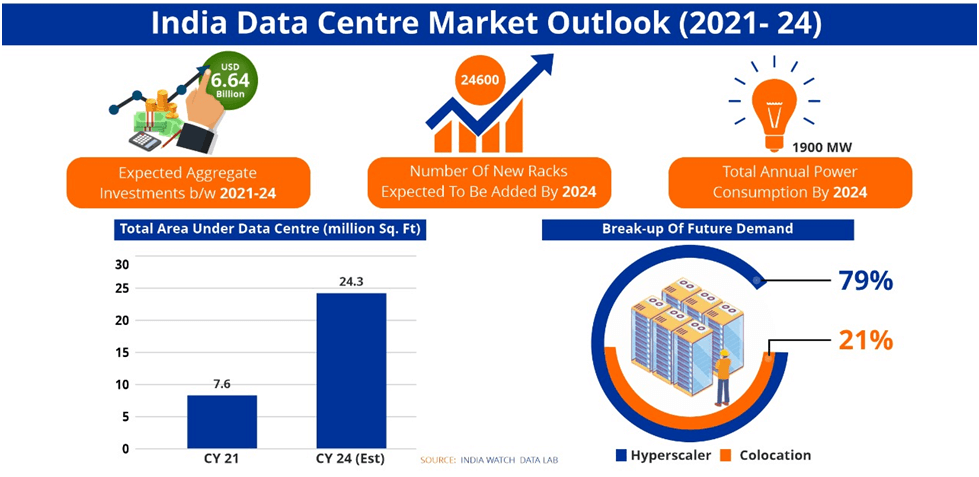
Important Points:
- India’s Data Centre Growth:
- Projected to double its capacity by FY27.
- Driven by digitalization, AI adoption, 5G rollout, and data localization laws.
- What Are Data Centres?
- Specialized facilities for storing, managing, and processing large volumes of data.
- Key components: servers, storage systems, networking equipment, power supply, cooling systems, and security infrastructure.
- Key Drivers of Growth:
- Digitalization: Increased adoption of AI, cloud computing, and data storage.
- AI & 5G: Surge in data consumption due to AI projects and 5G networks.
- RBI Mandate: Financial data must be stored within India for security.
- Data Localization Laws: Legal requirements for local data storage, including the Public Records Act and Digital Personal Data Protection Act.
- Economic Significance:
- Essential for cloud services, data analytics, AI, and machine learning.
- Supports sectors like e-commerce, banking, healthcare, and entertainment.
- Major cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud depend on data centres.
- Expected to contribute to job creation, infrastructure development, and economic growth.
- Challenges to Overcome:
- Infrastructure Constraints: Lack of reliable power, limited connectivity, and high capital costs.
- Environmental Sustainability: Need for greener energy solutions to reduce carbon emissions.
- Skill Shortages: Lack of qualified professionals in data centre management.
- Regional Disparities: Uneven distribution of data centres, with metros dominating.
- Competition: Global players like China offer advanced data centre infrastructure.
- Future Outlook:
- India’s data centre capacity growth presents significant investment opportunities.
- The sector could generate over Rs 50,000 crore in economic activity by FY27.
Why In News
India’s data centre sector is witnessing significant growth, projected to double its capacity by FY27, driven by digitalization, the adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI), the rollout of 5G, and data localization laws. This expansion is expected to position India as a key global hub for data processing and storage, attracting both domestic and international investments.
MCQs about The Growth and Challenges of India’s Data Centre Sector
-
What is the projected growth of India’s data centre capacity by FY27?
A. It will remain the same
B. It will double
C. It will increase by 10%
D. It will decrease by 5%
-
Which of the following is NOT a key component of a data centre?
A. Power supply systems
B. Networking equipment
C. Solar panel installation
D. Cooling systems
-
What is the main purpose of India’s data localization laws?
A. To increase global data sharing
B. To reduce data storage costs
C. To ensure sensitive data is stored within India
D. To promote data processing in other countries
-
Which challenge is hindering the growth of India’s data centre sector?
A. Excessive demand for data centres
B. Skilled labor shortages
C. Surplus infrastructure investments
D. High energy efficiency
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


