The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is a scientific research facility located at the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN). It is the world’s largest science experiment, and its primary objective is to conduct experiments with highly energized subatomic particles, specifically hadrons.
What is a hadron?
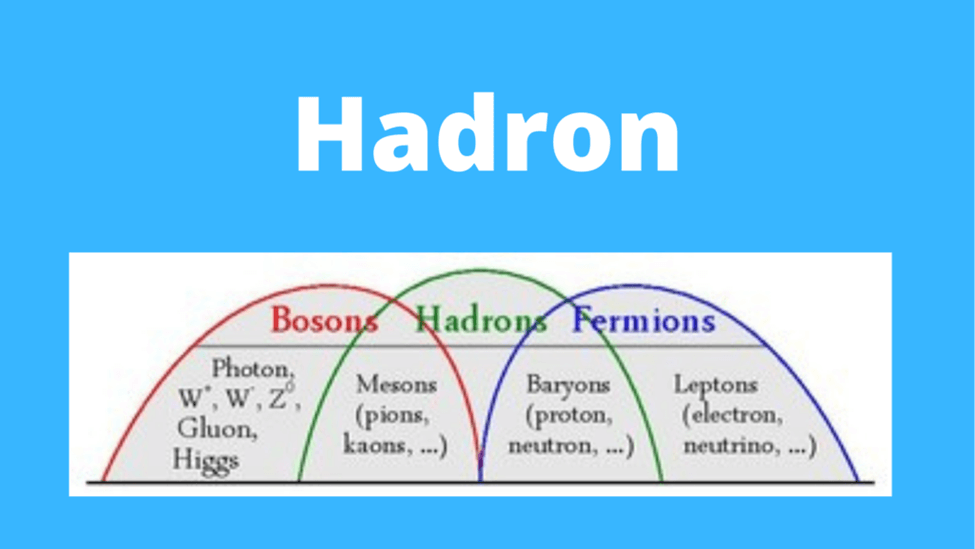
A hadron is a subatomic particle made up of smaller particles such as quarks and gluons. Protons and neutrons are examples of hadrons.
How does the LHC work?
The LHC is a collider that accelerates two beams of particles in opposite directions and smashes them head-on. It typically uses protons, which are energized by accelerating them through a 27-kilometer-long circular pipe. This pipe encircles two D-shaped magnetic fields, created by almost 9,600 magnets. By switching the direction of the magnetic field more and more rapidly, protons can be accelerated through the beam pipe. In the process, they accrue a tremendous amount of energy according to the special theory of relativity.
What happens during a collision?
When two antiparallel beams of energized particles collide head-on, the energy at the point of collision is equal to the sum of the energy carried by the two beams. There is a lot of energy available, and parts of it coalesce into different subatomic particles under the guidance of the fundamental forces of nature.
What are the findings of the LHC?
The LHC consists of nine detectors located over different points on the beam pipe, which study particle interactions in different ways. Scientists have used the LHC to energize and collide lead ions with each other and protons with lead ions. Using the data from all these collisions, they have:
- Tested the predictions of the Standard Model of particle physics, the reigning theory of subatomic particles.
- Observed exotic particles like pentaquarks and tetraquarks and checked if their properties are in line with theoretical expectations.
- Pieced together information about extreme natural conditions, like those that existed right after the Big Bang.
Why In News
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is a cutting-edge scientific facility at the forefront of particle physics research. It conducts groundbreaking experiments with highly energized subatomic particles, helping scientists unlock the secrets of the universe.
MCQs about The Large Hadron Collider
-
Which organization built the Large Hadron Collider (LHC)?
A. The United States Department of Energy
B. The Russian Academy of Sciences
C. The European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN)
D. The International Atomic Energy Agency
-
What is a hadron?
A. A subatomic particle made up of quarks and gluons
B. A type of subatomic particle that has no charge
C. A fundamental particle that makes up all matter
D. A type of energy produced by particle collisions
-
What is the purpose of the detectors located over different points on the beam pipe of the LHC?
A. To produce hadrons from subatomic particles
B. To slow down the protons as they travel through the beam pipe
C. To study particle interactions in different ways
D. To measure the speed of the protons in the beam pipe
-
What have scientists been able to do using the Large Hadron Collider?
A. They have been able to travel through time.
B. They have been able to create new types of matter.
C. They have been able to test the predictions of the Standard Model of particle physics.
D. They have been able to generate unlimited amounts of energy.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


