Recently, the Prime Minister praised the use of 3D printing technology in the construction of a post office. 3D printing is a fast-emerging technology that has many applications in various sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, automotive, aviation, and construction. This essay will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using 3D printing technology in construction.
What is 3D Printing Technology?
Three-dimensional (3D) printing is an additive manufacturing process that creates a physical object from a digital design by printing thin layers of material and fusing them together. This technology is widely used for the mass customization and production of open-source designs. It can print an object layer-by-layer directly from a computer-aided design (CAD) model.
Advantages of Using 3D Printing Technology in Construction
Ease of Access: 3D printers are becoming more accessible with local service providers offering outsourcing services for manufacturing work. This makes it easier for businesses and individuals to access the technology.
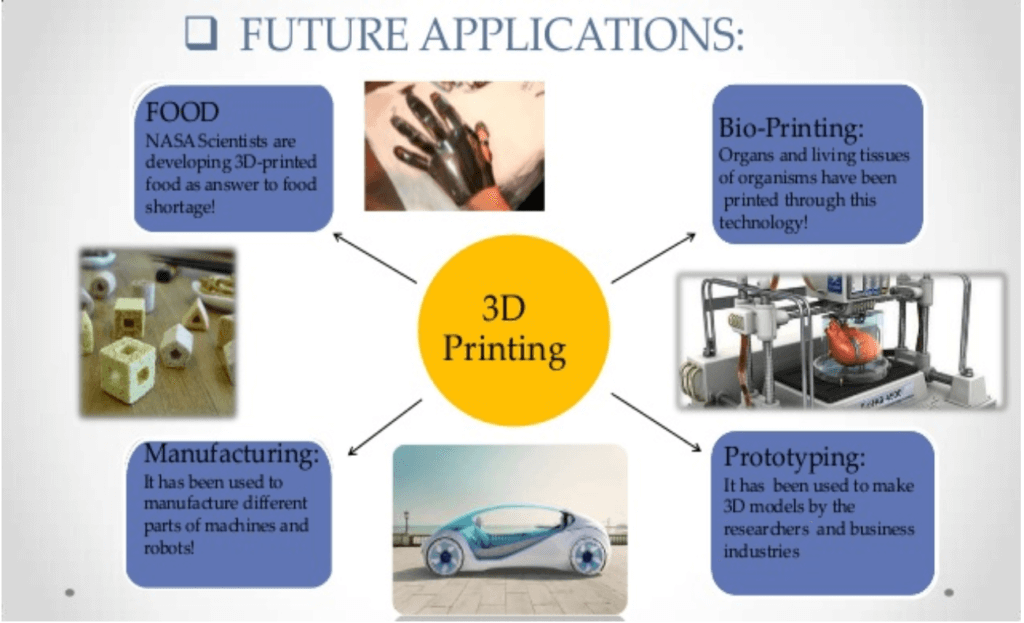
Advanced Healthcare: 3D printing is being used in the medical sector to help save lives by printing organs for the human body such as livers, kidneys, and hearts. Further advances and uses are being developed in the healthcare sector providing some of the biggest advances in using the technology.
Environmentally Friendly: This technology reduces material wastage and is inherently environmentally friendly.
Cost-Effective: 3D printing allows for customization of desired products in a short time, reducing costs associated with using different machines for manufacture.
Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing can manufacture parts within hours, speeding up the prototyping process.
Fast Design and Production: The technology allows for the creation of complex objects and shapes that might be impossible to create through any conventional method.
Strong and Lightweight Parts: 3D printing can create strong and lightweight parts that can be used in various applications.
Disadvantages of Using 3D Printing Technology in Construction
Design Inaccuracies: One potential problem with 3D printing is the type of machine or process used, with some printers having lower tolerances. This can lead to final parts that differ from the original design.
Copyright Issues: As 3D printing becomes more popular, there is a greater possibility for people to create fake and counterfeit products. This has evident issues around copyright as well as for quality control.
Reduction in Manufacturing Jobs: Another disadvantage of 3D technology is the potential reduction in human labor, since most of the production is automated and done by printers. This could put manufacturing jobs at risk by cutting out the need for production abroad.
Restricted Build Size: 3D printers currently have small print chambers, which restrict the size of parts that can be printed. Anything bigger will need to be printed in separate parts and joined together after production. This can increase costs and time for larger parts due to the printer needing to print more parts before manual labor is used to join the parts together.
Limited Materials: While 3D printing can create items in a selection of plastics and metals, the available selection of raw materials is not exhaustive.
Why In News
During a recent event, the Prime Minister praised the innovative use of 3D printing technology in the construction of a post office building, citing it as an excellent example of the potential of this emerging technology in the field of architecture and construction. The use of 3D printing technology allowed for greater precision and customization in the building process, resulting in a more efficient and cost-effective project.
MCQs about 3D Printing Technology
-
What is three-dimensional (3D) printing?
A. An additive manufacturing process in which a physical object is created from a digital design by printing thin layers of material and then fusing them together.
B. A subtractive manufacturing process in which a physical object is created from a digital design by removing material layer by layer.
C. A form of manual manufacturing in which a physical object is created by hand from a digital design.
D. None of the above.
-
Which industries use 3D printing technology?
A. Agriculture, healthcare, automotive, locomotive, and aviation industries.
B. Only the healthcare industry.
C. Only the aviation industry.
D. None of the above.
-
What is one advantage of using 3D printing technology?
A. Rapid prototyping.
B. Copyright issues.
C. Design inaccuracies.
D. Reduction in manufacturing jobs.
-
What is one disadvantage of using 3D printing technology?
A. Restricted build size.
B. Ease of access.
C. Advanced healthcare.
D. Environmentally friendly.
![]()


