The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) recently released two reports titled “Global Annual to Decadal Climate Update 2023-2027” and “State of Global Climate 2022.” These reports provide valuable insights into the current and future state of the global climate. This essay explores the major findings, the importance of the 1.5-degree Celsius target, issues related to climate action, global impacts, and India’s vulnerability to climate change.
Major Findings:
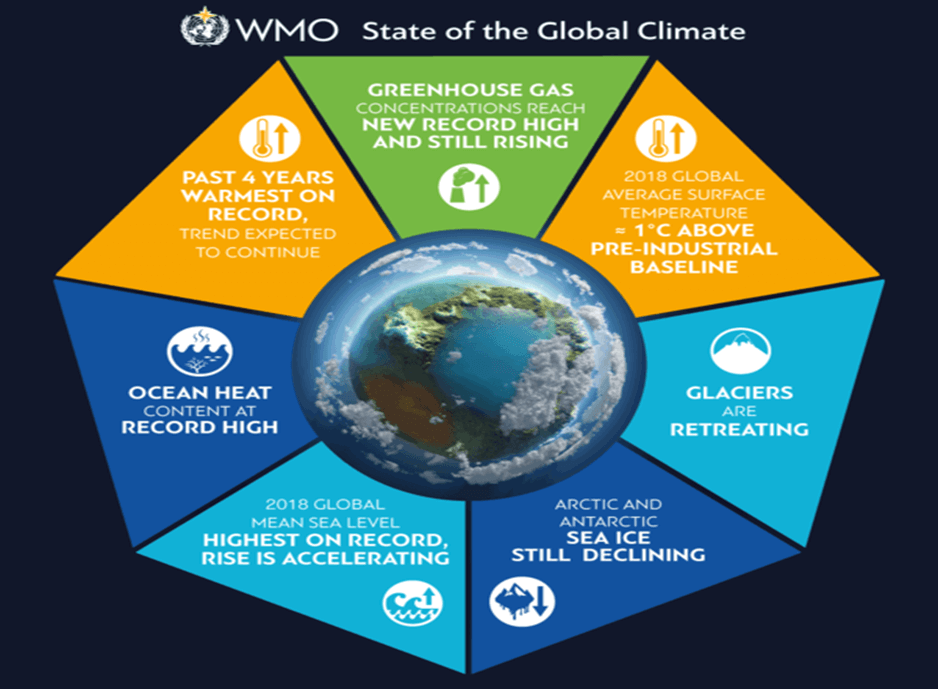
- Precipitation Anomalies and Marine Heat Waves: The reports indicate an increase in precipitation anomalies and marine heat waves compared to marine cold spells.
- El Niño and Rising Temperatures: The El Niño phenomenon is predicted to strengthen, leading to a 98% likelihood of experiencing higher temperatures than those recorded in 2016 at least once between 2023 and 2027.
- Global Surface Temperature: The annual mean global surface temperature between 2023 and 2027 is projected to be 1.1-1.8 degrees Celsius higher than the baseline temperature of 1850-1900 or pre-industrial levels. By 2027, the average temperature is expected to surpass 1.5 degrees Celsius, a critical threshold.
- Cryosphere and Sea Level Rise: The cryosphere, including glaciers in High-mountain Asia, Western North America, and South America, is shrinking. The melting of the Greenlandic ice sheet due to warming Arctic Ocean temperatures contributes to rising sea levels.
The 1.5-degree Celsius Target: The 1.5-degree Celsius target refers to the goal outlined in the Paris Agreement, a legally binding international treaty on climate change. The agreement, adopted in 2015, aims to limit global warming and pursue efforts to keep the temperature increase well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
Importance of the 1.5-degree Celsius Target:
- Mitigating Severe Climate Change Impacts: Crossing the 1.5-degree Celsius threshold poses significant risks, including more frequent and severe droughts, heatwaves, and rainfall, as highlighted by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
Issues in Climate Action:
- Responsibility of Developed Countries: Historically, developed countries have contributed a substantial portion of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. However, the Climate Performance Index reveals that some developed nations, such as Australia, the U.S., Japan, Russia, and Canada, have made limited progress in meeting their climate pledges.
- Low Climate Performance: Countries like China, Iran, and Saudi Arabia rank low in climate performance, emphasizing the need for greater efforts to reduce emissions and combat climate change.
- Unsustainable Recovery Measures: The socio-economic crisis caused by the pandemic led to recovery measures that often neglected sustainable development considerations.
Global Impacts:
- Food Insecurity and Displacement: Climate change exacerbates food insecurity, displacement, and deaths. Countries such as Ethiopia, Nigeria, South Sudan, Somalia, Yemen, and Afghanistan face acute food shortages, resulting in malnutrition and hunger, necessitating urgent humanitarian assistance.
- Crop Yield Decline and Ecosystem Disruption: Climate change negatively affects crop yields and increases the risks posed by agricultural pests and diseases. Aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems experience phenological shifts, mismatches, and declines in migratory species populations. Coral reefs, already prone to bleaching, face increased risks due to warming above 1.5 degrees Celsius.
Important Points:
- 🌍 Global Findings:
- 🌡️ Increase in global surface temperature by 1.1-1.8°C from 2023 to 2027.
- ❄️ Shrinking cryosphere and mass loss of glaciers in key regions.
- 🌊 Melting Greenlandic ice sheet contributing to rising sea levels.
- 🎯 1.5-Degree Celsius Target:
- 🌐 Paris Agreement’s goal to limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
- ✅ Importance of preventing severe climate change impacts.
- 🌍 Global Issues:
- 📉 Limited progress by developed countries in meeting climate pledges.
- 🌍 Low climate performance of countries like China, Iran, and Saudi Arabia.
- 🔄 Unsustainable recovery measures post-pandemic hindering climate action.
- ⚠️ Global Impacts:
- 🌾 Food insecurity, displacement, and deaths due to climate change.
- 🌱 Decline in crop yields and increased risks to agricultural systems.
- 🐠 Disruption of ecosystems, including phenological shifts and coral reef threats.
- 🇮🇳 Impact on India:
- 🔥 Hottest month recorded in February 2023.
- 🌩️ Increased frequency of extreme weather events in 2022.
- 🌽 Acute food shortages, wildfires, and vulnerability to climate change.
Why In News
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) recently unveiled two groundbreaking reports, “Global Annual to Decadal Climate Update 2023-2027” and “State of Global Climate 2022,” shedding light on the ever-evolving climate patterns and emphasizing the urgency of taking immediate action to combat climate change. These comprehensive reports provide invaluable insights into the current state of the global climate and its projected trajectory, serving as a wake-up call for governments, policymakers, and individuals alike to prioritize sustainable solutions for a resilient future.
MCQs about The State of Global Climate
-
What is the goal of the Paris Agreement?
A. To limit global warming to 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
B. To pursue efforts to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
C. To reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 50% by 2050.
D. To promote international cooperation on climate research.
-
Which region is experiencing mass loss of glaciers?
A. Sub-Saharan Africa
B. Western Europe
C. High-mountain Asia
D. Central America
-
Which countries have made limited progress in meeting their climate pledges?
A. Australia, Japan, and Canada
B. Russia, China, and Saudi Arabia
C. Iran, Nigeria, and South Sudan
D. Australia, the U.S., and Russia
-
What impact did the heatwaves in Pakistan and India in 2022 have?
A. Increase in agricultural productivity
B. Decrease in crop yields
C. Reduction in sea levels
D. Growth of coral reefs
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


