Hindu Editorial Analysis : 17-May-2023
Agriculture has been a crucial sector in India, providing livelihoods to approximately 55% of the population and making the country a major player in the global agricultural industry. However, several challenges persist, hampering the sector’s economic viability and sustainability. This essay explores the issues faced by Indian agriculture and proposes policy options to address them.
Issues Faced by the Sector
- Food Inflation: Despite achieving food security through increased production, India grapples with food inflation and its volatility.
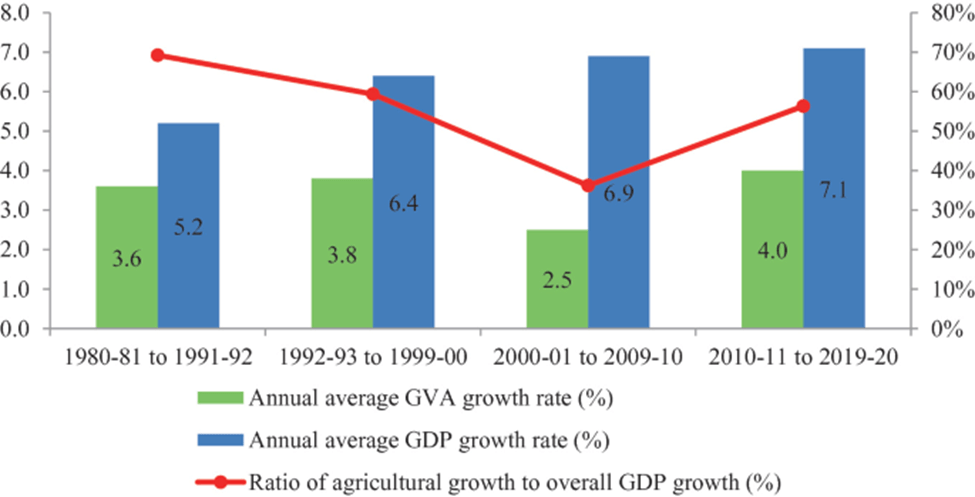
- Crop Productivity: Compared to advanced and emerging market economies, India’s crop productivity remains low due to factors such as fragmented landholdings, limited farm mechanization, and inadequate public and private investment in agriculture.
- Environmental Hazards: Overproduction of crops like rice, wheat, and sugarcane has led to groundwater depletion, soil degradation, and air pollution, raising concerns about the environmental sustainability of current practices.
- Overutilization of Fertilizers: Indiscriminate use of fertilizers, driven by government subsidies, has caused ecological damage, soil infertility, and a toxic food chain. Punjab, for instance, has an alarmingly high fertilizer usage rate.
- Depletion of Soils: Neglecting soil replenishment over thousands of years has resulted in depleted and exhausted soils with low productivity.
- Irrigation Challenges: While India is the second-largest irrigated country globally, only one-third of the cropped area is under irrigation, hindering agricultural productivity in a monsoon-dependent country.
- Conventional Cultivation Methods: Despite some mechanization, a significant portion of agricultural operations in India still relies on manual labor and conventional tools, hindering efficiency and productivity.
- Agricultural Marketing: Poor marketing facilities force farmers to rely on local traders and middlemen, resulting in low prices for their produce.
Policy Options for Agriculture
- Digitalization of Agriculture: The promotion of agri-startups and digital platforms enables farmers to access essential services such as seeds, fertilizers, crop insurance, and marketplaces. Examples like DeHaat showcase the potential of artificial intelligence and data analytics in empowering farmers.
- Integrated/Natural Farming: Encouraging integrated farming practices, combining livestock, fish ponds, and vermicomposting, can make small-scale farming economically self-reliant and environmentally sustainable.
- Climate Smart Agriculture: Promoting eco-friendly agri-inputs like Nano Urea, which enhances crop yields at a lower cost, can contribute to sustainable agriculture.
- Learning from Israel: Despite challenging climatic conditions, Israel has become a global leader in agriculture by implementing cooperative principles, emphasizing social equality, and leveraging agricultural technologies.
- Formal Credit Access: Educating farmers on the importance of formal financial institutions and discouraging informal credit sources like money lenders will improve financial prudence.
- Leveraging Collectives: Convergence of self-help groups (SHGs), Farmers Producer Organizations (FPOs), and cooperatives can enhance farmers’ bargaining power, bulk procurement, access to finance, and marketing efficiency.
- Development of Agri-Value Chains: Emphasizing customer focus, infrastructure development, technology adoption, and capacity building will strengthen agri-value chains. Examples like VAPCOL demonstrate the success of farmer producer companies in Maharashtra.
- Agri-Export Clusters: Encouraging the development of agri-export clusters and managing risks related to monsoons and market fluctuations can enhance India’s agricultural competitiveness in international markets.
Why In News
Policymakers have long been dedicated to enhancing the economic viability of Indian agriculture through persistent efforts. By implementing a range of initiatives, such as improving infrastructure, promoting technology adoption, and ensuring fair market access for farmers, policymakers aim to create a sustainable and prosperous agricultural sector that contributes to the overall economic growth and welfare of the nation.
MCQs about Transforming Indian Agriculture
-
How does food inflation affect Indian agriculture?
A. It increases crop productivity
B. It leads to environmental sustainability
C. It poses a challenge despite achieving food security
D. It improves access to credit
-
What farming practice is recommended for farmers with uneconomic land holdings?
A. Organic farming
B. Conventional farming
C. Integrated farming
D. Hydroponic farming
-
Which policy option promotes eco-friendly agriculture in India?
A. Promoting excessive use of fertilizers
B. Encouraging mechanized farming
C. Adopting eco-friendly agri-inputs
D. Subsidizing agricultural exports
-
How can farmers improve their bargaining power and marketing efficiency?
A. Relying on local traders and middlemen
B. Engaging in collective efforts through FPOs and cooperatives
C. Depending on informal sources of credit
D. Focusing on individual marketing strategies
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


